Such credentials in the wrong hands could be dangerous, experts say, potentially allowing physical access to data centers. The affected data center operators say the stolen information didn’t pose risks for customer IT systems.



Synchron’s BCI is inserted through the blood vessels, which Oxley calls the “natural highways” into the brain. Synchron’s stent, called the Stentrode, is fitted with tiny sensors and is delivered to the large vein that sits next to the motor cortex. The Stentrode is connected to an antenna that sits under the skin in the chest and collects raw brain data that it sends out of the body to external devices.
Peter Yoo, senior director of neuroscience at Synchron, said since the device is not inserted directly into the brain tissue, the quality of the brain signal isn’t perfect. But the brain doesn’t like being touched by foreign objects, Yoo said, and the less invasive nature of the procedure makes it more accessible.
“There’s roughly about 2,000 interventionalists who can perform these procedures,” Yoo told CNBC. “It’s a little bit more scalable, compared to, say, open-brain surgery or burr holes, which only neurosurgeons can perform.”

Humanity may soon generate more data than hard drives or magnetic tape can handle, a problem that has scientists turning to nature’s age-old solution for information-storage—DNA.
In a new study in Science, a pair of researchers at Columbia University and the New York Genome Center (NYGC) show that an algorithm designed for streaming video on a cellphone can unlock DNA’s nearly full storage potential by squeezing more information into its four base nucleotides. They demonstrate that this technology is also extremely reliable.
DNA is an ideal storage medium because it’s ultra-compact and can last hundreds of thousands of years if kept in a cool, dry place, as demonstrated by the recent recovery of DNA from the bones of a 430,000-year-old human ancestor found in a cave in Spain.
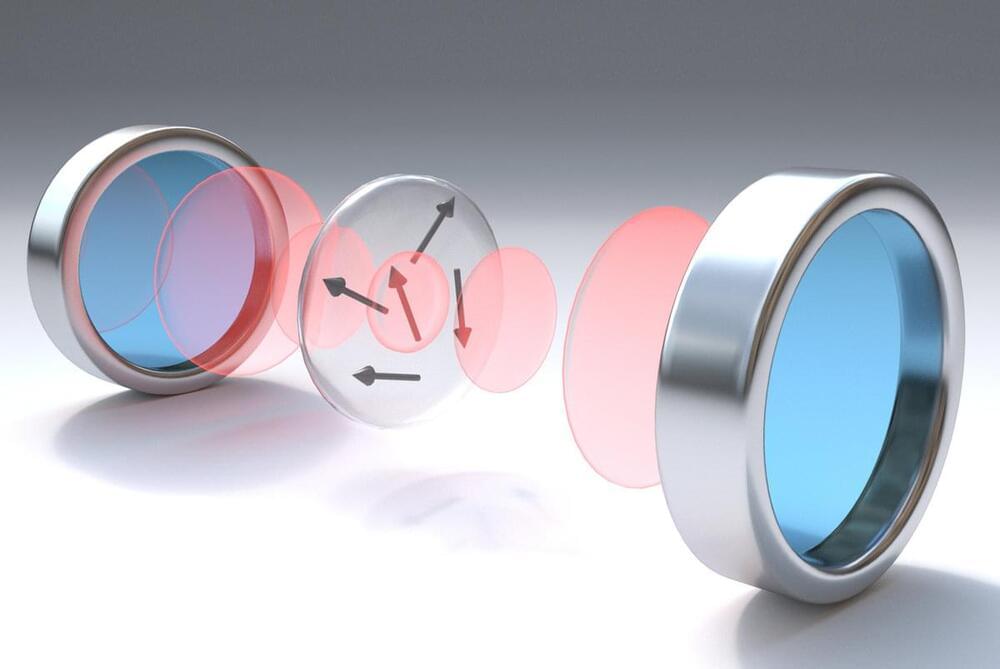
Physicists at the Max Planck Institute of Quantum Optics have developed the basic technology for a new “quantum modem”. It will allow users to connect to a future quantum internet that is based on the existing fibre optic network infrastructure.
The first quantum revolution brought about semiconductor electronics, the laser and finally the internet. The coming, second quantum revolution promises spy-proof communication, extremely precise quantum sensors and quantum computers for previously unsolvable computing tasks. But this revolution is still in its infancy. A central research object is the interface between local quantum devices and light quanta that enable the remote transmission of highly sensitive quantum information. The Otto-Hahn group “Quantum Networks” at the Max-Planck-Institute of Quantum Optics in Garching is researching such a “quantum modem”. The team has now achieved a first breakthrough in a relatively simple but highly efficient technology that can be integrated into existing fibre optic networks. The work is published this week in “Physical Review X”.
Advances in computing power over the decades have come thanks in part to our ability to make smaller and smaller transistors, a building block of electronic devices, but we are nearing the limit of the silicon materials typically used. A new technique for creating 2D oxide materials may pave the way for future high-speed electronics, according to an international team of scientists.
“One way we can make our transistors, our electronic devices, work faster is to shrink the distance electrons have to travel between point A and B,” said Joshua Robinson, professor of materials science and engineering at Penn State. “You can only go so far with 3D materials like silicon—once you shrink it down to a nanometer, its properties change. So there’s been a massive push looking at new materials, one of which are 2D materials.”
