And it could help in the development of quantum computers.
Category: computing – Page 777
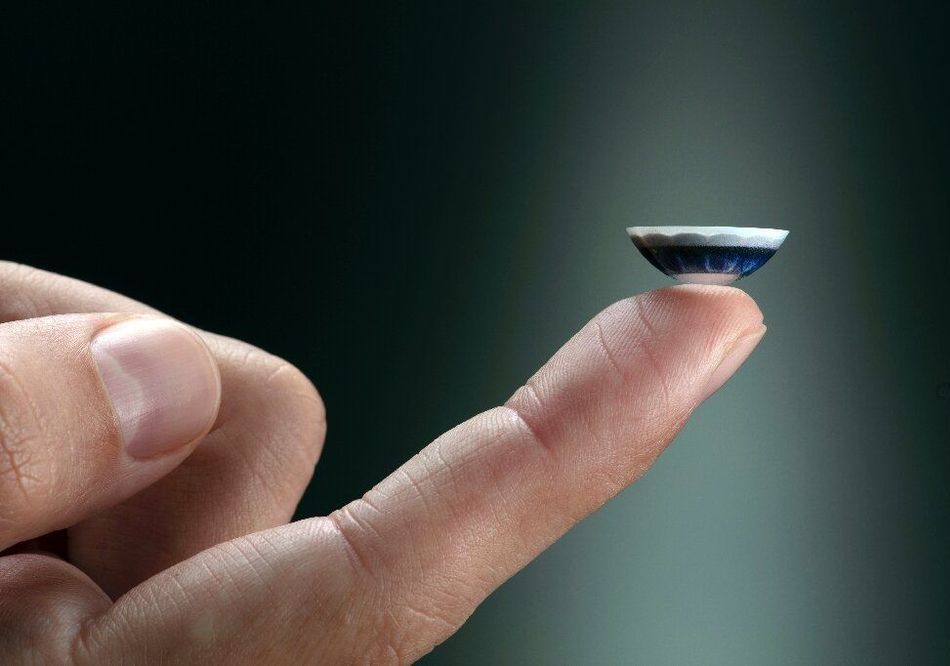

‘Invisible computing’ startup unveils smart contact lens
A startup focused on “invisible computing” Thursday unveiled a smart contact lens which delivers an augmented reality display in a user’s field of vision.
The Mojo Vision contact lens offers a display with information and notifications, and allows the user to interact by focusing on certain points.
The rigid contact lens, which the company has been developing in stealth mode for some 10 years, may also be used to help people with visual impairments by using enhanced image overlays, and has obtained US approval for testing it as a medical device.
360 Video: Go on a Mission With Zipline’s Delivery Drones
With 360 video, IEEE Spectrum takes you behind the scenes with one of the world’s first drone-delivery companies. Zipline, based in California, is using drones to deliver blood to hospitals throughout Rwanda. At an operations center in Muhanga, you’ll watch as Zipline technicians assemble the modular drones, fill their cargo holds, and launch them via catapult. You’ll see a package float down from the sky above a rural hospital, and you’ll get a closeup look at Zipline’s ingenious method for capturing returning drones.
You can follow the action in a 360-degree video in three ways: 1) Watch on your computer, using your mouse to click and drag on the video; 2) watch on your phone, moving the phone around to change your view; or 3) watch on a VR headset for the full immersive experience.
If you’re watching on an iPhone: Go directly to the YouTube page for the proper viewing experience.

The Anti-Deathist: Writings of a Radical Longevity Activist
Friends, I’m excited to say today is the day! I have a brand NEW book out and it’s FREE only today on Amazon. It’s called Please download a copy right now and save $7.99 today while it’s free. And please share with your friends! This books tells the tales and episodes of transhumanism and the longevity movement. Many major figures are in it:
Enter your mobile number or email address below and we’ll send you a link to download the free Kindle App. Then you can start reading Kindle books on your smartphone, tablet, or computer — no Kindle device required.

