A new study shows that extreme black holes could break the famous “no-hair” theorem, and in a way that we could detect.



The James Webb Space Telescope has made a shocking discovery. According to a new paper published in the journal Nature, astronomers have discovered enormous distant galaxies that some say shouldn’t exist. These enormous galaxies are believed to be some of the early galaxies that formed after the Big Bang, and their discovery by Webb has left many scratching their heads in confusion.
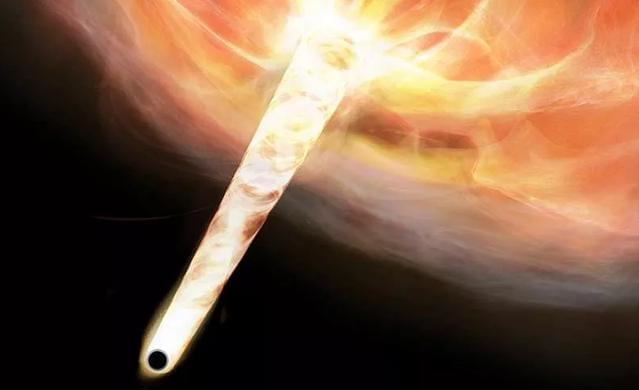
Astronomers have discovered a “runaway” black hole, potentially the first observational evidence that supermassive black holes can be ejected from their host galaxies. Astronomers have spotted a runaway supermassive black hole, seemingly ejected from its home galaxy and racing through space with a chain of stars trailing in its wake.

How the Big Bang gave us time, explained by theoretical physicist Sean Carroll.
Up next, The Universe in 90 minutes: Time, free will, God, & more ► https://youtu.be/tM4sLmt1Ui8
In this Big Think interview, theoretical physicist Sean Carroll discusses the concept of time and the mysteries surrounding its properties. He notes that while we use the word “time” frequently in everyday language, the real puzzles arise when we consider the properties of time, such as the past, present, and future, and the fact that we can affect the future but not the past.
Carroll also discusses the concept of entropy, which is a measure of how disorganized or random a system is, and the second law of thermodynamics, which states that there is a natural tendency for things in the universe to go from a state of low entropy to high entropy. He explains that the arrow of time, or the perceived difference between the past and the future, arises due to the influence of the Big Bang and the fact that the universe began in a state of low entropy.
Carroll also touches on the possibility of time travel and the concept of the multiverse.
Read the video transcript ► https://bigthink.com/series/explain-it-like-im-smart/the-Big-Bang-gave-us-time.
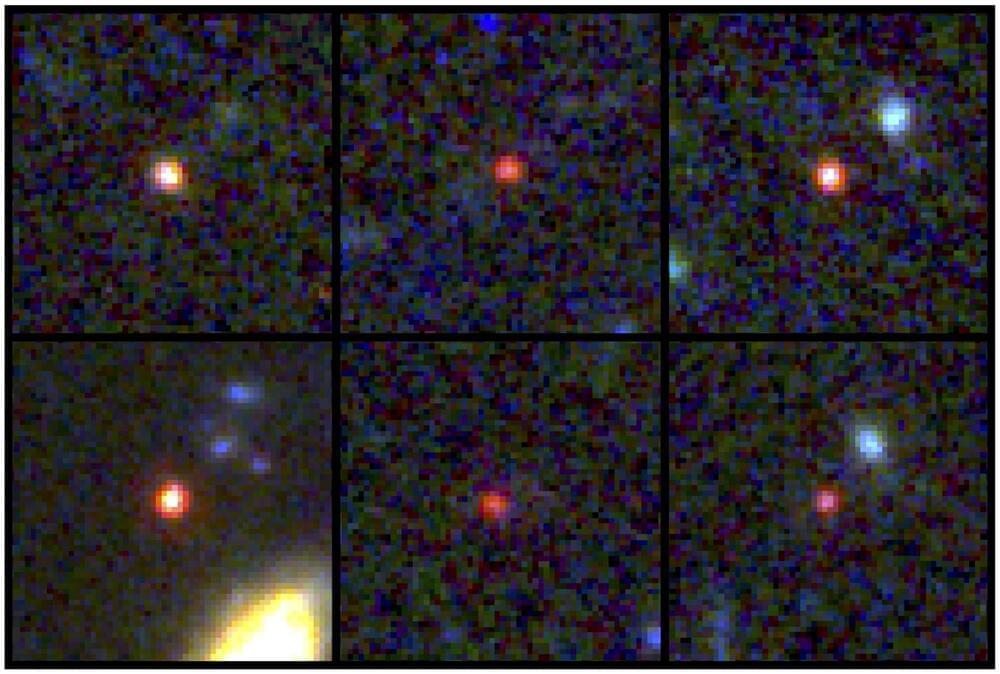

