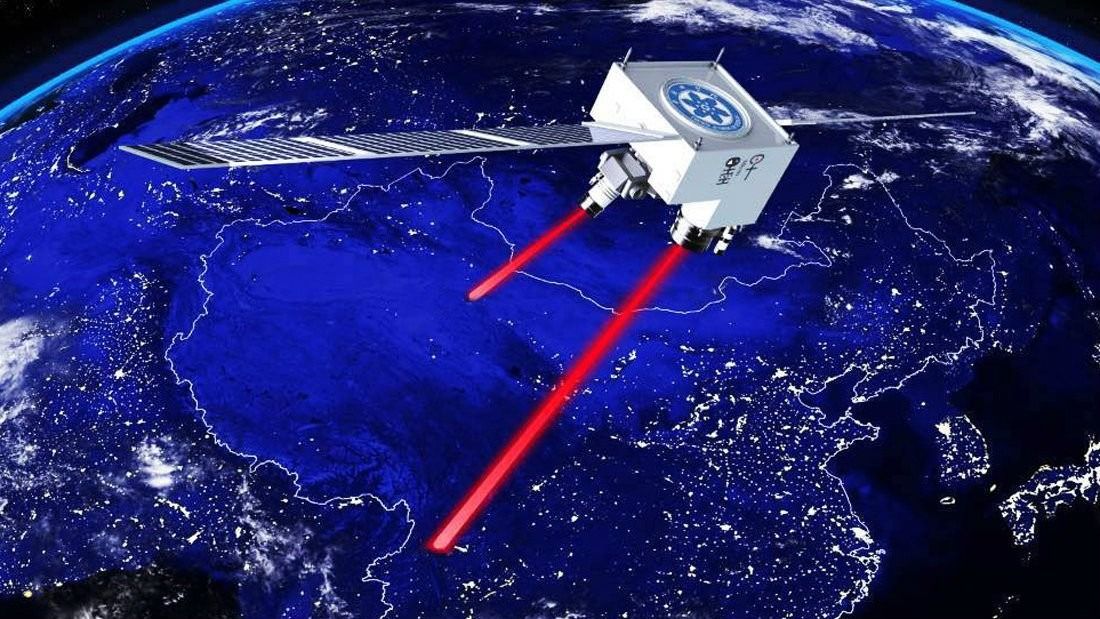
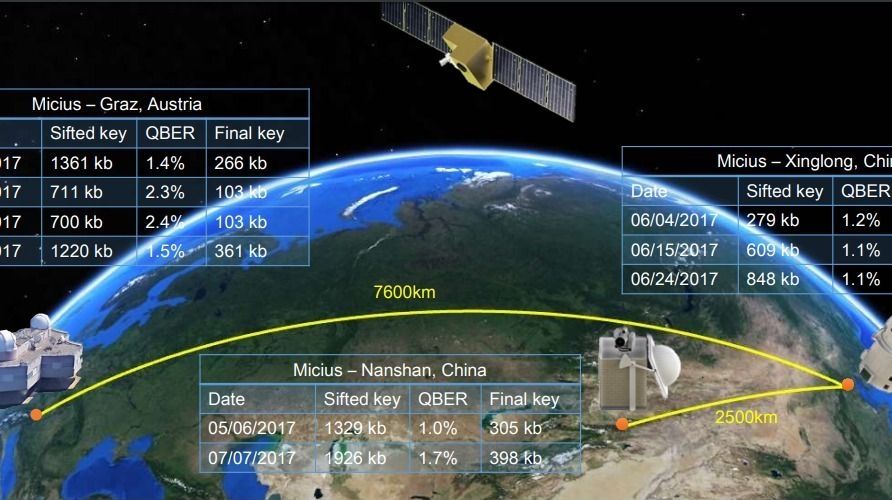
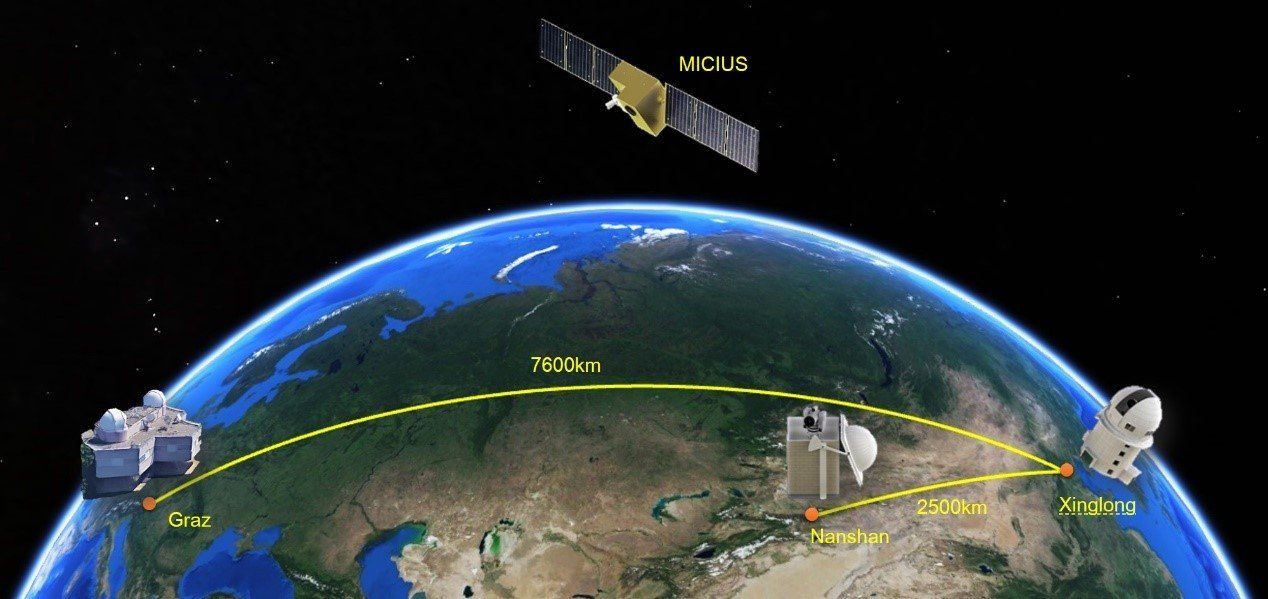
A joint China-Austria team has performed quantum key distribution between the quantum-science satellite Micius and multiple ground stations located in Xinglong (near Beijing), Nanshan (near Urumqi), and Graz (near Vienna). Such experiments demonstrate the secure satellite-to-ground exchange of cryptographic keys during the passage of the satellite Micius over a ground station. Using Micius as a trusted relay, a secret key was created between China and Europe at locations separated up to 7,600 km on the Earth.
Private and secure communications are fundamental for Internet use and e-commerce, and it is important to establish a secure network with global protection of data. Traditional public key cryptography usually relies on the computational intractability of certain mathematical functions. In contrast, quantum key distribution (QKD) uses individual light quanta (single photons) in quantum superposition states to guarantee unconditional security between distant parties. Previously, the quantum communication distance has been limited to a few hundred kilometers due to optical channel losses of fibers or terrestrial free space. A promising solution to this problem exploits satellite and space-based links, which can conveniently connect two remote points on the Earth with greatly reduced channel loss, as most of the photons’ propagation path is through empty space with negligible loss and decoherence.
A cross-disciplinary multi-institutional team of scientists from the Chinese Academy of Sciences, led by Professor Jian-Wei Pan, has spent more than 10 years developing a sophisticated satellite, Micius, dedicated to quantum science experiments, which was launched on August 2016 and orbits at an altitude of ~500 km. Five ground stations in China coordinate with the Micius satellite. These are located in Xinglong (near Beijing), Nanshan (near Urumqi), Delingha (37°22’44.43’‘N, 97°43’37.01” E), Lijiang (26°41’38.15’‘N, 100°1’45.55’‘E), and Ngari in Tibet (32°19’30.07’‘N, 80°1’34.18’‘E).