Microsoft’s new approach to quantum computing is “very close,” an executive says.


Our brain has 86 billion neurons connected by 3 million kilometers of nerve fibers and The Human Brain Project is mapping it all. One of the key applications is neuromorphic computing — computers inspired by brain architecture that may one day be able to learn as we do.
#BloombergGiantLeap #Science #Technology
——-
Like this video? Subscribe to Bloomberg on YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/Bloomberg?sub_confirmation=1
Bloomberg is the First Word in business news, delivering breaking news & analysis, up-to-the-minute market data, features, profiles and more: http://www.bloomberg.com
Connect with us on…
Twitter: https://twitter.com/business
Facebook: /redirect?v=Za21GOxVh18&redir_token=wTy_d5doeYpkktaDTR-C5Z5-KKB8MTU3MzIwMDIwMUAxNTczMTEzODAx&q=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.facebook.com%2Fbloombergbusiness&event=video_description
Instagram: /redirect?v=Za21GOxVh18&redir_token=wTy_d5doeYpkktaDTR-C5Z5-KKB8MTU3MzIwMDIwMUAxNTczMTEzODAx&q=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.instagram.com%2Fbloombergbusiness%2F&event=video_description
Twitter: https://twitter.com/business
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/bloombergbusiness
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/bloombergbusiness/
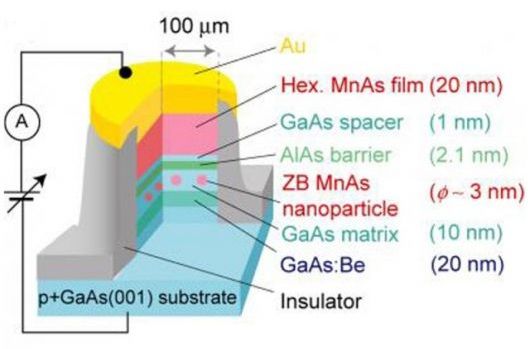
Circa 2009
March 19, 2009 Researchers at the University of Miami and at the Universities of Tokyo and Tohoku, Japan, have been able to prove the existence of a “spin battery,” that could have significant applications including much faster, less expensive and use less energy consuming computer hard drives with no moving parts, and could even be developed to power cars.
A “spin battery” is “charged” by applying a large magnetic field to nano-magnets in a device called a magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ). Like a toy car, the spin battery is “wound up” by applying a large magnetic field — no chemistry involved.
The secret behind this technology is the use of nano-magnets to induce an electromotive force. It uses the same principles as those in a conventional battery, except in a more direct fashion. The energy stored in a battery, be it in an iPod or an electric car, is in the form of chemical energy. When something is turned “on” there is a chemical reaction, which occurs and produces an electric current. The new technology converts the magnetic energy directly into electrical energy, without a chemical reaction. The electrical current made in this process is called a spin polarized current and finds use in a new technology called “spintronics.” Also known as magnetoelectronics, this is an emerging technology, which exploits the intrinsic spin of electrons and its associated magnetic movement, in addition to its fundamental electronic charge, in solid-state devices.

A lab-grown liver stand-in may better predict bad responses to drugs than animal testing does.
A human “liver chip” — liver cells grown on a membrane along with several types of supporting cells — formed structures reminiscent of bile ducts and reacted to drugs similarly to intact livers, researchers report November 6 in Science Translational Medicine. Similar rat and dog liver chips also processed drugs like normal livers in those species, allowing scientists to compare human liver cells’ reactions to drugs to those of the other species.
Rats, dogs and other animals are often used to test whether drugs are toxic to humans before the drugs are given to people. But a previous study found that the animal tests correctly identified only 71 percent of drug toxicities.



In 1935, physicist Erwin Schrödinger concocted a thought experiment to illustrate a pair of strange quantum physics phenomena: superposition and unpredictability.
The experiment became known as Schrödinger’s cat, and for more than 80 years, it’s served as a cornerstone of quantum physics. But in a newly published study, a team of Yale scientists essentially destroys the premise at the center of the experiment — groundbreaking work that could finally allow researchers to develop useful quantum computers.

