http://www.homomimeticus.eu/
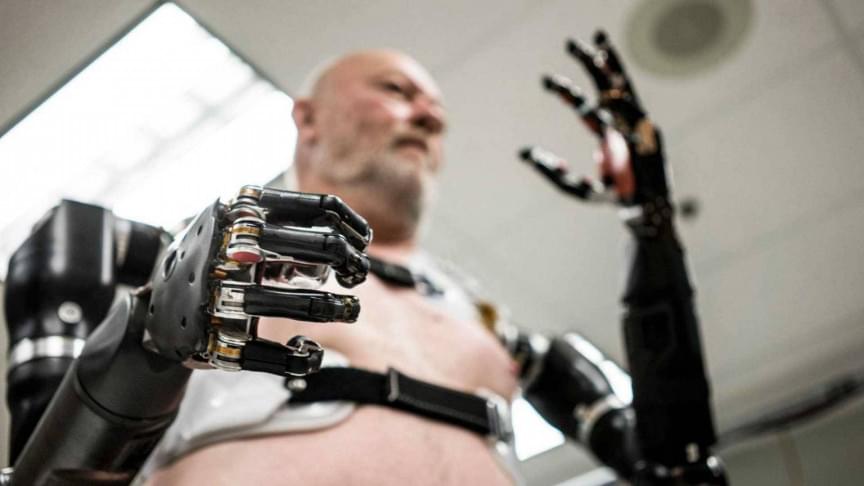
Part of the ERC-funded project Homo Mimeticus, the Posthuman Mimesis conference (KU Leuven, May 2021) promoted a mimetic turn in posthuman studies. In the first keynote Lecture, Prof. Kevin Warwick (U of Coventry) argued that our future will be as cyborgs – part human, part technology. Kevin’s own experiments will be used to explain how implant and electrode technology can be employed to create cyborgs: biological brains for robots, to enable human enhancement and to diminish the effects of neural illnesses. In all cases the end result is to increase the abilities of the recipients. An indication is given of a number of areas in which such technology has already had a profound effect, a key element being the need for an interface linking a biological brain directly with computer technology. A look will be taken at future concepts of being, for posthumans this possibly involving a click and play body philosophy. New, much more powerful, forms of communication will also be considered.
HOM Videos is part of an ERC-funded project titled Homo Mimeticus: Theory and Criticism, which has received funding from the European Research Council (ERC) under the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme (grant agreement n°716181)
Follow HOM on Twitter: https://twitter.com/HOM_Project.
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/HOMprojectERC