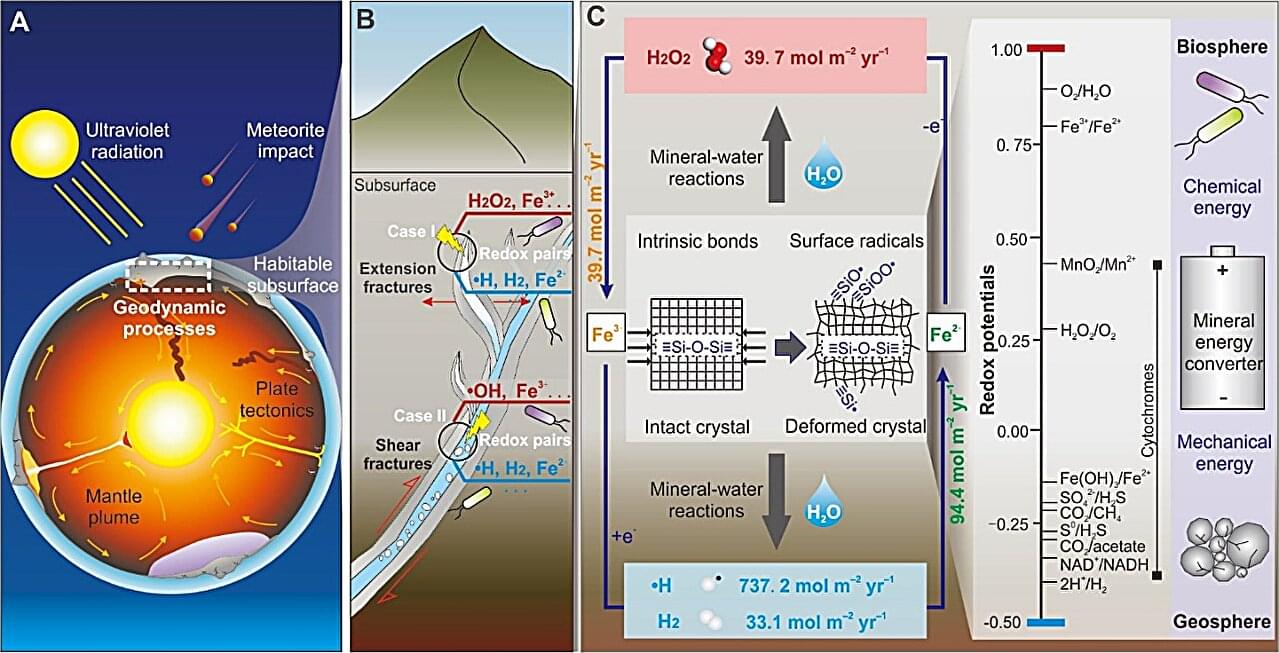
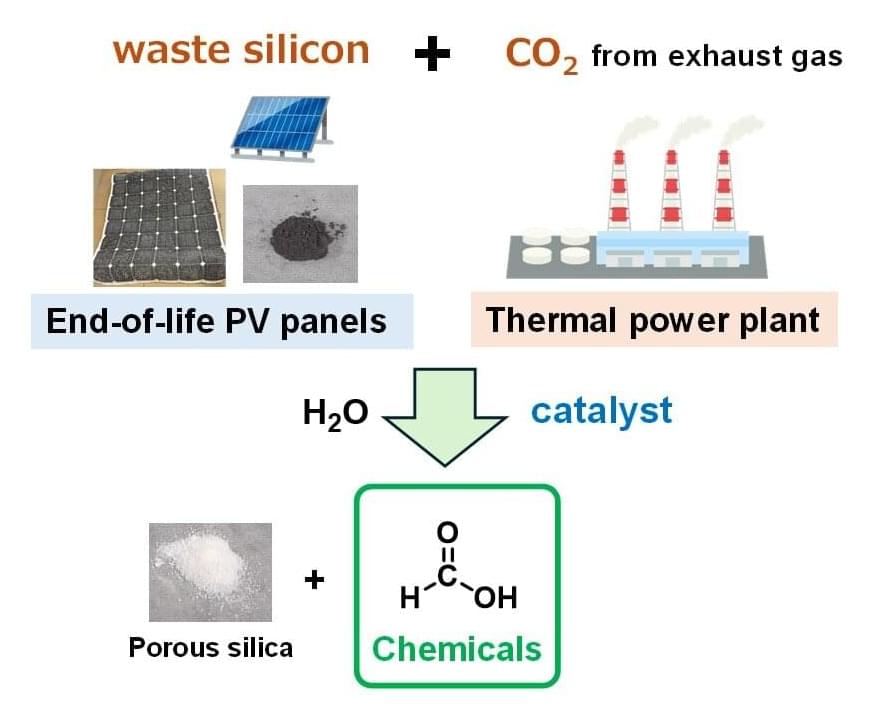
Centuries ago, alchemists worked furiously to convert the common metal lead to valuable gold. Today, chemists are repurposing discarded solar panels to create valuable organic compounds from carbon dioxide (CO2), a common greenhouse gas.
Significantly reducing greenhouse gases in the atmosphere to mitigate the most devastating effects of climate change will require a large reduction in emissions as well as strategies designed to sequester emitted CO2 and other offending gases. While simply sequestering greenhouse gases would fulfill this goal, creating useful organic chemicals from waste CO2 is akin to generating valuable materials from trash.
A team of chemists from Yokohama National University, Electric Power Development Co., Ltd. and the Renewable Energy Research Center at the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST) recently decided to tackle two waste problems—excess CO2 emissions and decommissioned solar panels —in the pursuit of creating value-added organic chemicals. The team designed a study to determine if recycled components of discarded solar panels could be used to efficiently convert CO2 into useful, carbon-based compounds.