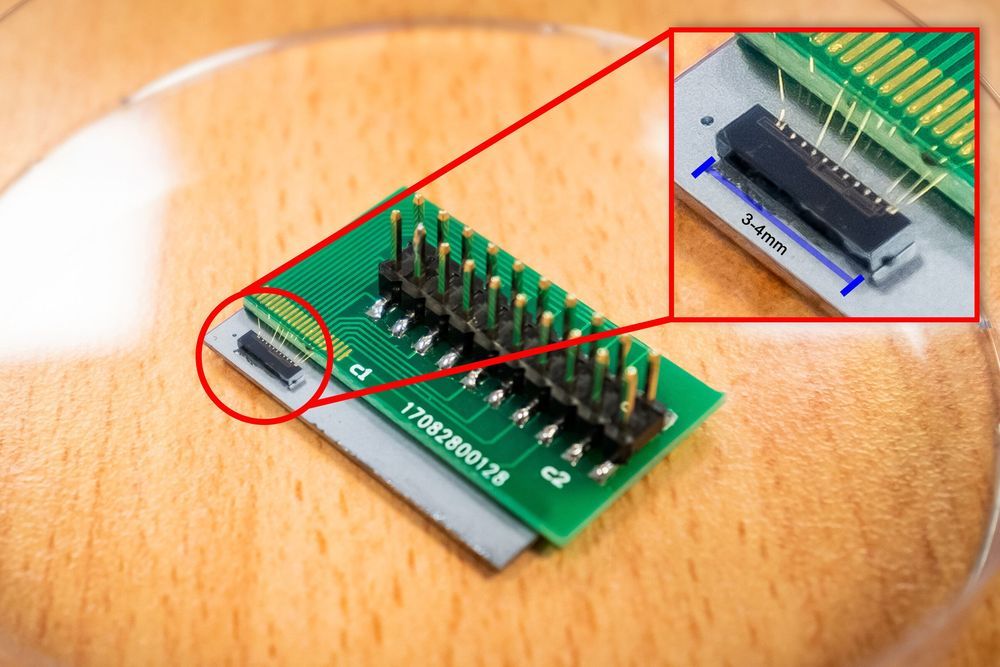
Researchers at Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) have developed a quantum communication chip that is 1,000 times smaller than current quantum setups, but offers the same superior security quantum technology is known for.
Most leading security standards used in secure communication methods—from withdrawing cash from the ATM to purchasing goods online on the smartphone—does not leverage quantum technology. The electronic transmission of the personal identification number (PIN) or password can be intercepted, posing a security risk.
Roughly three millimeters in size, the tiny chip uses quantum communication algorithms to provide enhanced security compared to existing standards. It does this by integrating passwords within the information that is being delivered, forming a secure quantum key. After the information is received, it is destroyed along with the key, making it an extremely secure form of communication.
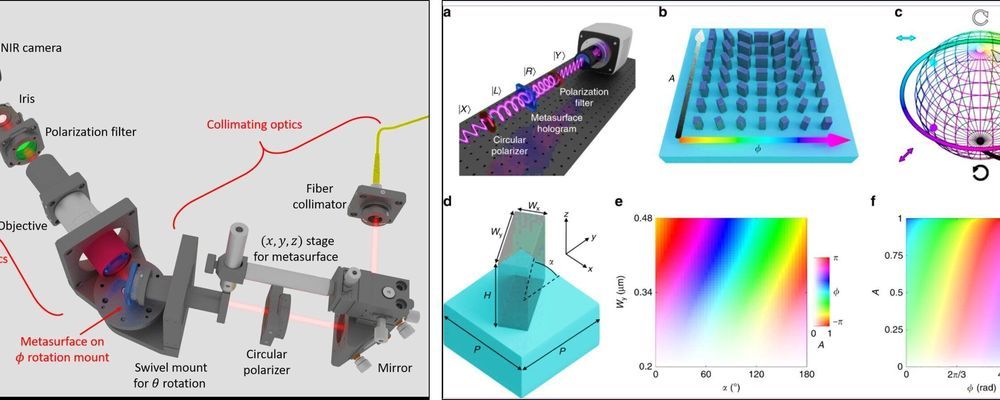
Metasurfaces are optically thin metamaterials that can control the wavefront of light completely, although they are primarily used to control the phase of light. In a new report, Adam C. Overvig and colleagues in the departments of Applied Physics and Applied Mathematics at the Columbia University and the Center for Functional Nanomaterials at the Brookhaven National Laboratory in New York, U.S., presented a novel study approach, now published on Light: Science & Applications. The simple concept used meta-atoms with a varying degree of form birefringence and angles of rotation to create high-efficiency dielectric metasurfaces with ability to control optical amplitude (maximum extent of a vibration) and phase at one or two frequencies. The work opened applications in computer-generated holography to faithfully reproduce the phase and amplitude of a target holographic scene without using iterative algorithms that are typically required during phase-only holography.
The team demonstrated all-dielectric metasurface holograms with independent and complete control of the amplitude and phase. They used two simultaneous optical frequencies to generate two-dimensional (2-D) and 3D holograms in the study. The phase-amplitude metasurfaces allowed additional features that could not be attained with phase-only holography. The features included artifact-free 2-D holograms, the ability to encode separate phase and amplitude profiles at the object plane and encode intensity profiles at the metasurface and object planes separately. Using the method, the scientists also controlled the surface textures of 3D holographic objects.
Light waves possess four key properties including amplitude, phase, polarization and optical impedance. Materials scientists use metamaterials or “metasurfaces” to tune these properties at specific frequencies with subwavelength, spatial resolution. Researchers can also engineer individual structures or “meta-atoms” to facilitate a variety of optical functionalities. Device functionality is presently limited by the ability to control and integrate all four properties of light independently in the lab. Setbacks include challenges of developing individual meta-atoms with varying responses at a desired frequency with a single fabrication protocol. Research studies previously used metallic scatterers due to their strong light-matter interactions to eliminate inherent optical losses relative to metals while using lossless dielectric platforms for high-efficiency phase control—the single most important property for wavefront control.