AlphaZero learns to rule the quantum world
The chess world was amazed when the computer algorithm AlphaZero learned, after just four hours on its own, to beat the best chess programs built on human expertise. Now a research group at Aarhus University in Denmark has used the very same algorithm to control a quantum computer.
All across the world, numerous research groups are attempting to build a quantum computer. Such a computer would be able to solve certain problems that cannot be solved with current classical computers, even if we combined all these computers in the world into one.
At Aarhus University, researchers share the ambition of building a quantum computer. For this reason, a research group under the direction of Professor Jacob Sherson has just used the computer algorithm AlphaZero to learn to control a quantum system.
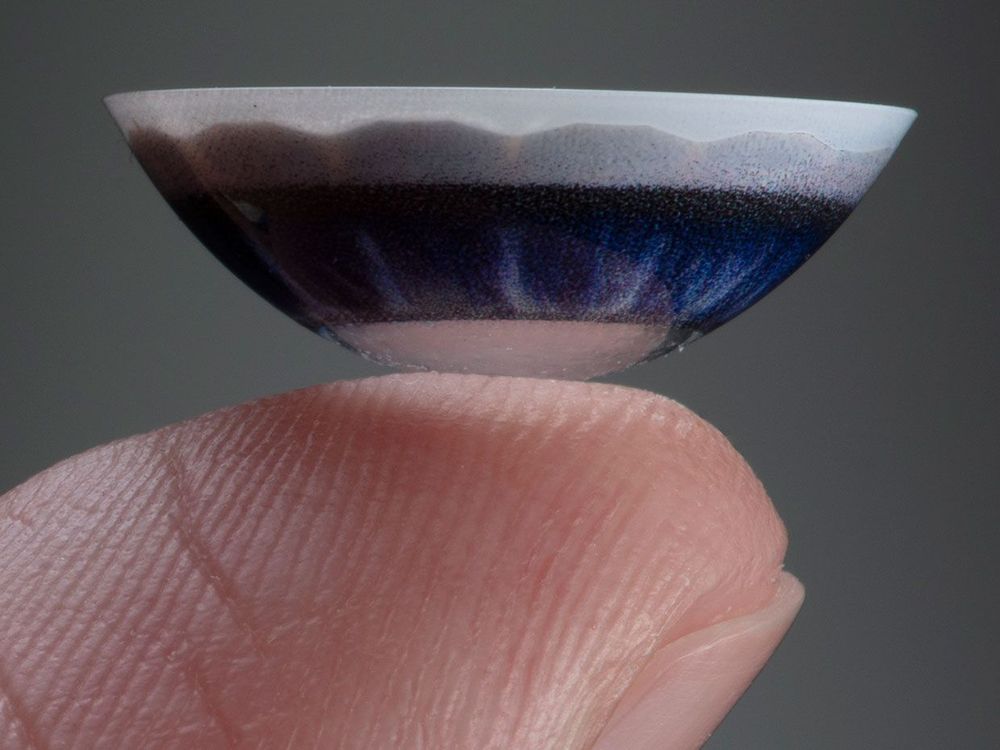

Augmented Reality in a Contact Lens
Science fiction writers envisioned the technology decades ago, and startups have been working on developing an actual product for at least 10 years.
Today, Mojo Vision announced that it has done just that—put 14K pixels-per-inch microdisplays, wireless radios, image sensors, and motion sensors into contact lenses that fit comfortably in the eyes. The first generation of Mojo Lenses are being powered wirelessly, though future generations will have batteries on board. A small external pack, besides providing power, handles sensor data and sends information to the display. The company is calling the technology Invisible Computing, and company representatives say it will get people’s eyes off their phones and back onto the world around them.
The first application, says Steve Sinclair, senior vice president of product and marketing, will likely be for people with low vision—providing real-time edge detection and dropping crisp lines around objects. In a demonstration last week at CES 2020, I used a working prototype (albeit by squinting through the lens rather than putting it into my eyes), and the device highlighted shapes in bright green as I looked around a dimly lit room.
