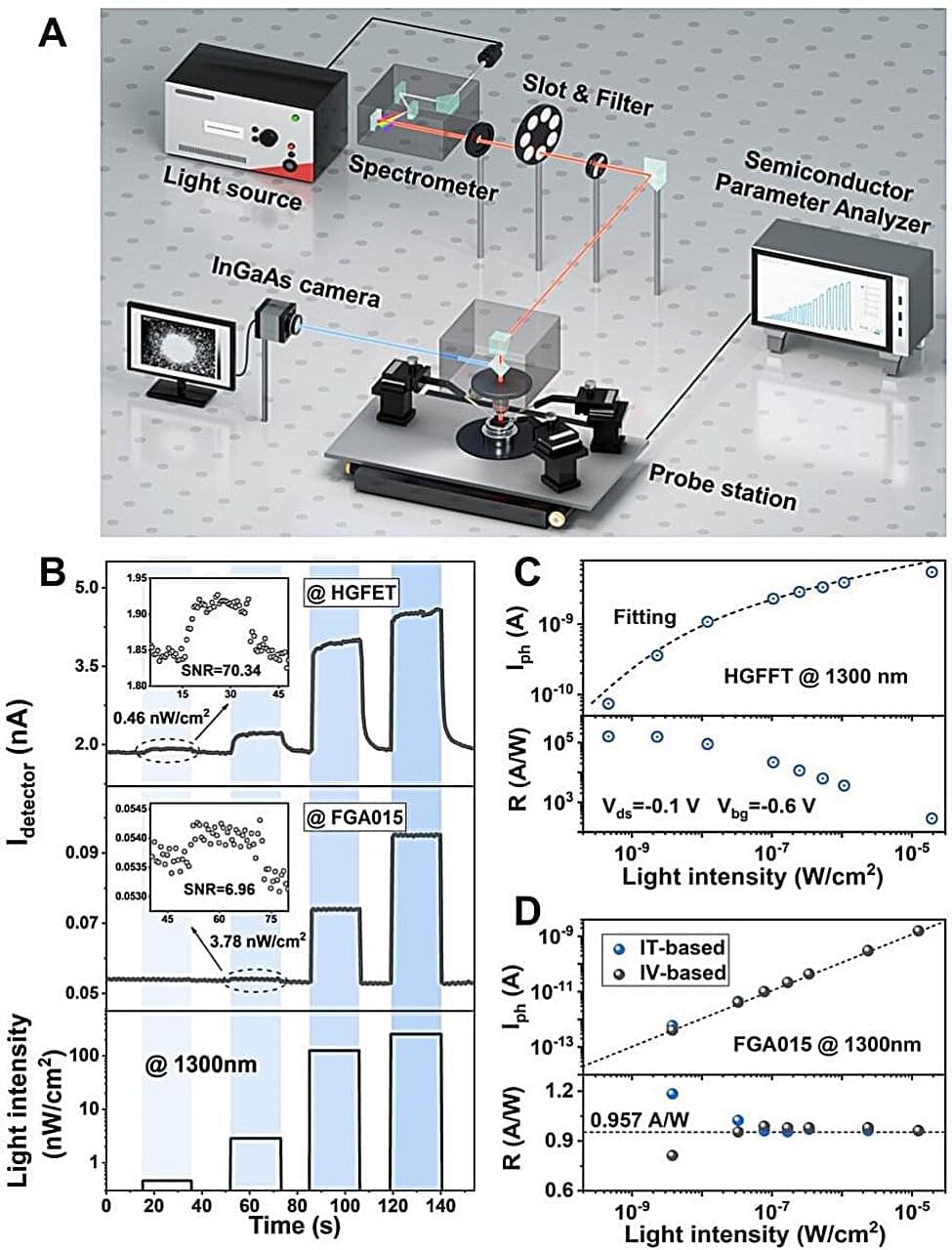
Prof Zhang Zhiyong’s team at Peking University developed a heterojunction-gated field-effect transistor (HGFET) that achieves high sensitivity in short-wave infrared detection, with a recorded specific detectivity above 1014 Jones at 1,300 nm, making it capable of starlight detection. Their research was recently published in the journal Advanced Materials, titled “Opto-Electrical Decoupled Phototransistor for Starlight Detection.”
Highly sensitive shortwave infrared (SWIR) detectors are essential for detecting weak radiation (typically below 10−8 W·Sr−1 ·cm−2 ·µm−1) with high-end passive image sensors. However, mainstream SWIR detection based on epitaxial photodiodes cannot effectively detect ultraweak infrared radiation due to the lack of inherent gain.
Filling this gap, researchers at the Peking University School of Electronics and collaborators have presented a heterojunction-gated field-effect transistor (HGFET) that achieves ultra-high photogain and exceptionally low noise in the short-wavelength infrared (SWIR) region, benefiting from a design that incorporates a comprehensive opto-electric decoupling mechanism.