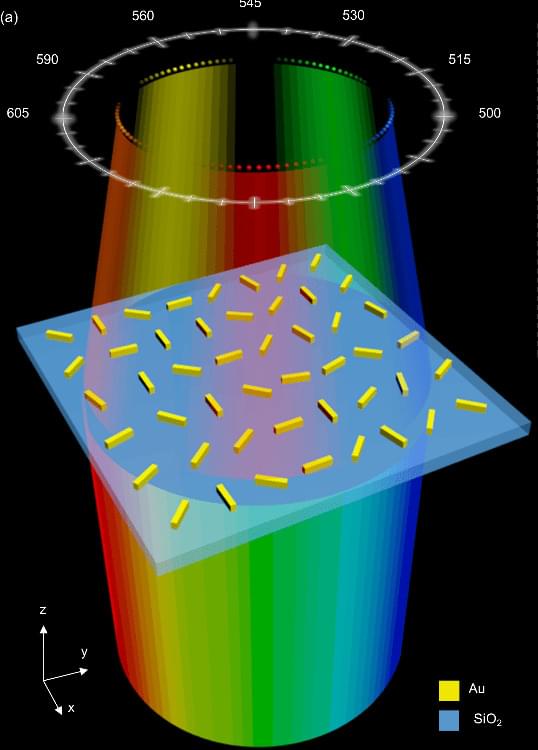
Metasurface performance: a) A schematic diagram of the proposed metasurface spectrometer based on w.


Chinese display maker BOE has unveiled a truly massive 110-inch 16K TV, putting the hordes of 4K TVs and projectors on the market to shame.
This seismically large prototype packs in a 16K resolution, with four times as many pixels as an 8K screen, and 16 times the pixel count of 4K. It was shown off at SID Display Week 2023 in Los Angeles, to celebrate BOE’s 30-year anniversary with a showcase of cutting-edge resolution far beyond the average television (via Heise.de).
A quarter century ago, theoretical physicists at the University of Innsbruck made the first proposal on how to transmit quantum information via quantum repeaters over long distances, which would open the door to the construction of a worldwide quantum information network.
Now, a new generation of Innsbruck researchers has built a quantum repeater node for the standard wavelength of telecommunication networks and transmitted quantum information over tens of kilometers. The study is published in the journal Physical Review Letters.
Quantum networks connect quantum processors or quantum sensors with each other. This allows tap-proof communication and high-performance distributed sensor networks. Between network nodes, quantum information is exchanged by photons that travel through optical waveguides. Over long distances, however, the likelihood of photons being lost increases dramatically.

