Cybersecurity researchers have disclosed that the LightSpy spyware recently identified as targeting Apple iOS users is in fact a previously undocumented macOS variant of the implant.
The findings come from both Huntress Labs and ThreatFabric, which separately analyzed the artifacts associated with the cross-platform malware framework that likely possesses capabilities to infect Android, iOS, Windows, macOS, Linux, and routers from NETGEAR, Linksys, and ASUS.
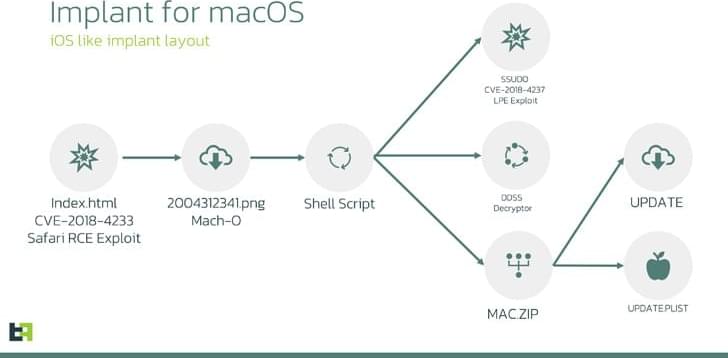
“The Threat actor group used two publicly available exploits (CVE-2018–4233, CVE-2018–4404) to deliver implants for macOS,” ThreatFabric said in a report published last week. “Part of the CVE-2018–4404 exploit is likely borrowed from the Metasploit framework. macOS version 10 was targeted using those exploits.”







 עברית (Hebrew)
עברית (Hebrew)