How do you integrate the advantages of a benchtop laser that fills a room onto a semiconductor chip the size of a fingernail?



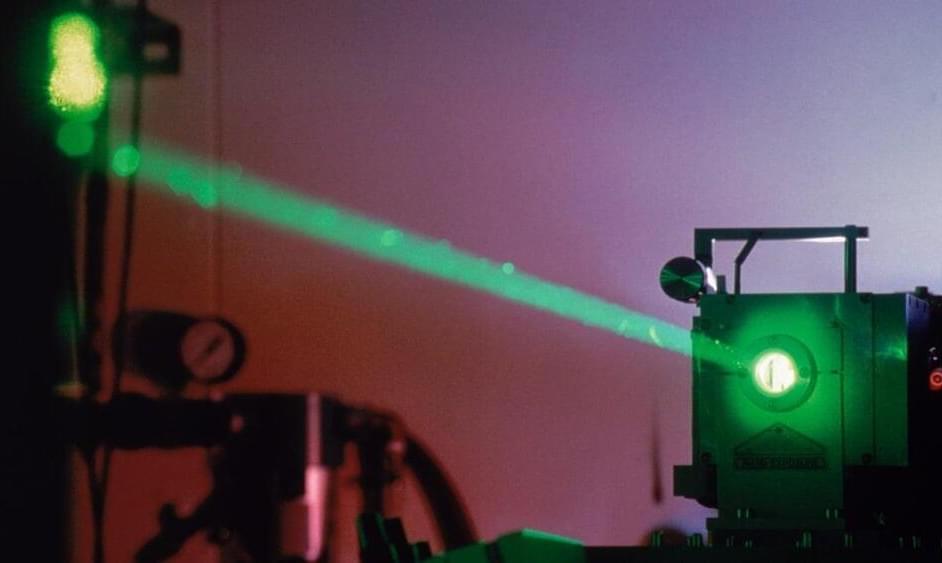
Researchers in Europe have developed an efficient way to deliver internet speeds at over 1 million gigabits per second through a single chip and laser system.
The experiment achieved a speed of 1.8 petabits per second, or nearly twice the amount of internet traffic the world transmits at the same rate. Amazingly, the feat was pulled off using only a single optical light source.
The research comes from a team at Technical University of Denmark and Chalmers University of Technology in Sweden. Last week, the group published a peer-reviewed paper (Opens in a new window) in Nature Photonics about the technology.
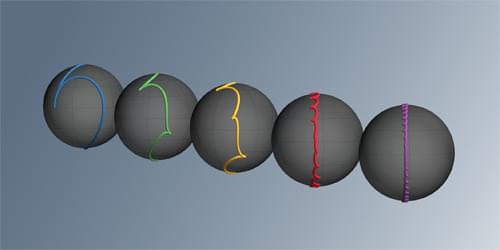
The engineering of so-called Floquet states leads to almost-perfect atom-optics elements for matter-wave interferometers—which could boost these devices’ ability to probe new physics.
Since Michelson and Morley’s famous experiment to detect the “luminiferous aether,” optical interferometry has offered valuable tools for studying fundamental physics. Nowadays, cutting-edge applications of the technique include its use as a high-precision ruler for detecting gravitational waves (see Focus: The Moon as a Gravitational-Wave Detector) and as a platform for quantum computing (see Viewpoint: Quantum Leap for Quantum Primacy). But as methods for cooling and controlling atoms have advanced, a new kind of interferometer has become available, in which light waves are replaced by matter waves [1]. Such devices can measure inertial forces with a sensitivity even greater than that of optical interferometers [2] and could reveal new physics beyond the standard model.
Foresight Biotech & Health Extension Meeting sponsored by 100 Plus Capital.
Program & apply to join: https://foresight.org/biotech-health-extension-program/
This video was recorded at the Foresight Longevity Workshop.
Join us:
► Twitter: https://twitter.com/foresightinst.
► Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/foresightinst.
► Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/existentialhope/
► LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/foresight-institute.
If you enjoy what we do please support us via Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/foresightinstitute.
If you’re interested in joining these meetings consider donating through our donation page: https://foresight.org/donate/
Foresight Institute advances technologies for the long-term future of life, focusing on molecular machine nanotechnology, biotechnology, and computer science.
Subscribe for videos concerning our programs on Molecular Machines, Biotechnology & Health Extension, Intelligent Cooperation, Neurotech, Space, and Existential Hope.

The drought affecting the Mississippi River has revealed a watery secret – a shipwreck that’s over a hundred years old. The skeleton of the craft emerged in Baton Rouge this summer, thanks to low water levels. Dr. Chip McGimsey, archaeologist for the State of Louisiana, believes the ruins belong to the Brookhill Ferry, which sank in 1915. He says the wreck provides a unique way to explore the past, noting, “It makes history alive in a way that you don’t get any other way.”

It can download 230 million photographs in one second.
We all want more internet power and now we may just get it. A single computer chip has transmitted a record 1.84 petabits of data per second via a fiber-optic cable.
230 million photographs downloaded in one second
That amount exhibited enough bandwidth to download 230 million photographs in that time. The initiative was led by Asbjørn Arvad Jørgensen at the Technical University of Denmark in Copenhagen.

It enables us to make extraordinary leaps of imagination.
We all have to make hard decisions from time to time. The hardest of my life was whether or not to change research fields after my Ph.D., from fundamental physics to climate physics. I had job offers that could have taken me in either direction — one to join Stephen Hawking’s Relativity and Gravitation Group at Cambridge University, another to join the Met Office as a scientific civil servant.
I wrote down the pros and cons of both options as one is supposed to do, but then couldn’t make up my mind at all. Like Buridan’s donkey, I was unable to move to either the bale of hay or the pail of water.
Metamorworks/iStock.
Since it was doing my head in, I decided to try to forget about the problem for a couple of weeks and get on with my life. In that intervening time, my unconscious brain decided for me. I simply walked into my office one day and the answer had somehow become obvious: I would make the change to studying the weather and climate.