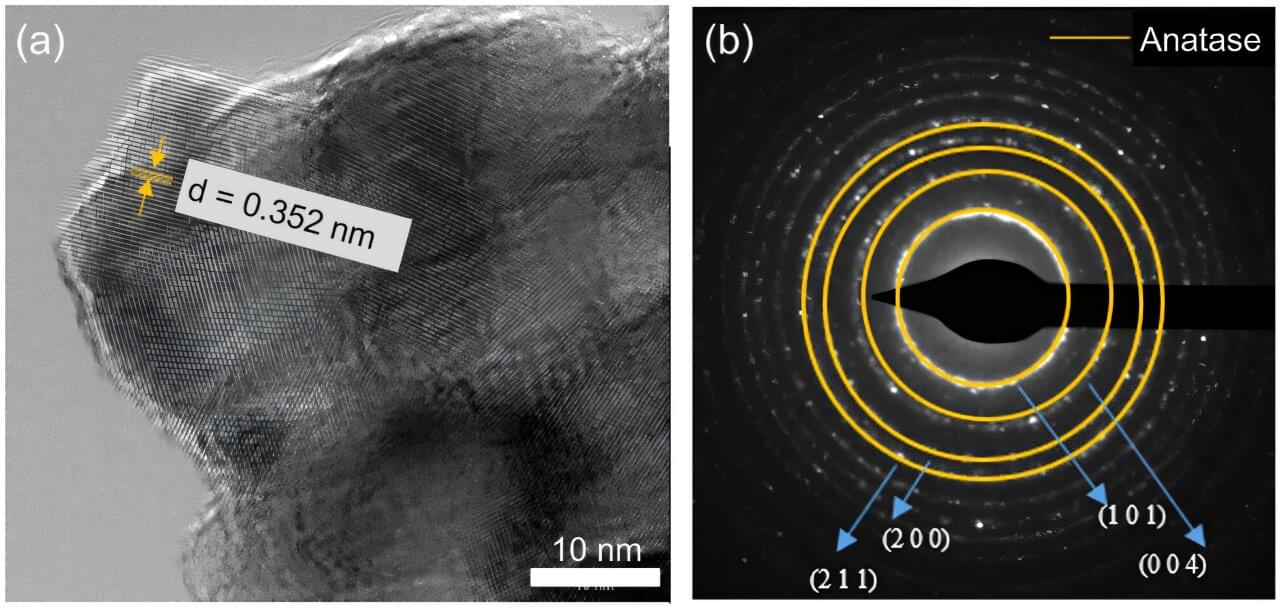
As the world makes more use of renewable energy sources, new battery technology is needed to store electricity for the times when the sun isn’t shining, and the wind isn’t blowing.
“Current lithium batteries have reached their limitations in terms of energy storage capability, life cycle, and safety,” says Xiaolei Wang, a professor of chemical engineering at the University of Alberta in Edmonton. “They’re good for applications like electric vehicles and portable electronics, but they’re not suitable for large-scale grid-level energy storage.”
With the help of the Canadian Light Source at the University of Saskatchewan, Wang and his team are developing new technologies to help make grid-level aqueous batteries that can use seawater as an electrolyte. The study is published in the journal Advanced Materials.