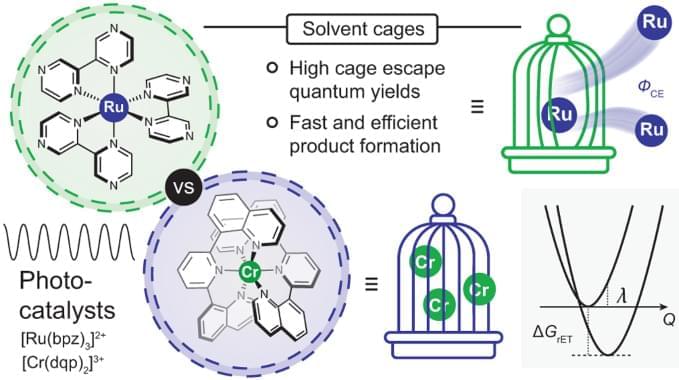
The 3 MLCT-excited [Ru(bpz)3]2+ and the spin-flip excited states of [Cr(dqp)2]3+ underwent photoinduced electron-transfer reactions with 12 amine-based electron donors similarly well, but provided cage escape quantum yields differing by up to an order of magnitude. In three exemplary benchmark photoredox reactions performed with different electron donors, the differences in the reaction rates observed when using either [Ru(bpz)3]2+ or [Cr(dqp)2]3+ as photocatalyst correlated with the magnitude of the cage escape quantum yields. These correlations indicate that the cage escape quantum yields play a decisive role in the reaction rates and quantum efficiencies of the photoredox reactions, and also illustrate that luminescence quenching experiments are insufficient for obtaining quantitative insights into photoredox reactivity.
From a purely physical chemistry perspective, these findings are not a priori surprising as the rate of photoproduct formation in an overall reaction comprising several consecutive elementary steps can be expressed as the product of the quantum yields of the individual elementary steps45,46. A recent report on solvent-dependent cage escape and photoredox studies suggested that the correlations between photoredox product formation rates and cage escape quantum yields might be observable11, but we are unaware of previous reports that have been able to demonstrate that the rate of product formation in several batch-type photoreactions correlates with the cage escape quantum yields determined from laser experiments. Synthetic photochemistry and mechanistic investigations are often conducted under substantially different conditions, which can lead to controversial discrepancies47,48,49, whereas here their mutual agreement seems remarkable, particularly given the complexity of the overall reactions.
The available data and the presented analysis suggest that the different cage escape behaviours of [Ru(bpz)3]2+ and [Cr(dqp)2]3+ originate in the fact that for any given electron donor, in-cage reverse electron transfer is ~0.3 eV more exergonic for the RuII complex than for the CrIII complex. Thermal reverse electron transfer between caged radical pairs therefore occurs more deeply in the Marcus inverted region with [Ru(bpz)3]2+ than with [Cr(dqp)2]3+, decelerating in-cage charge recombination in the RuII complex and increasing the cage escape quantum yields compared with the CrIII complex (Fig. 3D).