US semiconductor maker Wolfspeed plans to build a chip factory in Germany, which could benefit domestic EV production and the EU chip sector.



One of the most exciting applications of quantum computers will be to direct their gaze inwards, at the very quantum rules that make them tick. Quantum computers can be used to simulate quantum physics itself, and perhaps even explore realms that don’t exist anywhere in nature.
But even in the absence of a fully functional, large-scale quantum computer, physicists can use a quantum system they can easily control to emulate a more complicated or less accessible one. Ultracold atoms—atoms that are cooled to temperatures just a tad above absolute zero—are a leading platform for quantum simulation. These atoms can be controlled with laser beams and magnetic fields, and coaxed into performing a quantum dance routine choreographed by an experimenter. It’s also fairly easy to peer into their quantum nature using high-resolution imaging to extract information after—or while—they complete their steps.
Now, researchers at JQI and the NSF Quantum Leap Challenge Institute for Robust Quantum Simulation (RQS), led by former JQI postdoctoral fellow Mingwu Lu and graduate student Graham Reid, have coached their ultracold atoms to do a new dance, adding to the growing toolkit of quantum simulation. In a pair of studies, they’ve bent their atoms out of shape, winding their quantum mechanical spins around in both space and time before tying them off to create a kind of space-time quantum pretzel.
A new ultra-low-power method of communication at first glance seems to violate the laws of physics. It is possible to wirelessly transmit information simply by opening and closing a switch that connects a resistor to an antenna. No need to send power to the antenna.
Our system, combined with techniques for harvesting energy from the environment, could lead to all manner of devices that transmit data, including tiny sensors and implanted medical devices, without needing batteries or other power sources. These include sensors for smart agriculture, electronics implanted in the body that never need battery changes, better contactless credit cards and maybe even new ways for satellites to communicate.
Apart from the energy needed to flip the switch, no other energy is needed to transmit the information. In our case, the switch is a transistor, an electrically controlled switch with no moving parts that consumes a minuscule amount of power.
A study by chemists at the University of Chicago has uncovered a new key step in the process that HIV uses to replicate itself.
The study, published Jan. 6 in Science Advances, used computer modeling to focus on how HIV forms a capsule that carries its genetic material—in particular, the role of a particular ion known as IP6. Scientists had previously suspected IP6 has an important function but didn’t know exactly how it worked.
The theory may explain aspects of the success of a promising new drug, as well as point the way to other treatments.
Physical systems evolve at a particular speed, which depends on various factors including the system’s so-called topological structure (i.e., spatial properties that are preserved over time despite any physical changes that occur). Existing methods for determining the speed at which physical systems change over time, however, do not account for these structural properties.
Two researchers at Keio University in Japan have recently derived a speed limit for the evolution of physical states that also accounts for the topological structure of a system and of its underlying dynamics. This speed limit, outlined in a paper published in Physical Review Letters, could have numerous valuable applications for the study and development of different physical systems, including quantum technologies.
“Figuring out how fast a system state can change is a central topic in classical and quantum mechanics, which has attracted the great interest of scientists,” Tan Van Vu and Keiji Saito, the researchers who carried out the study, told Phys.org. “Understanding the mechanism of controlling time is relevant to engineering fast devices such as quantum computers.”
Paris-based quantum computing startup PASQAL announced today it has raised €100 million in a Series B funding round, led by a new investor, Singapore-based Temasek. It was joined by the European Innovation Council (EIC) Fund, Wa’ed Ventures and Bpifrance, through its Large Venture Fund and existing investors Quantonation, the Defense Innovation Fund, Daphni and Eni Next. This brings PASQAL’s total funding to date to more than €140 million.
Founded in 2019 as a spin-off from Institut d’Optique, PASQAL develops quantum processors based on ordered neutral atoms in 2D and 3D arrays. Physics Today.
PASQAL’s technology is based on research conducted by the winner of the 2022 Nobel Prize in Physics, and it plans to deliver major commercial advantages over classical computers by 2024.
Dr. Cody reveals private conversations about BCI and experience at CES2023.
►►►Mendi Affiliate Link (free shipping, 15% off Pre-Black Friday before 24Nov): https://www.mendi.io/?discount=mendiwithdrcody.
►►►Muse Headband (Black Friday 20% Off Dr. Cody Discount (applied at checkout 10Nov-23Nov applied at checkout)): https://mbsy.co/68Mq9h.
►►►FocusCalm $25 off: Enter “DrCody” at discount checkout: https://www.focuscalm.com.
►►►NeoRhythm Affiliate link: https://tidd.ly/3q8wNom (10% discount code is “drcody” at checkout)
►►►Start a Myndlift Clinic: $200 discount promo code-RFCZECCJ
►►►Neurosity Affiliate link https://neurosity.co/cody.
