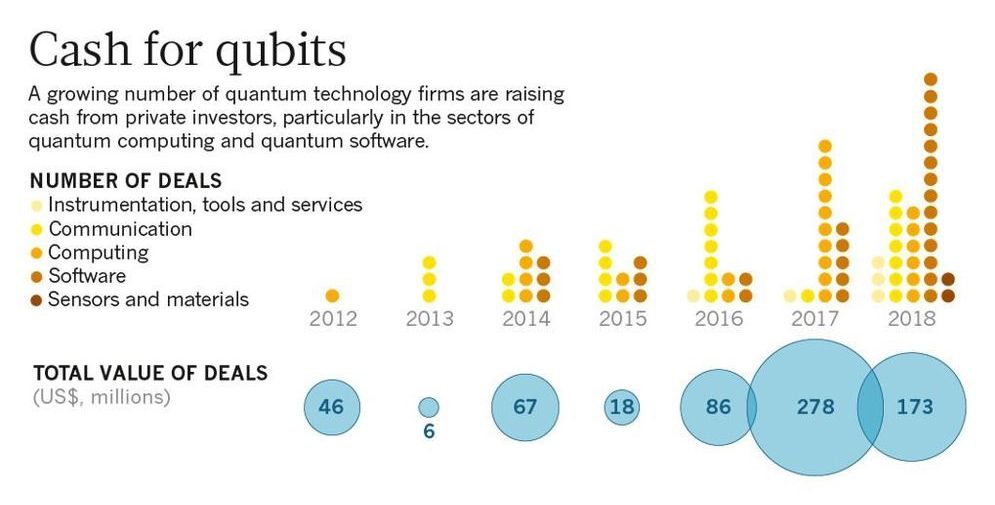
A Nature analysis explores the investors betting on quantum technology. The science is immature and a multi-purpose quantum computer doesn’t yet exist. But that isn’t stopping investors pouring cash into quantum start-ups.


SAN FRANCISCO—( BUSINESS WIRE )—Twist Bioscience Corporation (NASDAQ: TWST), a company enabling customers to succeed through its offering of high-quality synthetic DNA using its silicon platform, today announced that it has entered into an agreement with Imagene SA, where Imagene will provide Twist with an encapsulation service to store DNA through its DNAshell® technology to store digital data encoded in DNA for thousands of years.
“We are happy to be partnering with Twist and providing them with our disruptive DNAshell® technology to safely store DNA with digital data encoded.” Tweet this
“This agreement with Imagene provides the next step in the continuum on DNA digital data storage and fits within our strategy to cover all aspects of the process efficiently to enable the development of DNA as a digital storage medium,” commented Emily Leproust, Ph.D., CEO of Twist Bioscience. “We believe the DNAshell ® technology allows us to encapsulate the DNA-stored digital data securely, protecting it for eternity from any elements including radiation, and eliminating the need for continued copying of digital data due to degradation experienced in other forms of storage today.”
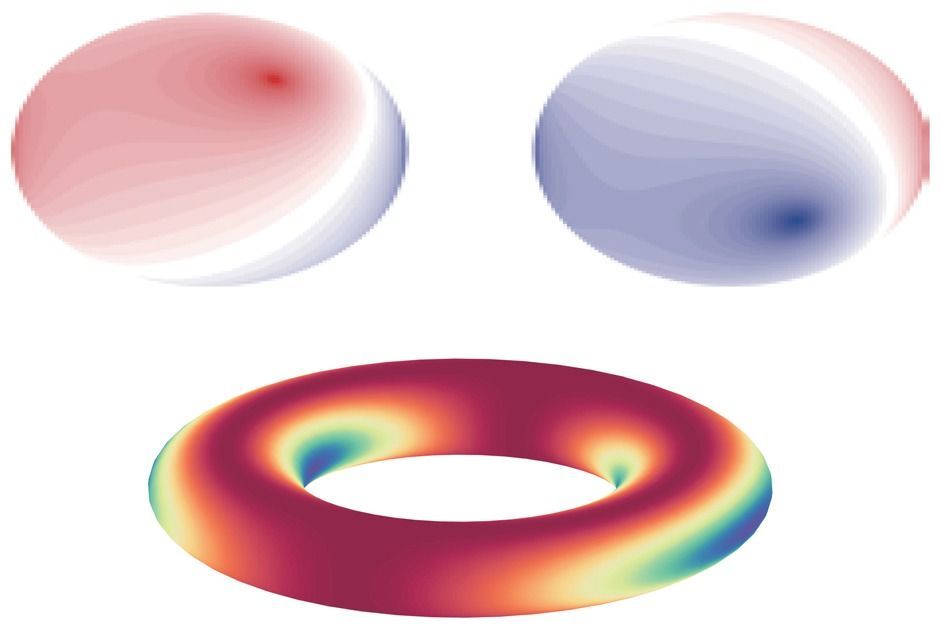
For the first time, physicists in the US have confirmed a decades-old theory regarding the breaking of time-reversal symmetry in gauge fields. Marin Soljacic at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and an international team of researchers have made this first demonstration of the “non-Abelian Aharonov-Bohm effect” in two optics experiments. With improvements, their techniques could find use in optoelectronics and fault-tolerant quantum computers.
