Here’s a very important article to me—and a part of my platform moving forward. Automation is coming, but we don’t need to raise taxes to pay for a Basic Income. There are other ways to deal with our jobless future and poverty in America.
Like the Titanic, capitalism is sinking, but few passengers are wondering yet if there are enough lifeboats.
I recently declared my run as a Libertarian for California governor in 2018, and I gently support the idea of a state-funded basic income to offset the effects of ubiquitous automation. A basic income would give every Californian some money — and it makes sense to start such a dramatic program here in the Golden State, since this is where much of the human-job-replacing-tech is created.
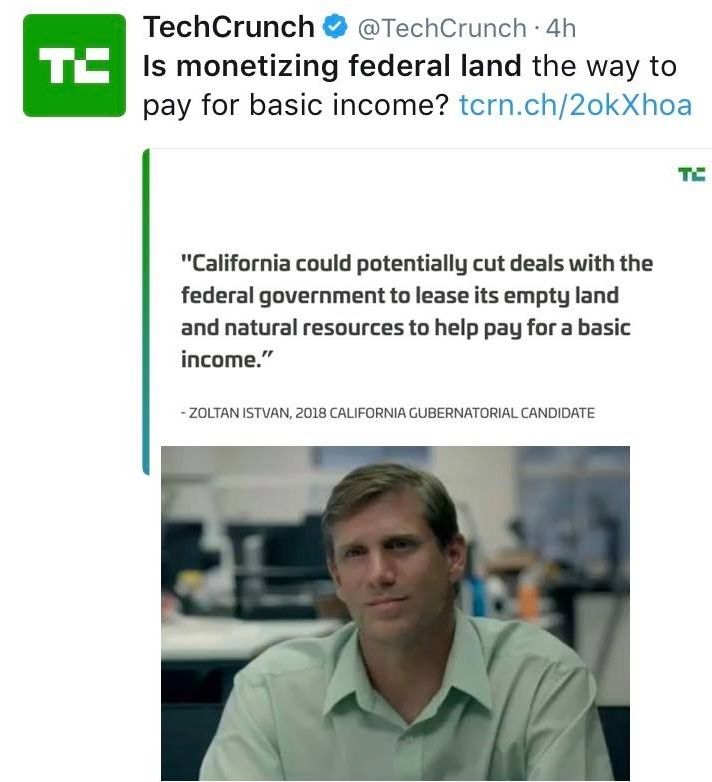
My Libertarian friends are skeptical of my support for a basic income. They insist the only way to pay for such a program is via higher taxes. This is not true; other ways exist. California could potentially cut deals with the federal government to lease its empty land and natural resources to help pay for a basic income.
After all, state and federal resources belong to the people, and 45 percent of California (more than 45 million acres) is government-controlled land, leaving vast areas idle and mostly undeveloped.
![]() smile Give the video a view: https://www.facebook.com/NowThisFuture/videos/1500983249942850/ #transhumanism
smile Give the video a view: https://www.facebook.com/NowThisFuture/videos/1500983249942850/ #transhumanism