American chemical society: chemistry for life.


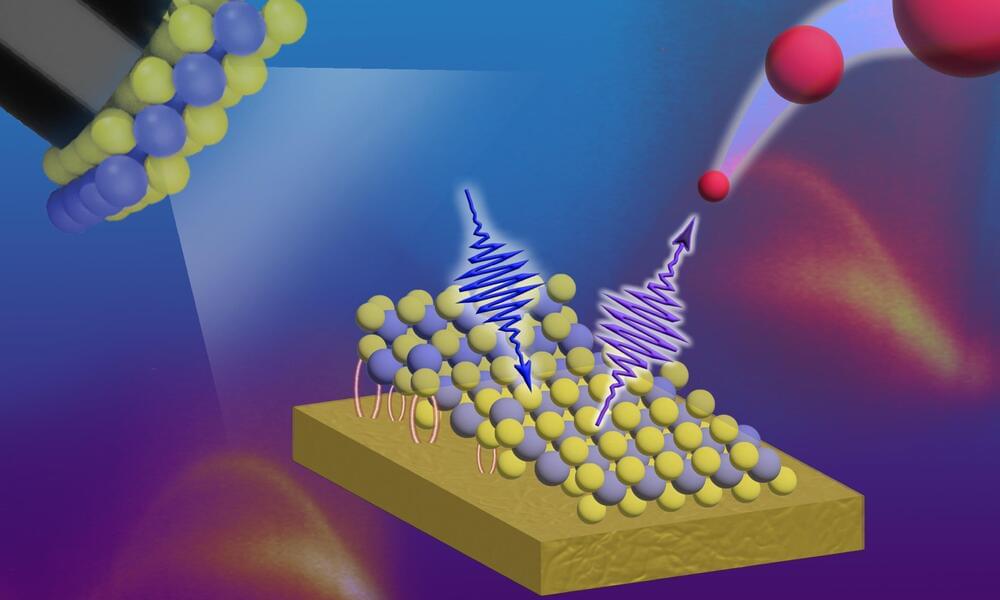
It has almost been 20 years since the establishment of the field of two-dimensional (2D) materials with the discovery of unique properties of graphene, a single, atomically thin layer of graphite. The significance of graphene and its one-of-a-kind properties was recognized as early as 2010 when the Nobel prize in physics was awarded to A. Geim and K. Novoselov for their work on graphene. However, graphene has been around for a while, though researchers simply did not realize what it was, or how special it is (often, it was considered annoying dirt on nice, clean surfaces of metals REF). Some scientists even dismissed the idea that 2D materials could exist in our three-dimensional world.
Today, things are different. 2D materials are one of the most exciting and fascinating subjects of study for researchers from many disciplines, including physics, chemistry and engineering. 2D materials are not only interesting from a scientific point of view, they are also extremely interesting for industrial and technological applications, such as touchscreens and batteries.
We are also getting very good at discovering and preparing new 2D materials, and the list of known and available 2D materials is rapidly expanding. The 2D materials family is getting very large and graphene is not alone anymore. Instead, it now has a lot of 2D relatives with different properties and vastly diverse applications, predicted or already achieved.
According to a news release from the Vienna University of Technology (TU Wien), oxygen-ion batteries don’t have the same aging issue that lithium batteries face, which means they can maintain effectiveness for an incredibly long period.
They can also be manufactured using incombustible materials and don’t require the same rare elements as lithium batteries, which means they won’t have nearly as substantial of an environmental footprint and won’t spontaneously explode if mishandled.
“In many batteries, you have the problem that at some point the charge carriers can no longer move,” said Alexander Schmid of TU Wien’s Institute for Chemical Technologies. “Then they can no longer be used to generate electricity, the capacity of the battery decreases. After many charging cycles, that can become a serious problem.”
