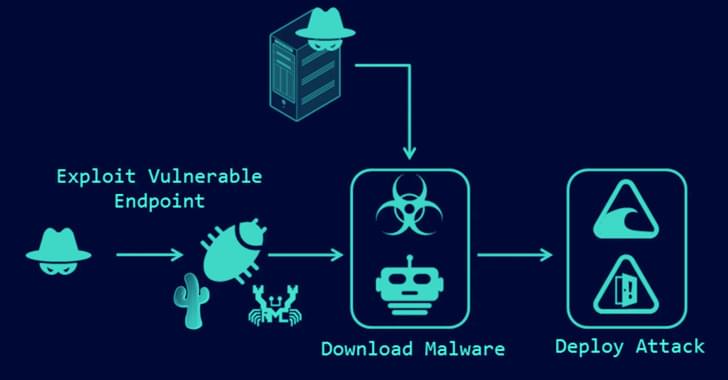
According to reports, the Taiwanese computer hardware company MSI (Micro-Star International) was recently joined to the list of victims of a new ransomware gang that goes by the name “Money Message.” The perpetrators of the cybercrime say that they have taken source code along with other critical material from the company’s network. MSI is a world-renowned leader in the production of computer components, such as motherboards, graphics cards, desktop computers, laptop computers, servers, and other electronic equipment. It brings in more than $6.5 billion in income every year.
Money Message has included MSI on the website that it maintains for the publication of leaked material and has published images of the company’s CTMS and ERP databases in addition to files that include software source code, private keys, and BIOS firmware. If MSI does not comply with the threat actors’ demand for a ransom payment, they will now threaten to release all of the information that was taken.
The perpetrators of the hack claim to have taken 1.5 terabytes worth of data, including databases and source code, from MSI’s servers. They are holding out for a ransom payment of four million dollars.