If your business needs backend services for its websites and apps, IT pros say these are the serverless computing providers to turn to.

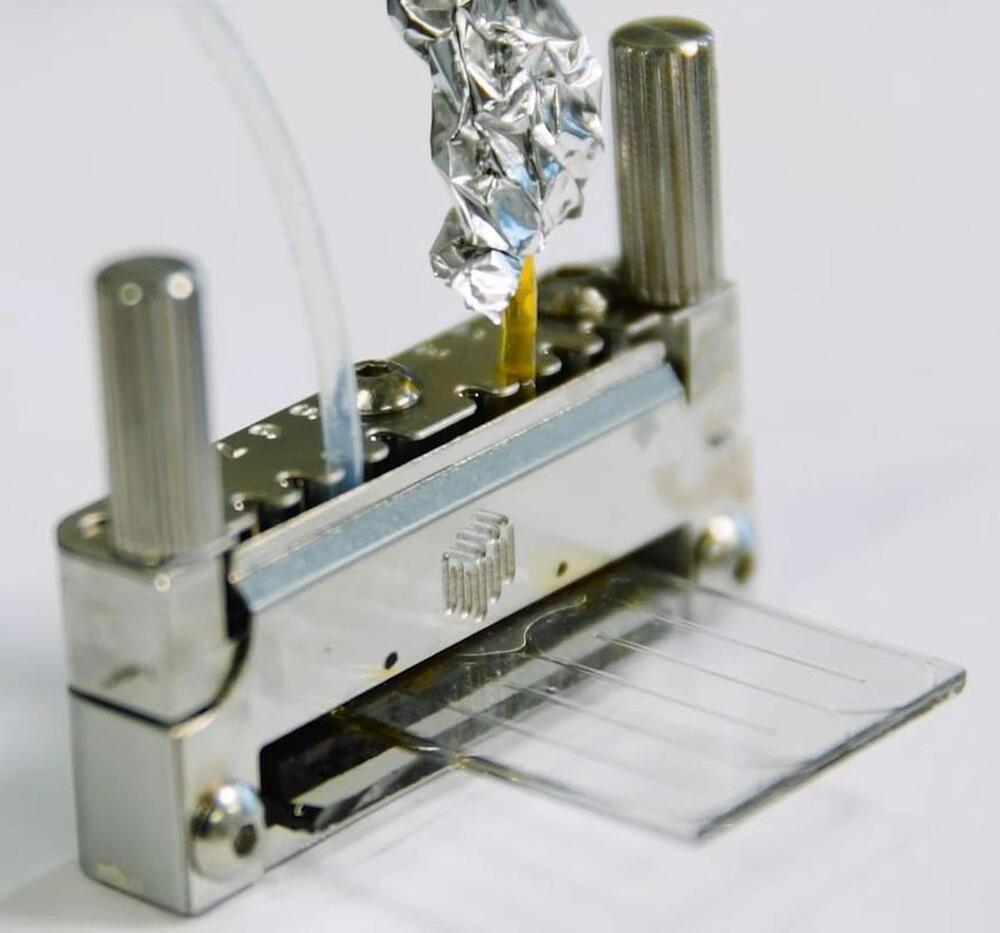
Developed by a Chinese-Swedish research group, the device is an ultra-thin chip that could be integrated into electronics such as headphones, smartwatches and telephones. It combines a Molecular Solar Thermal Energy Storage System (MOST) with a micro-fabricated system that includes a thermoelectric generator (TEG) with a low-dimensional material-based microelectromechanical system (MEMS).

Existing quantum devices can actually do things that we cannot compute with classical computers. The question is only can we harness this computational power that is apparently there,” van Bijnen says. “Maybe doing arbitrary computational problems is a bit much to ask, so we are now looking at whether we can match problems well to available quantum hardware.” Many current experiments involving Rydberg atoms would likely not require any radical changes in instrumentation that is already being used, he adds.