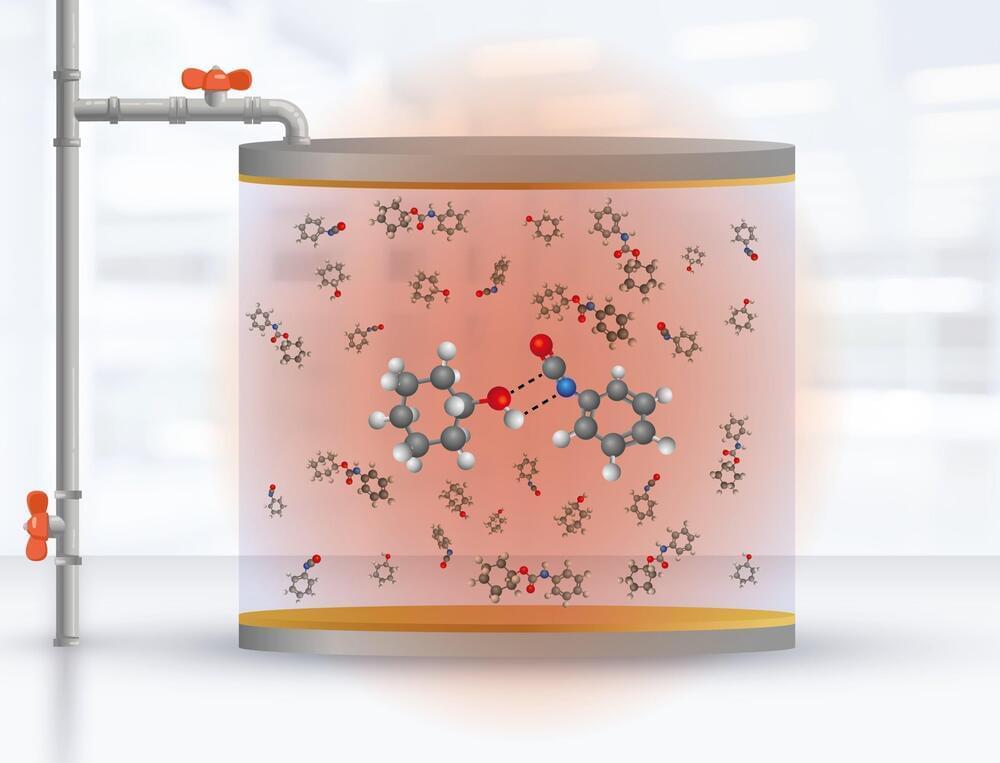
A team of researchers successfully constructed nanofiltration membranes with superior quality using the mussel-inspired deposition methods. Such was achieved via a two-part approach to fabricate the thin-film composite (TFC) nanofiltration membranes. Firstly, the substrate surface was coated through fast and novel deposition to form a dense, robust, and functional selective layer. Then, the structure controllability of the selective layer was enhanced by optimizing the interfacial polymerization (IP) process. As a result, the properties of nanofiltration membranes produced are with high durability and added functionality. When put into a bigger perspective, these high-performance TFC nanofiltration membranes are potential solutions to a number of fields, including water softening, wastewater treatment, and pharmaceutical purification. Hence, there is a need to further explore and expand the application in an industrial scale instead of being bound within the walls of the laboratories.
Membrane-based technologies, especially enhanced nanofiltration systems, have been highly explored due to their myriad of distinct properties, primarily for their high efficiency, mild operation, and strong adaptability. Among these, the TFC nanofiltration membranes are favoured for their smaller molecular weight cutoff, and narrower pore size distribution which lead to higher divalent and multivalent ion rejection ability. Moreover, these membranes show better designability owing to their thin selective layer make-up and porous support with different chemical compositions. However, the interfacial polymerization (IP) rate of reaction is known to affect the permeability and selectivity of the TFC nanofiltration membranes by weakening the controllability of the selective layer structure. Therefore, this study was designed to improve the structural quality of the TFC nanofiltration membranes through surface and interface engineering, and subsequently, increase the functionality.
It is one of the ambitions of the United Nations to ensure availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all (SDG 6: Clean water and sanitation). A report by the United Nations’ Water for Life initiative stated that one in four people do not have access to safe drinking water, and up to 50% of the global population are at risk of living in water stressed areas by 2025. With such concerns looming close, undoubtably, there is a demand for advanced and efficient wastewater treatment technology to be put in place. Thus, the successful designing of improved and highly functional TFC nanofiltration membranes through innovative approaches portrayed in this study could be the much-needed solution in addressing these issues.

ALBUQUERQUE, N.M. — A team at Sandia National Laboratories is developing materials to tackle what has become one of the biggest problems in the world: human exposure to a group of chemicals known as PFAS through contaminated water and other products. Sandia is now investing more money to take their research to the next level.
“It’s in the news constantly. It seems every day we hear of another product that is contaminated. We saw sparkling water with PFAS, toilet paper with PFAS, so it’s not just a groundwater problem; it’s popping up everywhere,” said Andrew Knight, a chemist at Sandia who has a passion for solving PFAS contamination. “It has become clear to the world it is a growing problem. It is a national security issue of a large scale.”
PFAS, an abbreviation for perfluoroalkyl and polyfluoroalkyl substances, are a group of chemicals used to make fluoropolymer products that resist heat, oil, stains and water. They are also known as “forever chemicals” because they do not break down in the environment but can move through soil and water and build up in wildlife and humans.
Researchers have used a machine learning model to identify three compounds that could combat aging. They say their approach could be an effective way of identifying new drugs, especially for complex diseases.
Cell division is necessary for our body to grow and for tissues to renew themselves. Cellular senescence describes the phenomenon where cells permanently stop dividing but remain in the body, causing tissue damage and aging across body organs and systems.