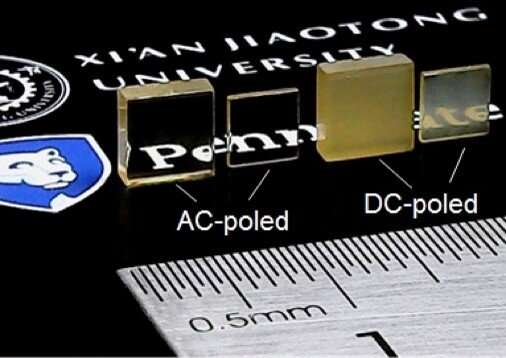
Transparency discovered in crystals with ultrahigh piezoelectricity
Use of an AC rather than a DC electric field can improve the piezoelectric response of a crystal. Now, an international team of researchers say that cycles of AC fields also make the internal crystal domains in some materials bigger and the crystal transparent.
“There have been reports that the use of AC fields could significantly improve the piezoelectric responses—for example by 20% to 40%—over DC fields and the improvements have always been attributed to the smaller internal ferroelectric domain sizes that resulted from the cycles of AC fields,” said Long-Qing Chen, Hamer Professor of Materials Science and Engineering, professor of engineering science and mechanics, and professor of mathematics at Penn State. “About three years ago, Dr. Fei Li, then a research associate at the Materials Research Institute at Penn State, largely confirmed the improvement of piezoelectric performances from application of AC fields. However, it was not clear at all how the internal ferroelectric domains evolved during AC cycles.
”Our group does mostly computer modeling, and more than a year ago we started looking into what happens to the internal domain structures if we apply AC fields to a ferroelectric piezoelectric crystal. We are very curious about how the domain structures evolve during AC cycles. Our computer simulations and theoretical calculations did show an improved piezoelectric response, but our simulations also demonstrated that the ferroelectric domain sizes actually got bigger during AC cycles rather than smaller as reported in the literature.”

IBM’s Plan to Design Solid-State Batteries Using Quantum Tech
Batteries are the key to decarboni z ing both transport and the grid, but today’s technology is still a long way from living up to this promise. IBM seems to have decided its computing chops are the key to solving the problem.
Lithium-ion batteries are still the gold standard technology in this field, and they’ve come a long way; 10 years ago they could just about get your iPod through the day, today they can power high-performance cars over hundreds of miles.