Six massive galaxies discovered in the early universe are upending what scientists previously understood about the origins of galaxies in the universe.
“These objects are way more massive than anyone expected,” said Joel Leja, assistant professor of astronomy and astrophysics at Penn State, who modeled light from these galaxies. “We expected only to find tiny, young, baby galaxies at this point in time, but we’ve discovered galaxies as mature as our own in what was previously understood to be the dawn of the universe.”
Using the first dataset released from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, the international team of scientists discovered objects as mature as the Milky Way when the universe was only 3% of its current age, about 500–700 million years after the Big Bang. The telescope is equipped with infrared-sensing instruments capable of detecting light that was emitted by the most ancient stars and galaxies. Essentially, the telescope allows scientists to see back in time roughly 13.5 billion years, near the beginning of the universe as we know it, Leja explained.
😗
The measurements from ancient and dormant galaxies show black holes growing more than expected, aligning with a phenomenon predicted in Einstein’s theory of gravity. The result potentially means nothing new has to be added to our picture of the Universe to account for dark energy: black holes combined with Einstein’s gravity are the source.
Study co-author Dr Chris Pearson, from STFC RAL Space, said: “If the theory holds, then this is going to revolutionize the whole of cosmology, because at last we’ve got a solution for the origin of dark energy that’s been perplexing cosmologists and theoretical physicists for more than 20 years.”
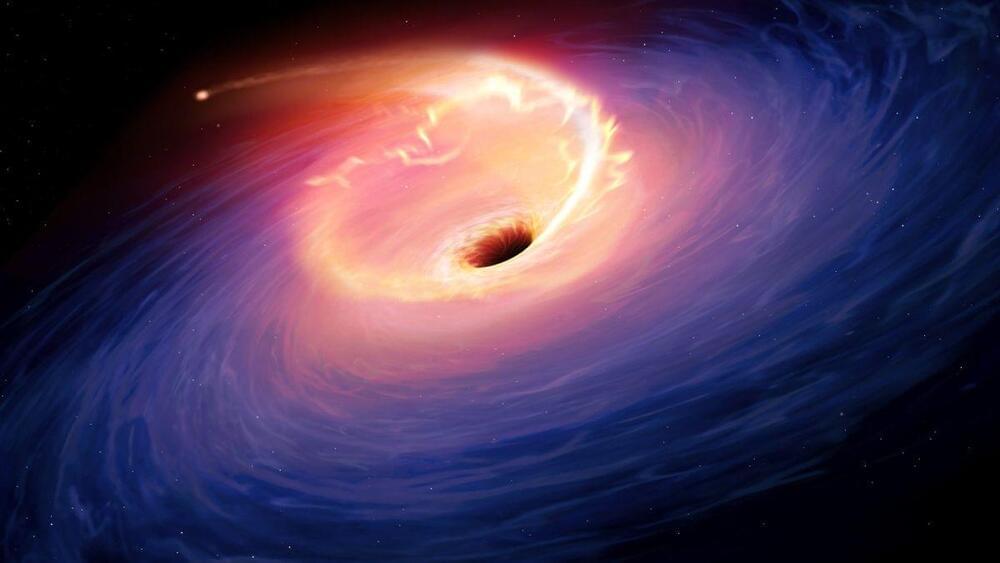

A supermassive black hole at the centre of a galaxy some 8.5 billion years way has ripped apart a nearby star, producing some of the most luminous jets ever seen.
When stars and other objects stray too close to a supermassive black hole they are destroyed by the black hole’s immense gravity.
These occurrences, known as tidal-disruption events (TDEs), result in a circling disk of material that is slowly pulled into the black hole and very occasionally, as in the case of supermassive black hole AT2022cmc, ejecting bright beams of material travelling close to the speed of light.
Astronomers from the UCLA Galactic Center Orbits Initiative (GCOI) and Keck Observatory have been tracking the evolution of this dusty gas filament since 2002; high-angular resolution near-infrared images captured with Keck Observatory’s powerful adaptive optics system show X7 has become so elongated that it now has a length of 3,000 times the distance between the Earth and sun (or 3,000 astronomical units).
The study is published in today’s issue of The Astrophysical Journal.
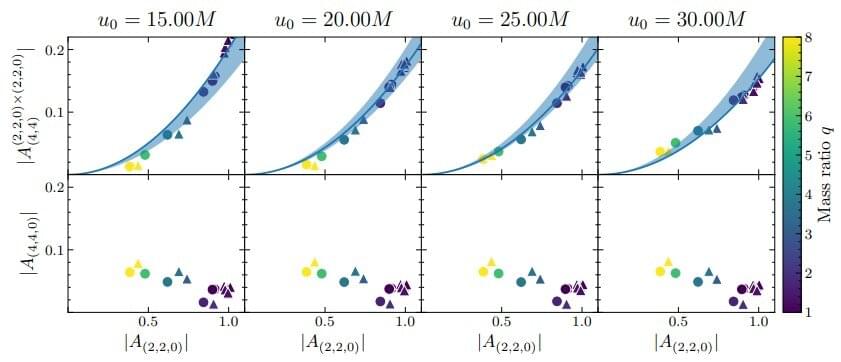
When two black holes collide into each other to form a new bigger black hole, they violently roil spacetime around them, sending ripples, called gravitational waves, outward in all directions. Previous studies of black hole collisions modeled the behavior of the gravitational waves using what is known as linear math, which means that the gravitational waves rippling outward did not influence, or interact, with each other. Now, a new analysis has modeled the same collisions in more detail and revealed so-called nonlinear effects.
“Nonlinear effects are what happens when waves on the beach crest and crash,” says Keefe Mitman, a Caltech graduate student who works with Saul Teukolsky (Ph. D. ‘74), the Robinson Professor of Theoretical Astrophysics at Caltech with a joint appointment at Cornell University.
“The waves interact and influence each other rather than ride along by themselves. With something as violent as a black hole merger, we expected these effects but had not seen them in our models until now. New methods for extracting the waveforms from our simulations have made it possible to see the nonlinearities.”