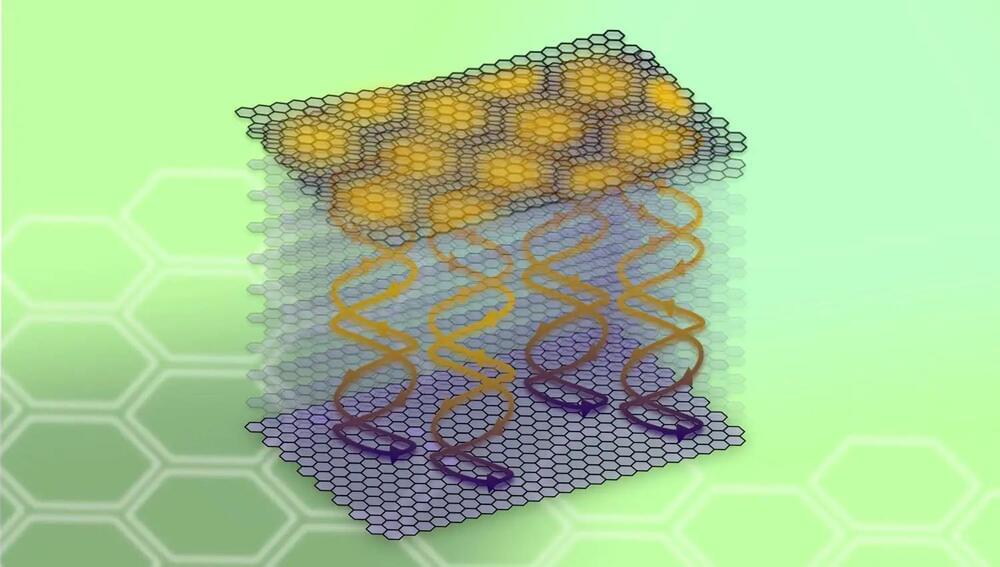
A team of researchers led by Associate Professor Kazuhiro Nakazawa from Nagoya University.
Nagoya University, sometimes abbreviated as NU, is a Japanese national research university located in Chikusa-ku, Nagoya. It was the seventh Imperial University in Japan, one of the first five Designated National University and selected as a Top Type university of Top Global University Project by the Japanese government. It is one of the highest ranked higher education institutions in Japan.