But if we want to reach a point w h ere batteries can outperform gasoline or store huge amounts of solar energy, we need some breakthroughs. So IBM has teamed up with Mercedes-Benz and its parent company Daimler to develop new batteries that could match up to our needs.
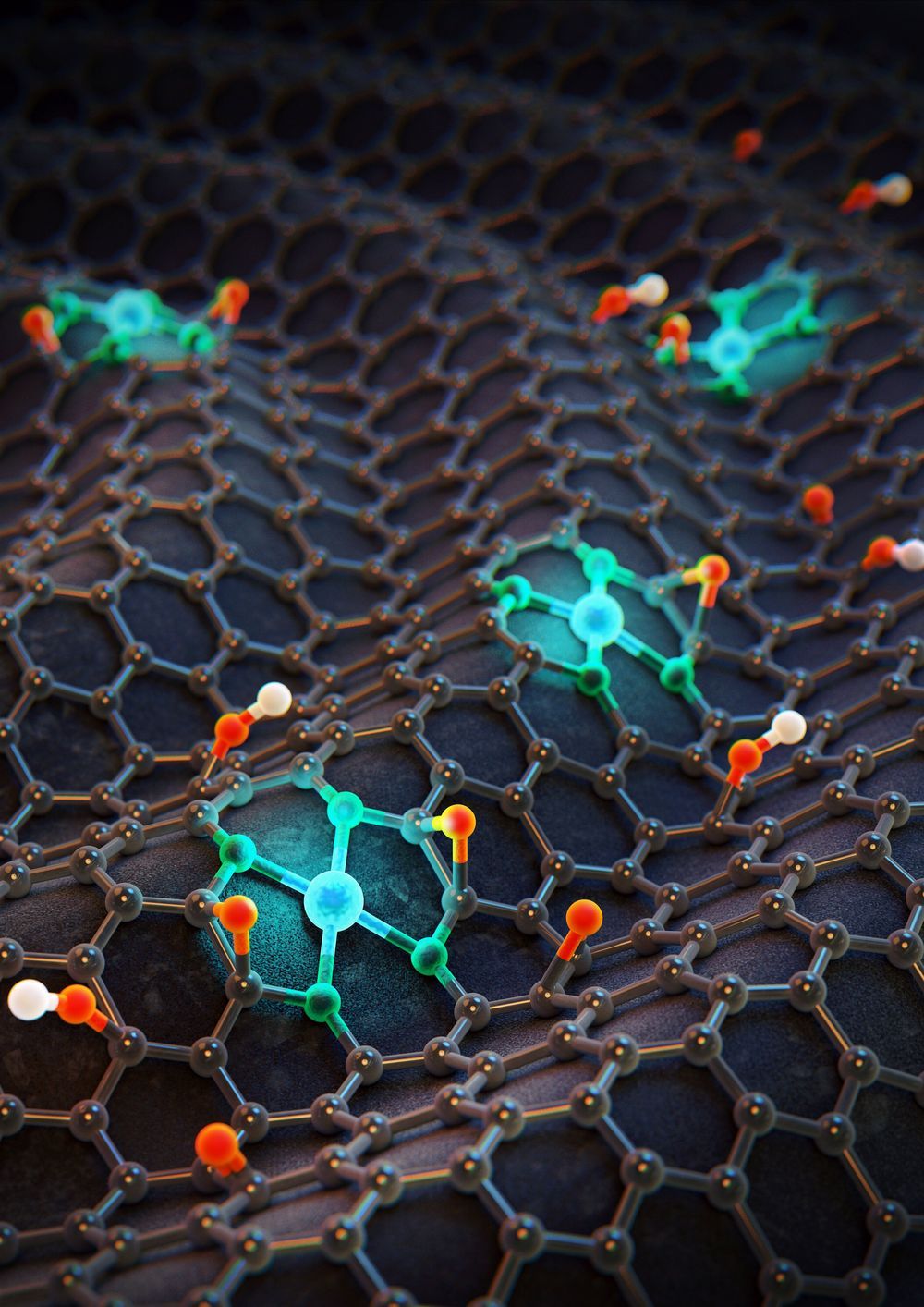
Atomic tuning on cobalt enables an eightfold increase of hydrogen peroxide production
IBS scientists and their colleagues have recently report an ultimate electrocatalyst that addresses all of the issues that trouble H2O2 production. This new catalyst comprising the optimal Co-N4 molecules incorporated in nitrogen-doped graphene, Co1-NG(O), exhibits a record-high electrocatalytic reactivity, producing up to 8 times higher than the amount of H2O2 that can be generated from rather expensive noble metal-based electrocatalysts.
Just as we take a shower to wash away dirt and other particles, semiconductors also require a cleaning process. However, its cleaning goes to extremes to ensure even trace contaminants “leave no trace.” After all the chip fabrication materials are applied to a silicon wafer, a strict cleaning process is taken to remove residual particles. If this high-purity cleaning and particle-removal step goes wrong, electrical connections in the chip are likely to suffer from it. With ever-miniaturized gadgets on the market, the purity standards of the electronics industry reach a level equivalent to finding a needle in a desert.
That explains why hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), a major electronic cleaning chemical, is one of the most valuable chemical feedstocks that underpins the chip-making industry. Despite the ever-growing importance of H2O2, its industry has been left with an energy-intensive and multi-step method known as the anthraquinone process. This is an environmentally unfriendly process which involves the hydrogenation step using expensive palladium catalysts. Alternatively, H2O2 can be synthesized directly from H2 and O2 gas, although the reactivity is still very poor and it requires high pressure. Another eco-friendly method is to electrochemically reduce oxygen to H2O2 a via 2-electron pathway. Recently, noble metal-based electrocatalysts (for example, Au-Pd, Pt-Hg, and Pd-Hg) have been demonstrated to show H2O2 productivity although such expensive investments have seen low returns that fail to meet the scalable industry needs.