►►► GET YOUR FREE MEDITATION GUIDE HERE: https://bit.ly/2XIRDNa.
►►► INSTAGRAM (Behind The Scenes with Cody Rall MD): https://www.instagram.com/codyrall_techforpsych/
Cody Rall, M.D., is a United States Navy trained Psychiatrist who specializes in neurotechnology wearables. He is a co-founder of Stanford Brainstorm, the world’s first academic laboratory dedicated to transforming brain health through entrepreneurship.
Dr. Rall also served as a board member of the psychiatry innovation lab, an annual national competition at the American Psychiatric Association that works as an incubator for groups developing technological solutions to problems in mental health care. He is the founder of Techforpsych, a media and relations company that covers advancements in technology related to neuroscience.
What’s your favorite number? There are literally infinite options, and yet only a few which seem to stand out as more popular than others: there’s seven, obviously; 13 or 666 for the badasses among us; and √2 for anyone who just likes annoying Pythagoreans.
But there’s really only one number out there that can claim to be World Champion: pi. What other mathematical constant is literally used as a benchmark for computing power, or forms the basis for a never-ending worldwide grudge match over who can list the most random digits in the correct order (current record: 111,700)?
The reason pi is able to capture our imagination like this is because it is an irrational number – in other words, its decimal expansion is never-ending and entirely random. It’s thought that any sequence of numbers you can possibly think of can be found somewhere in the expansion of pi, and yet knowing any particular sequence somewhere in the expansion tells you no information about which digit comes next.

Large Language Models (LLM) are on fire, capturing public attention by their ability to provide seemingly impressive completions to user prompts (NYT coverage). They are a delicate combination of a radically simplistic algorithm with massive amounts of data and computing power. They are trained by playing a guess-the-next-word game with itself over and over again. Each time, the model looks at a partial sentence and guesses the following word. If it makes it correctly, it will update its parameters to reinforce its confidence; otherwise, it will learn from the error and give a better guess next time.
While the underpinning training algorithm remains roughly the same, the recent increase in model and data size has brought about qualitatively new behaviors such as writing basic code or solving logic puzzles.
How do these models achieve this kind of performance? Do they merely memorize training data and reread it out loud, or are they picking up the rules of English grammar and the syntax of C language? Are they building something like an internal world model—an understandable model of the process producing the sequences?
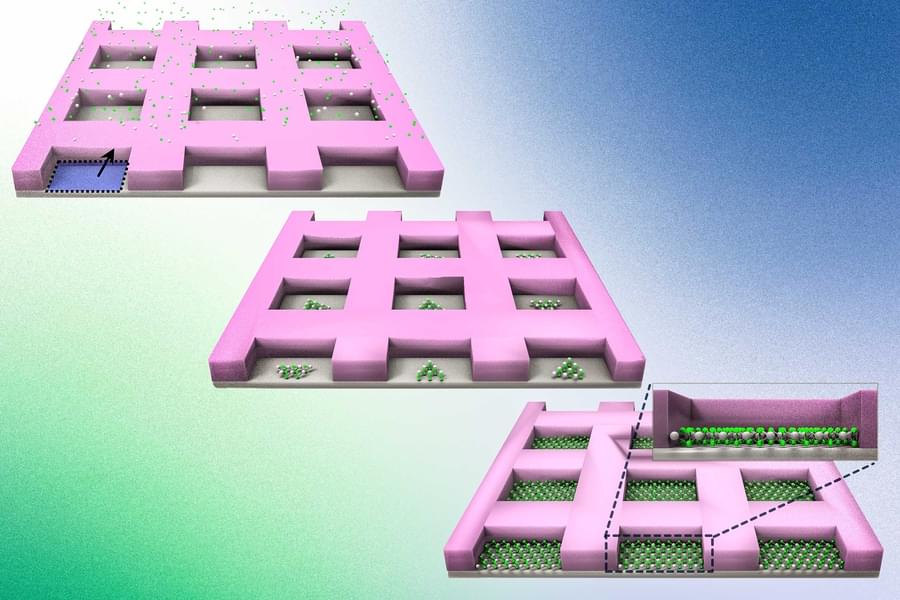
True to Moore’s Law, the number of transistors on a microchip has doubled every year since the 1960s. But this trajectory is predicted to soon plateau because silicon — the backbone of modern transistors — loses its electrical properties once devices made from this material dip below a certain size.
Enter 2D materials — delicate, two-dimensional sheets of perfect crystals that are as thin as a single atom. At the scale of nanometers, 2D materials can conduct electrons far more efficiently than silicon. The search for next-generation transistor materials therefore has focused on 2D materials as potential successors to silicon.
But before the electronics industry can transition to 2D materials, scientists have to first find a way to engineer the materials on industry-standard silicon wafers while preserving their perfect crystalline form. And MIT engineers may now have a solution.