Chemical structures called cyclopropanes can increase the potency and fine-tune the properties of many drugs, but traditional methods to create this structure only work with certain molecules and require highly reactive—potentially explosive—ingredients.
Now, a team of researchers from Penn State has identified and demonstrated a safe, efficient and practical way to create cyclopropanes on a wide variety of molecules using a previously undescribed chemical process. With additional development, the new method—described in a paper publishing Aug. 4 in the journal Science —could transform how this important process occurs during drug development and creation.
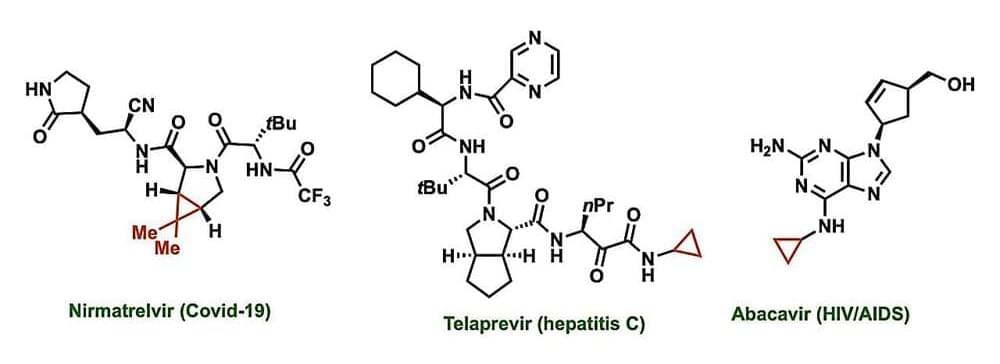
Cyclopropanes are a key feature in many drugs currently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, including those used to treat COVID-19, asthma, hepatitis C, and HIV/AIDs. These structures can increase a drug’s potency, alter its ability to dissolve in the body, minimize its interactions with unintended targets, and otherwise fine-tune performance. Cyclopropanes are a ring of three connected carbon atoms, with one carbon attached to the rest of the drug molecule and the other two each attached to two hydrogen atoms.