A cryptographic master tool called indistinguishability obfuscation has for years seemed too good to be true. Three researchers have figured out that it can work.



Three-dimensional (3D) nanostructured materials—those with complex shapes at a size scale of billionths of a meter—that can conduct electricity without resistance could be used in a range of quantum devices. For example, such 3D superconducting nanostructures could find application in signal amplifiers to enhance the speed and accuracy of quantum computers and ultrasensitive magnetic field sensors for medical imaging and subsurface geology mapping. However, traditional fabrication tools such as lithography have been limited to 1-D and 2-D nanostructures like superconducting wires and thin films.
Now, scientists from the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory, Columbia University, and Bar-Ilan University in Israel have developed a platform for making 3D superconducting nano-architectures with a prescribed organization. As reported in the Nov. 10 issue of Nature Communications, this platform is based on the self-assembly of DNA into desired 3D shapes at the nanoscale. In DNA self-assembly, a single long strand of DNA is folded by shorter complementary “staple” strands at specific locations—similar to origami, the Japanese art of paper folding.
“Because of its structural programmability, DNA can provide an assembly platform for building designed nanostructures,” said co-corresponding author Oleg Gang, leader of the Soft and Bio Nanomaterials Group at Brookhaven Lab’s Center for Functional Nanomaterials (CFN) and a professor of chemical engineering and of applied physics and materials science at Columbia Engineering. “However, the fragility of DNA makes it seem unsuitable for functional device fabrication and nanomanufacturing that requires inorganic materials. In this study, we showed how DNA can serve as a scaffold for building 3D nanoscale architectures that can be fully “converted” into inorganic materials like superconductors.”
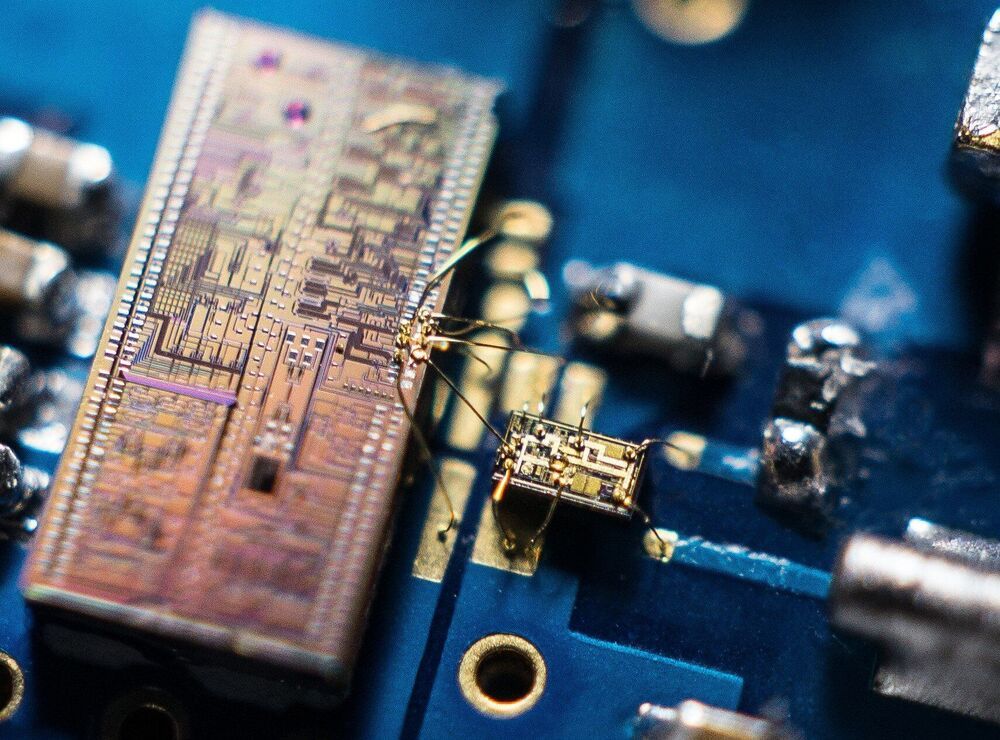
Bristol researchers have developed a tiny device that paves the way for higher performance quantum computers and quantum communications, making them significantly faster than the current state-of-the-art.
Researchers from the University of Bristol’s Quantum Engineering Technology Labs (QET Labs) and Université Côte d’Azur have made a new miniaturized light detector to measure quantum features of light in more detail than ever before. The device, made from two silicon chips working together, was used to measure the unique properties of “squeezed” quantum light at record high speeds.
Harnessing unique properties of quantum physics promises novel routes to outperform the current state-of-the-art in computing, communication and measurement. Silicon photonics—where light is used as the carrier of information in silicon micro-chips—is an exciting avenue towards these next-generation technologies.
Scientists have successfully teleported a three-dimensional quantum state. The international effort between Chinese and Austrian scientists could be crucial for the future of quantum computers.
The researchers, from Austrian Academy of Sciences, the University of Vienna, and University of Science and Technology of China, were able to teleport the quantum state of one photon to another distant state. The three-dimensional transportation is a huge leap forward. Previously, only two-dimensional quantum teleportation of qubits has been possible. By entering a third dimension, the scientists were able to transport a more advanced unit of quantum information known as a “qutrit.”
Quantum computing is different than what’s known as classical computing, which is what powers phones and laptops. These traditional devices store information in bits, which are represented with a binary 0 or 1. A good metaphor is to imagine a circle, where each 0 and 1 are on opposite points. In Quantum computing, which deals with atomic and subatomic particles, qubits can exist at both of those points as well as anywhere else in the circle.

