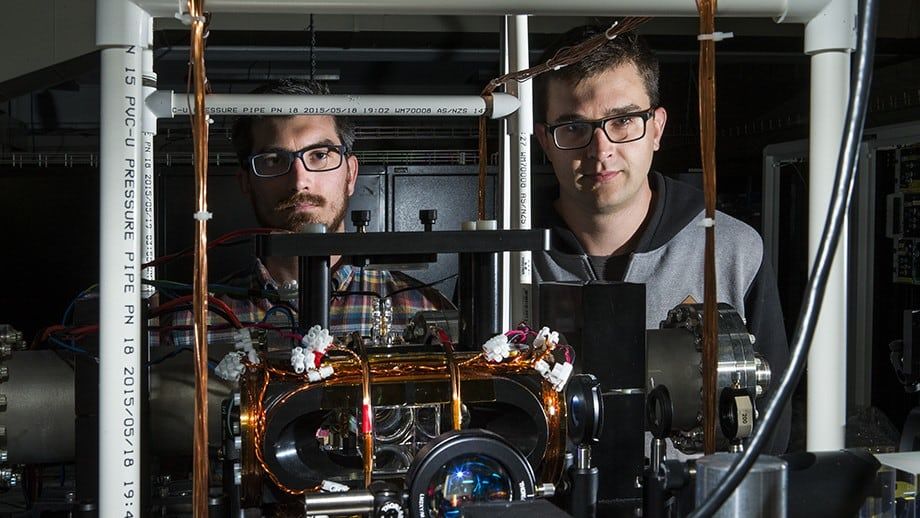
“It’s clear that the light is trapped — there are photons circulating around the atoms,” Everett says. “The atoms absorbed some of the trapped light, but a substantial proportion of the photons were frozen inside the atomic cloud.”
Co-researcher Geoff Campbell from ANU explained that while photons commonly pass by each other at the speed of light without any interactions, atoms interact with each other more freely.
“Corralling a crowd of photons in a cloud of ultra-cold atoms creates more opportunities for them to interact,” Campbell says.