A chip-based infection model developed by researchers in Jena, Germany, enables live microscopic observation of damage to lung tissue caused by the invasive fungal infection aspergillosis. The team developed algorithms to track the spread of fungal hyphae as well as the response of immune cells. The development is based on a “lung-on-chip” model also developed in Jena and can help reduce the number of animal experiments. The results were presented in the journal Biomaterials.
Aspergillosis is a mold infection caused by Aspergillus fumigatus, which often affects the lungs. The disease can be fatal, especially in immunocompromised individuals. In these cases, invasive aspergillosis usually occurs with fungal hyphae invading blood vessels. So far, there are only a few active substances that can combat such fungal infections. “That’s why it was so important for us to be able to represent this invasive growth in a model,” says Marie von Lilienfeld-Toal, who co-led the study. The internist is a professor at the Department of Internal Medicine II at Jena University Hospital and conducts research at the Leibniz Institute for Natural Product Research and Infection Biology—Hans Knöll Institute (Leibniz-HKI) in Jena, Germany.
The new aspergillosis infection model should help to better observe both the growth of the fungus and the reaction of the immune system and to find possible new approaches for therapies. In addition, new active substances can be tested. The expertise for this is available in Jena: Organ chips have long been developed at the university hospital. The startup Dynamic42, which manufactures the lung chips used in the study, was founded there. First author Mai Hoang also joined the company after completing her doctorate.

AMD is at it again. 😃
The launch of AMD’s Ryzen 7 5800X3D is imminent. Chips are out in the wild and early bird reviews and benchmarks are popping up on the web. Given that AMD has been touting the gaming prowess of the 5800X3D, we’ve been waiting to see if that claim holds up. And it appears that it does.
Peruvian hardware site Xanxo Gaming (via 3DCenter) managed to get hold of a retail Ryzen 7 5800X3D and put it through a comprehensive suite of benchmarks, comparing it to Intel’s Core i9 12900KF. As the site wasn’t sampled by AMD, it’s not subject to an embargo.
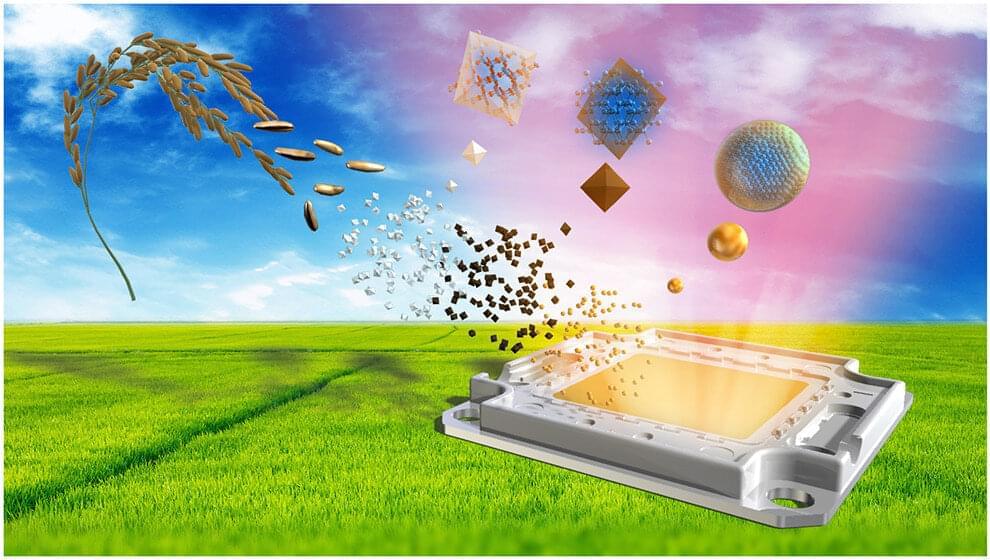


Milling rice to separate the grain from the husks produces about 100 million tons of rice husk waste globally each year. Scientists searching for a scalable method to fabricate quantum dots have developed a way to recycle rice husks to create the first silicon quantum dot (QD) LED light. Their new method transforms agricultural waste into state-of-the-art light-emitting diodes in a low-cost, environmentally friendly way.
The research team from the Natural Science Center for Basic Research and Development, Hiroshima University, published their findings on January 28, 2022, in the American Chemical Society journal ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering.
“Since typical QDs often involve toxic material, such as cadmium, lead, or other heavy metals, environmental concerns have been frequently deliberated when using nanomaterials. Our proposed process and fabrication method for QDs minimizes these concerns,” said Ken-ichi Saitow, lead study author and a professor of chemistry at Hiroshima University.
