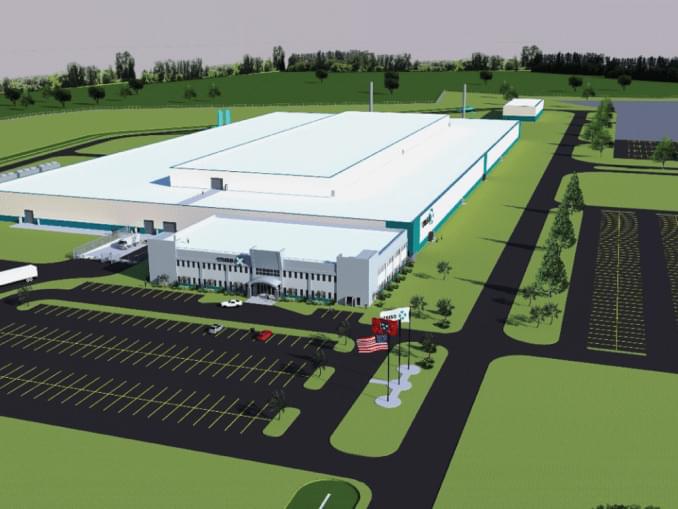
The TRISO-X, LLC Fuel Fabrication Facility (TF3) will be the nation’s first High-Assay, Low-Enriched Uranium (HALEU) fuel fabrication facility. TRISO-X is a wholly owned subsidiary of advanced reactor designer X-energy, LLC. TF3 will use uranium enriched between 5% and 20% to produce fuel for advanced and small modular reactors of the future. TF3 will manufacture TRi-structural ISOtropic (TRISO) fuel, an advanced fuel that is tough enough to handle the higher operating temperatures of several advanced reactors under development.
The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) is supporting the development of TF3 through an award with X-energy, LLC under the Advanced Reactor Demonstration Program (ARDP) 0, which aims to speed the demonstration of advanced reactors through cost-shared partnerships with the U.S. nuclear industry. The design and license application development of TF3 was also supported through an $18M (federal cost share) industry FOA that was awarded to X-energy in 2018. TF3 will initially provide the TRISO fuel for X-energy’s Xe-100 high-temperature gas reactor.
“The TRISO-X Fuel Fabrication Facility represents the intersection of some of DOE’s hard work to bring advanced reactors to commercialization,” said Alice Caponiti, DOE’s Deputy Assistant Secretary for Reactor Fleet and Advanced Reactor Deployment. “We’ve been investing in R&D on TRISO fuels for decades. Now, with funding through ARDP, TF3 will bring the next evolution of nuclear fuel to reality, advancing new nuclear technology, creating new jobs, and supporting the clean energy economy.”