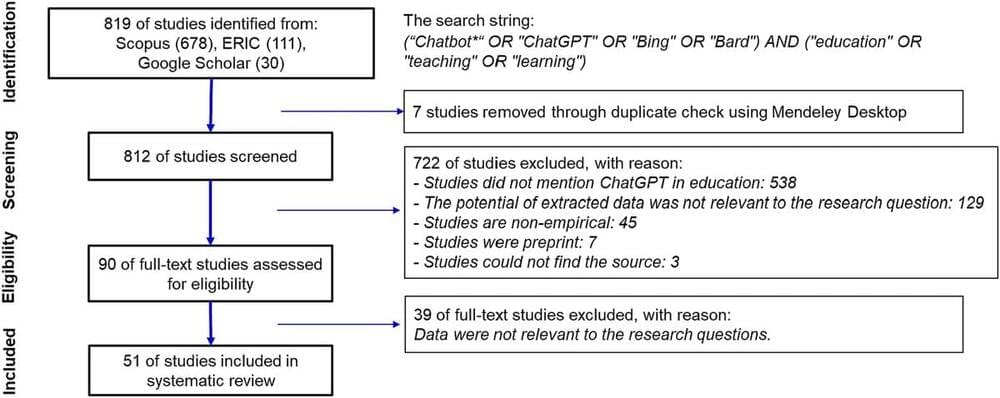
Link :
Imagine a life where your body’s internal “battery” runs low every single day, demanding constant recharging just to keep going. For millions of people living with Type 1 diabetes, this is the exhausting reality—one where insulin injections act as the lifeline, replacing what the body can no longer produce on its own. But what if the body could be taught to recharge itself again?
In a world-first medical breakthrough, this question has moved from possibility to reality. A woman’s own stem cells have been successfully used to reverse her Type 1 diabetes, a condition once thought to be irreversible. Scientists turned her blood stem cells into insulin-producing powerhouses, effectively “rebooting” her pancreas and allowing her body to produce insulin naturally for the first time in years.
This achievement isn’t just a milestone for one patient; it’s a bold step toward a future where Type 1 diabetes may no longer require a lifetime of management. So, how did this groundbreaking transformation happen? And what does it mean for millions waiting for a cure?