The team, led by Furkan Turker, graduate student in the Department of Materials Sciences, used a technique called confinement hetroepitaxy, or CHet, to create 2D oxides, materials with special properties that can serve as an atomically thin insulating layer between layers of electrically conducting materials.
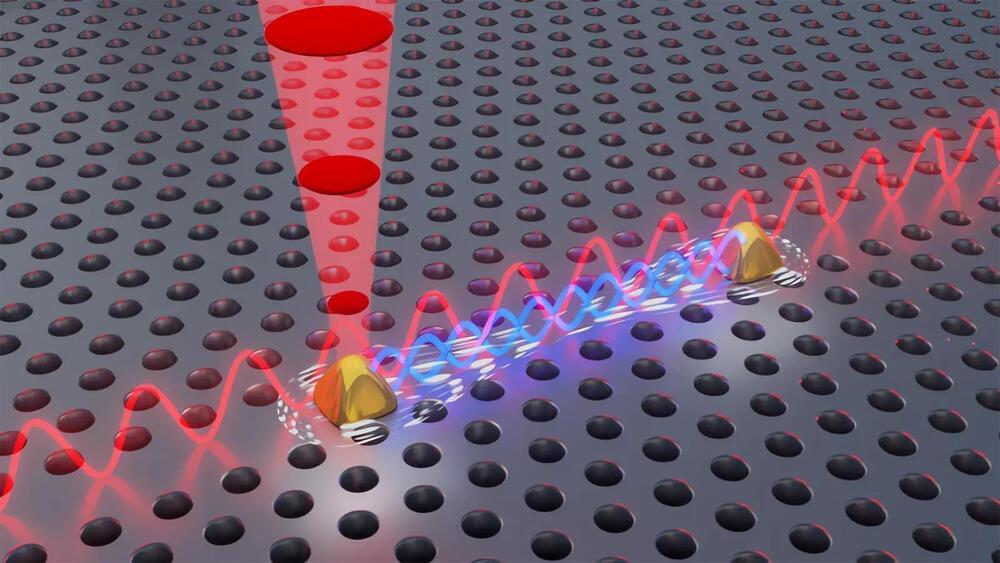
In a new breakthrough, researchers at the University of Copenhagen, in collaboration with Ruhr University Bochum, have solved a problem that has caused quantum researchers headaches for years. The researchers can now control two quantum light sources rather than one. Trivial as it may seem to those uninitiated in quantum, this colossal breakthrough allows researchers to create a phenomenon known as quantum mechanical entanglement. This, in turn, opens new doors for companies and others to exploit the technology commercially.
Going from one to two is a minor feat in most contexts. But in the world of quantum physics, doing so is crucial. For years, researchers around the world have strived to develop stable quantum light sources and achieve the phenomenon known as quantum mechanical entanglement – a phenomenon, with nearly sci-fi-like properties, where two light sources can affect each other instantly and potentially across large geographic distances. Entanglement is the very basis of quantum networks and central to the development of an efficient quantum computer.
Researchers from the Niels Bohr Institute published a new result in the highly esteemed journal Science, in which they succeeded in doing just that. According to Professor Peter Lodahl, one of the researchers behind the result, it is a crucial step in the effort to take the development of quantum technology to the next level and to “quantize” society’s computers, encryption, and the internet.
It actually makes a lot of sense from a computing standpoint.
If life is common in our Universe, and we have every reason to suspect it is, why do we not see evidence of it everywhere?
This is the essence of the Fermi Paradox, a question that has plagued astronomers and cosmologists almost since the birth of modern astronomy.
It is also the reasoning behind the Hart-TIpler Conjecture, one of the many (many!) proposed resolutions, which asserts that if advanced life had emerged in our galaxy sometime in the past, we would see signs of their activity everywhere we looked. Possible indications include self-replicating probes, megastructures, and other Type III-like activity.
(TQI) is the leading online resource dedicated exclusively to Quantum Computing.
Significantly reduces its advanced chip order with TSMC. The 3nm chip will be very expensive.

LCARS is the fictional computer operating system used by Starfleet starships in several Star Trek TV shows and films. The system is currently displayed in the animated comedy Trek series Lower Decks. Now, one intrepid fan has adapted the Lower Decks version of LCARS into a “crazy fan project:” Project RITOS.
RITOS is a webpage that recreates the LCARS system. It’s a fun little site to poke around on. But, since this is just a recreation, there’s no actual functionality you can incorporate onto your computer. As the RITOS About page states, you just “point & click & watch. There are no goals nor wrong thing to do here. It’s just a mindless site.”
It may be mindless, but it’s also a faithful recreation of the LCARS system as depicted not just in Star Trek: Lower Decks but also in The Next Generation, Deep Space Nine, and Voyager. Users can click around into various displays that show crew quarters, a ship map of the Cerritos (the Federation starship in Lower Decks), JWST (James Webb Space Telescope) images, and a Sick Bay screen. There are plenty of fun things to click on and little easter eggs to uncover for dedicated Trek fans.