Experts say quantum computing is the future of computers. Unlike conventional computers, quantum computers leverage the properties of quantum physics such as superposition and interference, theoretically outperforming current equipment to an exponential degree.
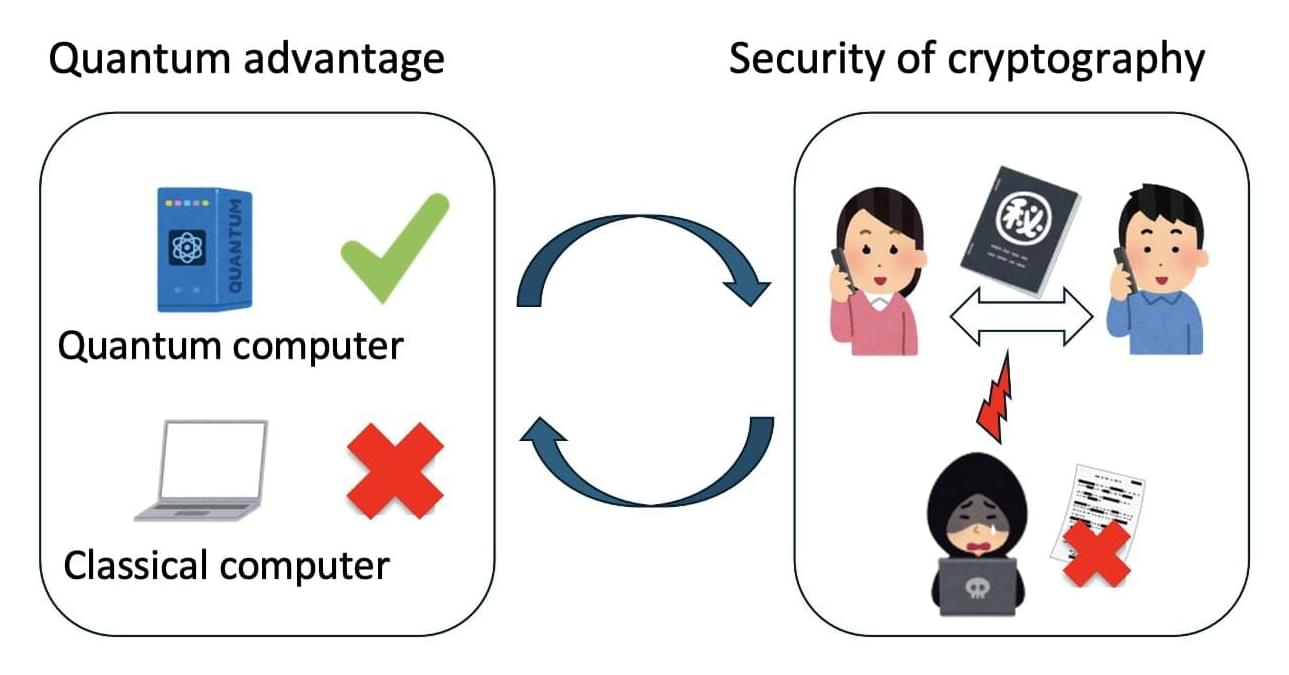
When a quantum computer is able to solve a problem unfeasible for current technologies, this is called the “quantum advantage.” However, this edge is not guaranteed for all calculations, raising fundamental questions regarding the conditions under which such an advantage exists. While previous studies have proposed various sufficient conditions for quantum advantage, the necessity of these conditions has remained unclear.
Motivated by this uncertainty, a team of researchers at Kyoto University has endeavored to understand the necessary and sufficient conditions for quantum advantage, using an approach combining techniques from quantum computing and cryptography, the science of coding information securely.