Ordinarily, senescent cells are cleared from the body by our immune system. But, as we age, our immune system is less effective at clearing out these cells and their number increases. An increase in senescent cells has been associated with diseases such as cancer, Alzheimer’s disease and the hallmarks of aging such as worsening eyesight and reduced mobility. Given the potentially deleterious effects on the body, there has been a push to develop effective senolytics, compounds that clear out senescent cells.
Researchers from North Carolina State University have identified a microRNA (miRNA) that could promote hair regeneration. This miRNA – miR-218-5p – plays an important role in regulating the pathway involved in follicle regeneration, and could be a candidate for future drug development.
Hair growth depends on the health of dermal papillae (DP) cells, which regulate the hair follicle growth cycle. Current treatments for hair loss can be costly and ineffective, ranging from invasive surgery to chemical treatments that don’t produce the desired result. Recent hair loss research indicates that hair follicles don’t disappear where balding occurs, they just shrink. If DP cells could be replenished at those sites, the thinking goes, then the follicles might recover.
A research team led by Ke Cheng, Randall B. Terry, Jr. Distinguished Professor in Regenerative Medicine at NC State’s College of Veterinary Medicine and professor in the NC State/UNC Joint Department of Biomedical Engineering, cultured DP cells both alone (2D) and in a 3D spheroid environment. A spheroid is a three-dimensional cellular structure that effectively recreates a cell’s natural microenvironment.
Circa 2020
Imagine a dressing that releases antibiotics on demand and absorbs excessive wound exudate at the same time. Researchers at Eindhoven University of Technology hope to achieve just that, by developing a smart coating that actively releases and absorbs multiple fluids, triggered by a radio signal. This material is not only beneficial for the health care industry, it is also very promising in the field of robotics or even virtual reality.
TU/e-researcher Danqing Liu, from the Institute of Complex Molecular Systems and the lead author of this paper, and her PhD student Yuanyuan Zhan are inspired by the skins of living creatures. Human skin secretes oil to defend against bacteria and sweats to regulate the body temperature. A fish secretes mucus from its skin to reduce friction from the water to swim faster. Liu now presents an artificial skin: a smart surface that can actively and repeatedly release and reabsorb substances under environmental stimuli, in this case radio waves. And that is special, as in the field of smart materials, most approaches are limited to passive release.
The potential applications are numerous. Dressings using this type of material could regulate drug delivery, to administer a drug on demand over a longer time and then ‘re-load’ with a different drug. Robots could use the layer of skin to ‘sweat’ for cooling themselves, which reduces the need for heavy ventilators inside their bodies. Machines could release lubricant to mechanical parts when needed. Or advanced controllers for virtual reality gaming could be made, that get wet or dry to enhance the human perception.
The basis of the material, the coating, is made of liquid-crystal molecules, well-known from LCD screens. These molecules have so-called responsive properties. Liu: “You could imagine this as a communication material. It communicates with its environment and reacts to stimuli.” With her team at the department of Chemical Engineering and Chemistry she discovered that the liquid-crystal molecules react to radio waves. When the waves are turned on, the molecules twist to orient with the waves’ direction of travel.
Controlling chemical reactions to generate new products is one of the biggest challenges in chemistry. Developments in this area impact industry, for example, by reducing the waste generated in the manufacture of construction materials or by improving the production of catalysts to accelerate chemical reactions.
For this reason, in the field of polariton chemistry—which uses tools of chemistry and quantum optics—in the last 10 years different laboratories around the world have developed experiments in optical cavities to manipulate the chemical reactivity of molecules at room temperature, using electromagnetic fields. Some have succeeded in modifying chemical reactions products in organic compounds, but to date, and without relevant advances in the last two years, no research team has been able to come up with a general physical mechanism to describe the phenomenon and to reproduce it to obtain the same measurements in a consistent manner.
Now a team of researchers from Universidad de Santiago (Chile), part of the Millennium Institute for Research in Optics (MIRO), led by principal investigator Felipe Herrera, and the laboratory of the chemistry division of the US Naval Research Laboratory, (United States), led by researcher Blake Simpkins, for the first time report the manipulation of the formation rate of urethane molecules in a solution contained inside an infrared cavity.

During photosynthesis, a symphony of chemicals transforms light into the energy required for plant, algal, and some bacterial life. Scientists now know that this remarkable reaction requires the smallest possible amount of light – just one single photon – to begin.
A US team of researchers in quantum optics and biology showed that a lone photon can start photosynthesis in the purple bacterium Rhodobacter sphaeroides, and they are confident it works in plants and algae since all photosynthetic organisms share an evolutionary ancestor and similar processes.
The team says their findings bolster our knowledge of photosynthesis and will lead to a better understanding of the intersection of quantum physics in a wide range of complex biological, chemical, and physical systems, including renewable fuels.