All monkeys appeared clinically normal on Day 0 of the study. Monkeys began to show evidence of exanthema, enanthema, mild anorexia, fever, cough, and nasal discharge on Days 6 and 7 postexposure. Dyspnea, noted as early as Day 8 postexposure, was evident in all animals by Day 10. By Days 9 and 10, all animals had exanthema and enanthema, were depressed and severely anorectic, and showed signs of weakness. Clinical signs progressed until the animals died naturally or were killed 9 to 17 days postexposure (mean 11.7 days). There was no correlation of inhaled dose to survival time. Leukocytosis (absolute and relative monocytosis) developed with the onset of clinical signs on Day 6. There were no trends detected in clinical chemistry data. Virus was first isolated from buffy coat cells of one of eight animals tested on Day 6. Nine of 11 animals were positive on Day 9, and 2 of 7 remained positive on Days 12 or 13. There was no cell-free viremia detected at any time.
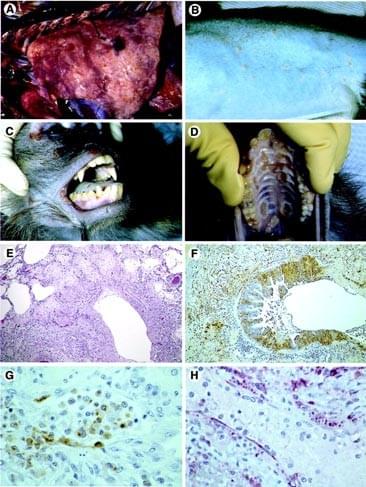
Principal gross necropsy findings are presented in Table 1. All deaths were attributed to bronchopneumonia, although secondary bacterial septicemia was considered to be a contributing factor in one animal. Lungs were heavy and congested and failed to collapse. A dark red, lobular, mottled pattern of edema, atelectasis, and necrosis was distributed throughout all lung lobes (Fig. 1A). Occasionally, there was fibrinous pleuritis with pleural adhesions and multifocal, white, plaque-like thickenings of the visceral pleura. We observed a clear pericardial effusion in two monkeys.
Dermatitis, present in all monkeys, varied from barely detectable, single, small papules to extensive involvement primarily affecting the inguinal, ventral abdominal, ventral thoracic, perineal, and facial regions (Fig. 1, B and C). Palmar surfaces of the hands and plantar surfaces of the feet were only occasionally involved. The extent of involvement and the stage of skin lesion development noted at necropsy exhibited a positive correlation with the number of days elapsed since initial onset of the lesions was noted clinically. In animals necropsied 1 to 2 days after onset of exanthema, lesions were generally minimal in extent and were in the papular stage, appearing as pale tan to white, slightly raised foci, 2 to 4 mm in diameter. At 3 to 5 days post onset, lesion distribution was characterized as mild. Papules were accompanied by 1 to 2 mm vesicles. Vesicle formation, however, was not prominent grossly.