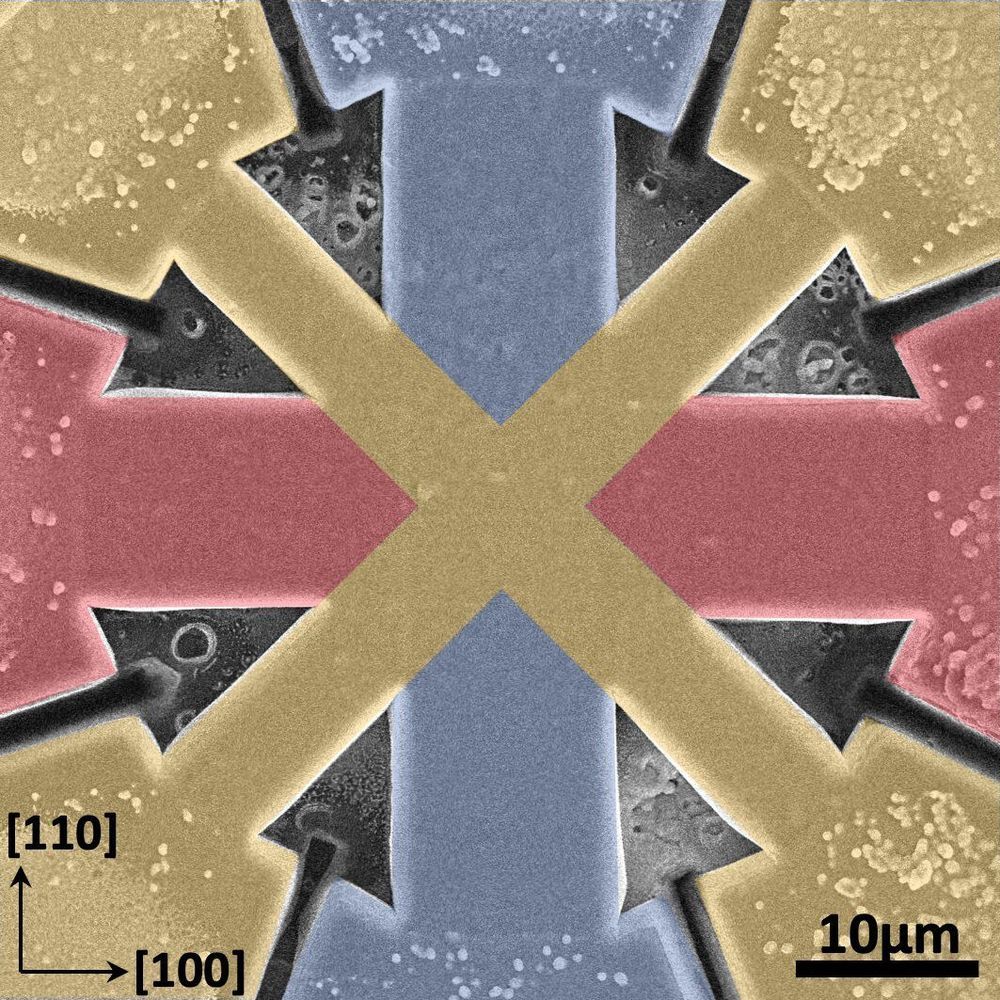
If you’ve been interested in nanotech, but have been too afraid to ask, here is an introductory and interesting article that I’d like to recommend.
My interest in nanotech is based on my hope that nanotech can lead to methods of constructing substrates that are suitable for mind uploading. It may lead to a technique to create duplicate minds.
“These ‘biological engineering’ technologies have made real one of the dreams of the nanotechnology pioneers: the deployment of molecular assemblers able to construct any shape with atomic precision, following a rational design.”
“…hybrid bioinorganic devices that mimic biological processes will soon be used in new computers and electronic devices.”
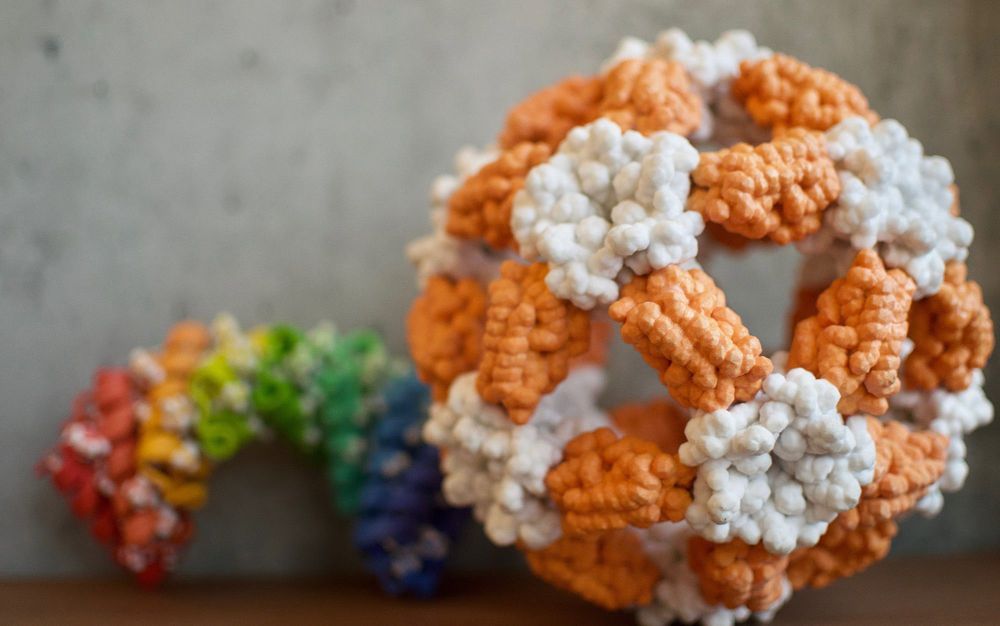
In the mid-1980s, evidence started to emerge from labs across the world confirming that scientists were finally able to reach the nano level in experimental conditions and not just with their theories. Working at scales defined in millionths of a millimetre, Richard Smalley, Robert Curl and Harold Kroto reported the discovery of ‘buckminsterfullerene’ – a nanosized polyhedron, with 32 faces fused into a cage-like, soccer-ball structure, and with carbon atoms sitting in each of its 60 vertices.
These miniature ‘Bucky’ balls (named for their similarity to the geodesic dome structures made by the architect R Buckminster Fuller in the 1950s), are found in tiny quantities in soot, in interstellar space and in the atmospheres of carbon-rich red giant stars, but Kroto was able to recreate them in chemical reactions in the lab while visiting Rice University in Texas. Then, in 1991, Nadrian Seeman’s lab at New York University used 10 artificial strands of DNA to create the first human-made nanostructure, connecting up the DNA strands to resemble the edges of a cube, so marking the beginning of the field now known as ‘DNA nanotechnology’. Clever scientists with broad visions started to realise that a new kind of technology, prophesied by Richard Feynman in the 1950s, was finally materialising, as researchers achieved the capacity to visualise, fabricate and manipulate matter at the nanometre scale.