Apple Inc.’s annual WWDC developers’ conference is fast approaching — and this one promises to be a bit more eventful than most, as the consumer-electronics giant is expected to debut its long-awaited mixed-reality headset.
The company hasn’t made a major product introduction since it rolled out the Apple Watch in 2015, but with an expensive headset supporting augmented and virtual reality, Apple AAPL,-0.88% will be entering into a market that has so far failed to catch on in a mainstream way. Meta Platforms Inc. META, +0.85% has bet big on virtual reality with its Oculus headset, with only limited traction.
Summary: Scientists present a hypothesis dubbed “Cytoelectric Coupling” suggesting electrical fields within the brain can manipulate neuronal sub-cellular components, optimizing network stability and efficiency. They propose these fields allow neurons to tune the information-processing network down to the molecular level.
Comparatively, this process is akin to households arranging their TV setup for optimal viewing experience. The theory, open for testing, could significantly enhance our understanding of the brain’s inner workings.
Jiangnan University, via SCMP
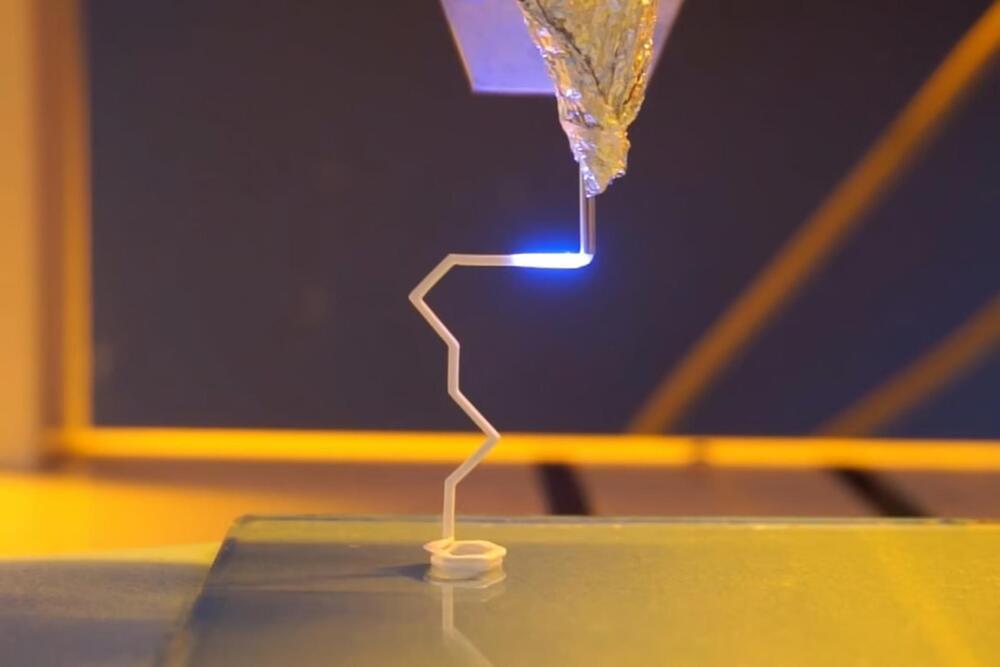
Ceramics are commonly used in the fields of electronics, mechanical engineering, and aerospace because of their structural integrity. They are also common because they are resistant to wear while also having endurance to high temperatures. Yet, because of their brittleness and hardness, designing and manufacturing certain ceramic parts.
Share your videos with friends, family, and the world.
Twenty years ago, Ferenc Krausz, Theodor Hänsch, and their collaborators used a femtosecond near-infrared (NIR) laser to compel neon atoms to emit pulses of extreme ultraviolet (XUV) light that lasted a few hundred attoseconds. The landmark feat depended on the laser’s strong oscillating electric field, which tore away the atoms’ valence electrons and hurled them back half a cycle later. Now Tobias Heldt of the Max Planck Institute for Nuclear Physics in Germany and his collaborators have developed a new experimental technique that is, in a sense, a mirror image of the 2003 demonstration: they used attosecond XUV pulses to free the valence electrons and to then track their response to femtosecond NIR laser pulses [1].
When a few-cycle femtosecond NIR pulse passes through helium gas, the atoms’ dipole moments fluctuate as the electrons move away and then recollide. Those fluctuations in turn are manifest in the gas’s absorption spectrum. Heldt and his collaborators set out to measure the fluctuations and, from them, infer the electrons’ trajectories.
The attosecond XUV pulse in their experiment did double duty. It ionized the helium atoms to bring the electrons under the influence of the NIR pulse. It also interfered with the fluctuating dipole moments. As a result, the XUV pulse carried away the dipoles’ spectral imprint, which the team measured with a grating spectrometer.
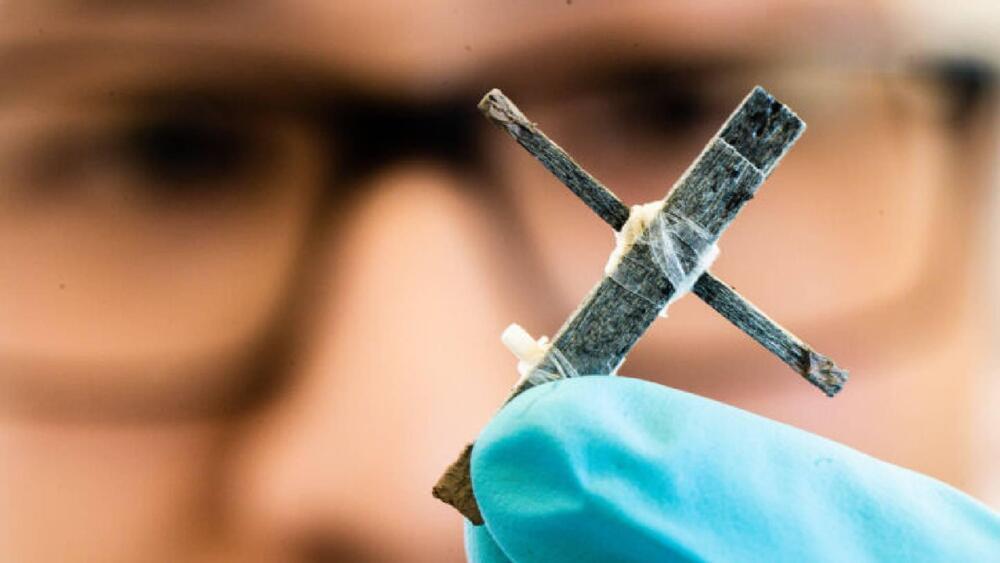

This is according to a press release by the institutions published on Thursday.
“We’ve come up with an unprecedented principle. Yes, the wood transistor is slow and bulky, but it does work, and has huge development potential,” said Isak Engquist, senior associate professor at the Laboratory for Organic Electronics at Linköping University.
This isn’t the first time scientists have attempted to produce wooden transistors but previous trials resulted in versions that could regulate ion transport only. Making matters worse was the fact that when the ions ran out, the transistor stopped functioning.