First emerging in Maxwell’s famous equations for classical electrodynamics, a gauge theory is a description of the physics of fields. Gauge theories have since become an important part of physicists’ descriptions of the dynamics of elementary particles – notably the theory of quantum electrodynamics.
A salient feature of a gauge theory is that the physics it describes does not change when certain transformations are made to the underlying equations describing the system. An example is the addition of a constant scalar potential or a “curl-free” vector potential to Maxwell’s equations. Mathematically, this does not change the electric and magnetic fields that act on a charged particle such as an electron – and therefore the behaviour of the electron – so Maxwell’s theory is gauge invariant.
The World Economic Forum has partnered with the Inter-American Development Bank and the Colombian Inspector General’s Office to explore how distributed ledger technology can improve public transparency and integrity in school meal procurement.
The project, which is taking place this year, is multi-faceted and includes a software implementation with blockchain technology for the selection of school food vendors. It is co-designed with several partners from academia, the IT industry, and the non-profit world, including economists and computer scientists from the blockchain economics and governance consulting firm Prysm Group, the National University of Colombia, U.C. Berkeley, and the blockchain security firm Quantstamp.
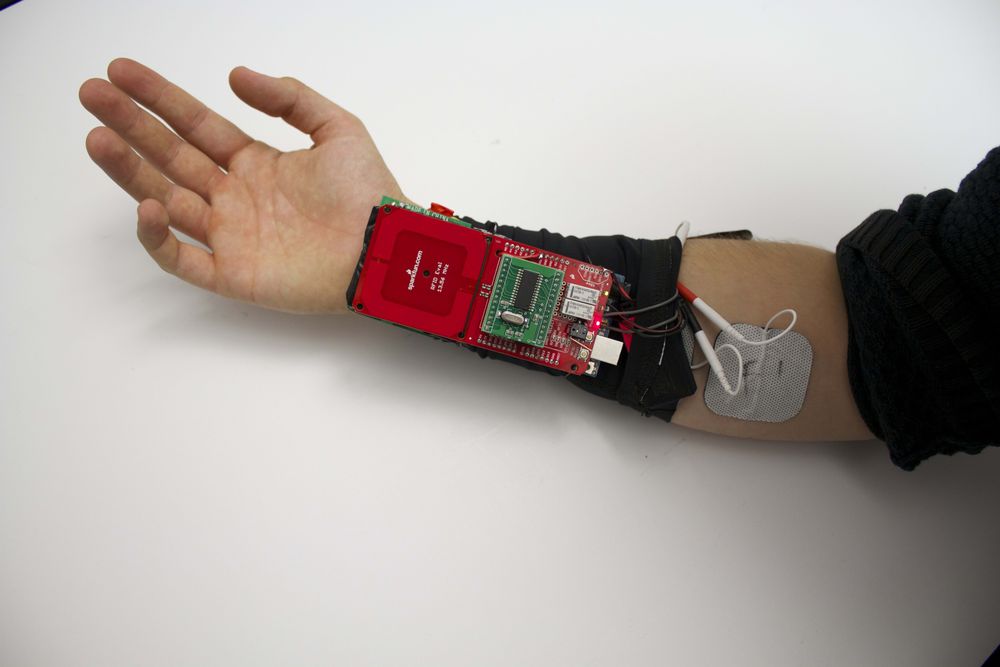
A professor at the University of Chicago believes he is on his way to creating a wearable for market that will manipulate your muscles with electrical impulses to cause you to move involuntarily so you can perform a physical task you otherwise didn’t know how to do, like playing a musical instrument or operating machinery.
