“Discovering liquid water oceans inside the moons of Uranus would transform our thinking about the range of possibilities for where life could exist,” said Dr. Douglas Hemingway.
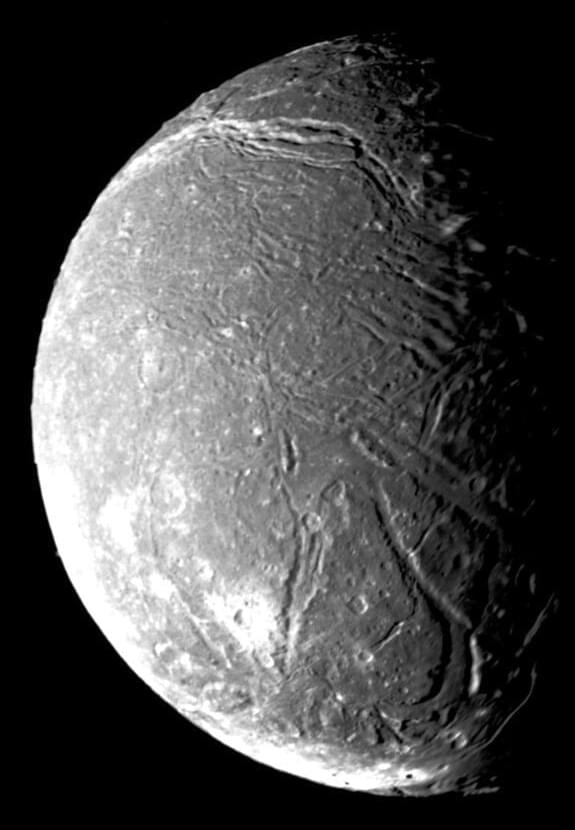
Do the moons of Uranus have interior liquid oceans like the moons of Jupiter and Saturn? This is what a recent study published in Geophysical Research Letters hopes to address as a pair of researchers investigated the likelihood of five Uranus moons, Miranda, Ariel, Umbriel, Titania, and Oberon possessing interior oceans. This study holds the potential to not only help researchers better understand the compositions of these moons, but also establish a framework for sending a spacecraft to Uranus for the first time since NASA’s Voyager 2 in 1986.
For the study, the researchers used computer models to simulate changes in each moon’s wobble with the goal of estimating the potential amount of liquid water that each moon could be harboring. This technique could be used to detect liquid oceans within these moons, thus increasing the feasibility of a future spacecraft mission to Uranus.
In the end, the researchers found that oceans greater than 40 kilometers (25 miles) thick could be detectable, but ocean thickness less than that could prove difficult to detect without better resolution of the wobble calculations. Using these wobble calculations, the researchers estimate that a wobble of 300 feet could indicate an ocean 100 miles thick with an ice shell of 20 miles, using Ariel as an example.