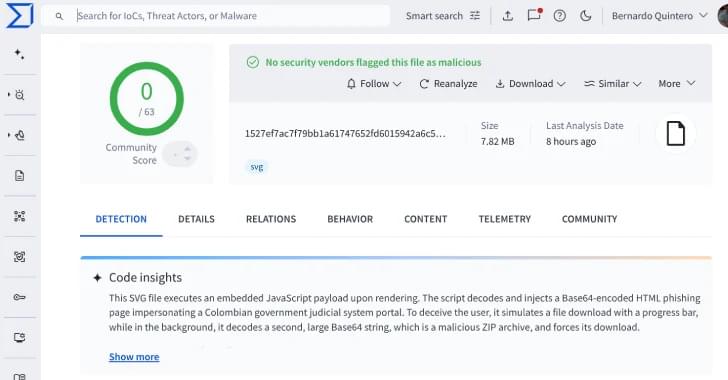
523 malicious SVG phishing files since Aug 2025 bypassed antivirus, evolving tactics expose macOS to AMOS.

A debate/discussion on ASI (artificial superintelligence) between Foresight Senior Fellow Mark S. Miller and MIRI founder Eliezer Yudkowsky. Sharing similar long-term goals, they nevertheless reach opposite conclusions on best strategy.
“What are the best strategies for addressing risks from artificial superintelligence? In this 4-hour conversation, Eliezer Yudkowsky and Mark Miller discuss their cruxes for disagreement. While Eliezer advocates an international treaty that bans anyone from building it, Mark argues that such a pause would make an ASI singleton more likely – which he sees as the greatest danger.”
What are the best strategies for addressing extreme risks from artificial superintelligence? In this 4-hour conversation, decision theorist Eliezer Yudkowsky and computer scientist Mark Miller discuss their cruxes for disagreement.
They examine the future of AI, existential risk, and whether alignment is even possible. Topics include AI risk scenarios, coalition dynamics, secure systems like seL4, hardware exploits like Rowhammer, molecular engineering with AlphaFold, and historical analogies like nuclear arms control. They explore superintelligence governance, multipolar vs singleton futures, and the philosophical challenges of trust, verification, and control in a post-AGI world.
Moderated by Christine Peterson, the discussion seeks the least risky strategy for reaching a preferred state amid superintelligent AI risks. Yudkowsky warns of catastrophic outcomes if AGI is not controlled, while Miller advocates decentralizing power and preserving human institutions as AI evolves.

Cybersecurity researchers have lifted the lid on a previously undocumented threat cluster dubbed GhostRedirector that has managed to compromise at least 65 Windows servers primarily located in Brazil, Thailand, and Vietnam.
The attacks, per Slovak cybersecurity company ESET, led to the deployment of a passive C++ backdoor called Rungan and a native Internet Information Services (IIS) module codenamed Gamshen. The threat actor is believed to be active since at least August 2024.
“While Rungan has the capability of executing commands on a compromised server, the purpose of Gamshen is to provide SEO fraud as-a-service, i.e., to manipulate search engine results, boosting the page ranking of a configured target website,” ESET researcher Fernando Tavella said in a report shared with The Hacker News.

Cybersecurity researchers have flagged a new technique that cybercriminals have adopted to bypass social media platform X’s malvertising protections and propagate malicious links using its artificial intelligence (AI) assistant Grok.
The findings were highlighted by Nati Tal, head of Guardio Labs, in a series of posts on X. The technique has been codenamed Grokking.
The approach is designed to get around restrictions imposed by X in Promoted Ads that allow users to only include text, images, or videos, and subsequently amplify them to a broader audience, attracting hundreds of thousands of impressions through paid promotion.

Threat actors have been exploiting a zero-day vulnerability in legacy Sitecore deployments to deploy WeepSteel reconnaissance malware.
The flaw, tracked under CVE-2025–53690, is a ViewState deserialization vulnerability caused by the inclusion of a sample ASP.NET machine key in pre-2017 Sitecore guides.
Some customers reused this key in production, allowing attackers with knowledge of the key to craft valid, but malicious ‘_VIEWSTATE’ payloads that tricked the server into deserializing and executing them, leading to remote code execution (RCE).


Cybersecurity researchers have discovered two new malicious packages on the npm registry that make use of smart contracts for the Ethereum blockchain to carry out malicious actions on compromised systems, signaling the trend of threat actors constantly on the lookout for new ways to distribute malware and fly under the radar.
“The two npm packages abused smart contracts to conceal malicious commands that installed downloader malware on compromised systems,” ReversingLabs researcher Lucija Valentić said in a report shared with The Hacker News.