Dr. Pedro Lopes, who heads the Human Computer Integration lab at the university, is all about integrating humans and computers, closing the gap between human and machine. His team, which focuses on engineering the next generation of wearable and haptic devices, is exploring the endless possibilities if wearables could intentionally share parts of our body for input and output, allowing computers to be more directly interwoven in our bodily senses and actuators.
Lopes’ vision: a wearable EMS device that would look like a sleeve and be able to send electrical impulses in the right timing and in the right fashion to make a user’s muscles move involuntarily to perform a physical task. EMS stands for electrical muscle stimulation.
“Dark silicon” sounds like a magical artifact out of a fantasy novel. In reality, it’s one branch of a three-headed beast that foretells the end of advances in computation.
Ok—that might be too dramatic. But the looming problems in silicon-based computer chips are very real. Although computational power has exploded exponentially in the past five decades, we’ve begun hitting some intractable limits in further growth, both in terms of physics and economics.
Moore’s Law is dying. And chipmakers around the globe are asking, now what?

In years to come, quantum computers and quantum networks might be able to tackle tasks that are inaccessible to traditional computer systems. For instance, they could be used to simulate complex matter or enable fundamentally secure communications.
The elementary building blocks of quantum information systems are known as qubits. For quantum technology to become a tangible reality, researchers will need to identify strategies to control many qubits with very high precision rates.
Spins of individual particles in solids, such as electrons and nuclei have recently shown great promise for the development of quantum networks. While some researchers were able to demonstrate an elementary control of these qubits, so far, no one has reported entangled quantum states containing more than three spins.
The cryptocurrency Bitcoin is limited by its astronomical electricity consumption and outsized carbon footprint. A nearly zero-energy alternative sounds too good to be true, but as School of Computer and Communication Sciences (IC) Professor Rachid Guerraoui explains, it all comes down to our understanding of what makes transactions secure.
To explain why the system developed in his Distributed Computing Lab (DCL) represents a paradigm shift in how we think about cryptocurrencies—and about digital trust in general—Professor Rachid Guerraoui uses a legal metaphor: all players in this new system are “innocent until proven guilty.”
This is in contrast to the traditional Bitcoin model first described in 2008 by Satoshi Nakamoto, which relies on solving a difficult problem called “consensus” to guarantee the security of transactions. In this model, everyone in a distributed system must agree on the validity of all transactions to prevent malicious players from cheating—for example, by spending the same digital tokens twice (double-spending). In order to prove their honesty and achieve consensus, players must execute complex—and energy-intensive—computing tasks that are then verified by the other players.
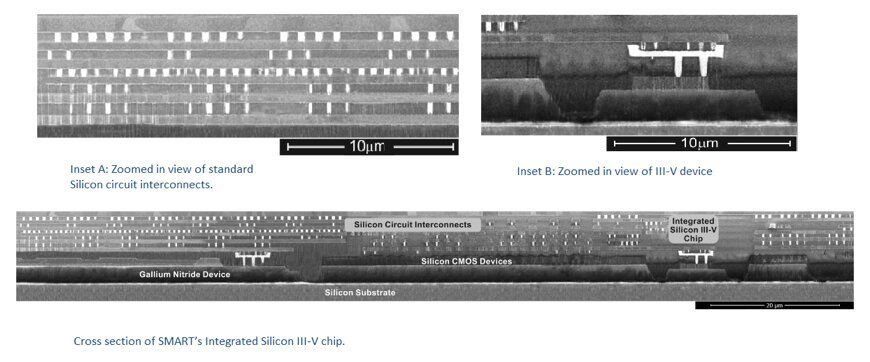
The Singapore-MIT Alliance for Research and Technology (SMART), MIT’s Research Enterprise in Singapore, has announced the successful development of a commercially viable way to manufacture integrated Silicon III-V Chips with high-performance III-V devices inserted into their design.
In most devices today, silicon-based CMOS chips are used for computing, but they are not efficient for illumination and communications, resulting in low efficiency and heat generation. This is why current 5G mobile devices on the market get very hot upon use and would shut down after a short time.
This is where III-V semiconductors are valuable. III-V chips are made from elements in the 3rd and 5th columns of the elemental periodic table such as Gallium Nitride (GaN) and Indium Gallium Arsenide (InGaAs). Due to their unique properties, they are exceptionally well suited for optoelectronics (LEDs) and communications (5G etc) — boosting efficiency substantially.