We probably think we know gravity pretty well. After all, we have more conscious experience with this fundamental force than with any of the others (electromagnetism and the weak and strong nuclear forces). But even though physicists have been studying gravity for hundreds of years, it remains a source of mystery.
In our video Why Is Gravity Different? We explore why this force is so perplexing and why it remains difficult to understand how Einstein’s general theory of relativity (which covers gravity) fits together with quantum mechanics.
Gravity is extraordinarily weak and nearly impossible to study directly at the quantum level. We cannot scrutinize it using particle accelerators like we can with the other forces, so we need other ways to get at quantum gravity.
The Raspberry Pi 400 comes with 4GB RAM, a faster Raspberry Pi 4 and a built-in heatsink to keep it cool.
Researchers at MIT and the University of Waterloo have developed a high-power, portable version of a device called a quantum cascade laser, which can generate terahertz radiation outside of a laboratory setting. The laser could potentially be used in applications such as pinpointing skin cancer and detecting hidden explosives.
Until now, generation of terahertz radiation powerful enough to perform real-time imaging and fast spectral measurements required temperatures far below 200 Kelvin (−100 degrees Fahrenheit) or lower. These temperatures could only be achieved with bulky equipment that limited the technology’s use to a laboratory setting. In a paper published in Nature Photonics, MIT Distinguished Professor of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Qing Hu and his colleagues report that their terahertz quantum cascade laser can function at temperatures of up to 250 K (−10 degrees Fahrenheit), meaning that only a compact portable cooler is required.
Terahertz quantum cascade lasers, tiny chip-embedded semiconductor laser devices, were first invented in 2002, but adapting them to operate far above 200 K proved to be so difficult that many people in the field speculated that there was a fundamental physical reason preventing it, Hu says.
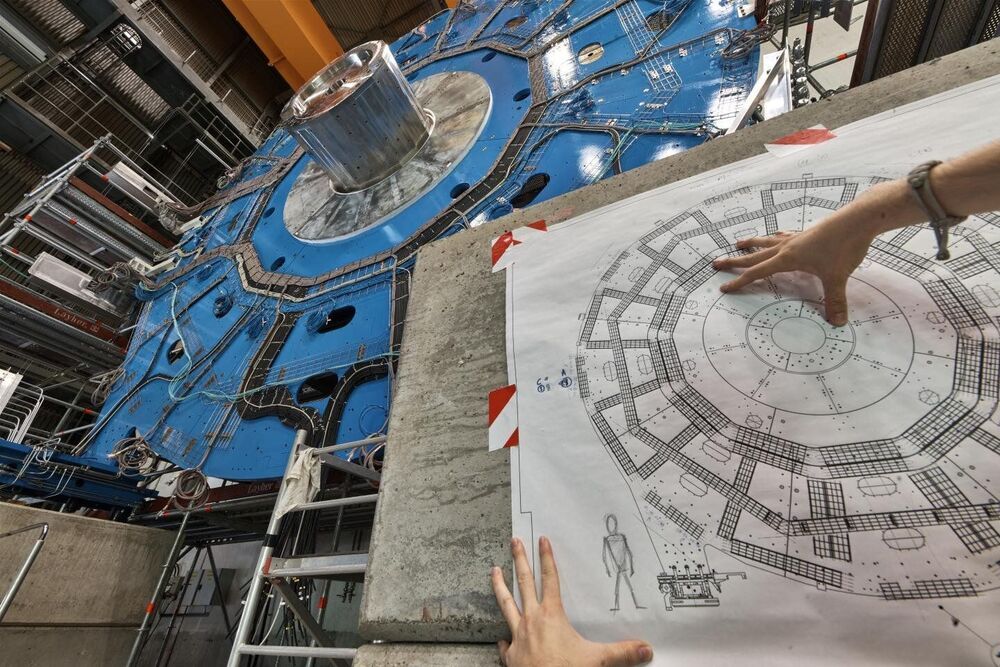
Borrowing a page from high-energy physics and astronomy textbooks, a team of physicists and computer scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) has successfully adapted and applied a common error-reduction technique to the field of quantum computing.
In the world of subatomic particles and giant particle detectors, and distant galaxies and giant telescopes, scientists have learned to live, and to work, with uncertainty. They are often trying to tease out ultra-rare particle interactions from a massive tangle of other particle interactions and background “noise” that can complicate their hunt, or trying to filter out the effects of atmospheric distortions and interstellar dust to improve the resolution of astronomical imaging.
Also, inherent problems with detectors, such as with their ability to record all particle interactions or to exactly measure particles’ energies, can result in data getting misread by the electronics they are connected to, so scientists need to design complex filters, in the form of computer algorithms, to reduce the margin of error and return the most accurate results.

For those that like really fast personal computers. 😃
Considering how powerful computers nowadays need to be, I think everyone will benefit overall.
These workloads are comprised of a fixed amount of work, so we can plot the task energy against the time required to finish the job (bottom axis), thus generating a really useful power chart. Bear in mind that faster compute times, and lower task energy requirements, are ideal.
This measure really separates the wheat from the chaff, and the best results fall to the lower left-hand corner of the chart. The Intel chips populate the less-desirable upper right-hand side. Although the Core i9-10980XE makes a valiant attempt to get down to Ryzen territory, it still can’t match the previous-gen Ryzen 3000 processors in terms of efficiency. Meanwhile, the Ryzen 5000 series leverages the Zen 3 architecture to great effect and falls further inside the performance-per-watt sweet spot, marking a new level of efficiency for a modern desktop chip.
To the world of enthusiasts that have long been pining for a huge gen-on-gen upgrade, AMD’s Ryzen 9 5950X and Ryzen 9 5900X deliver an almost unbelievable amount of performance improvement over not only AMD’s previous-gen Ryzen processors, but also over Intel’s Comet Lake flagships. The fact that the Ryzen 9 chips regularly break the 5GHz barrier, even at stock settings, is simply icing on the cake.