🧬 🔬 💉
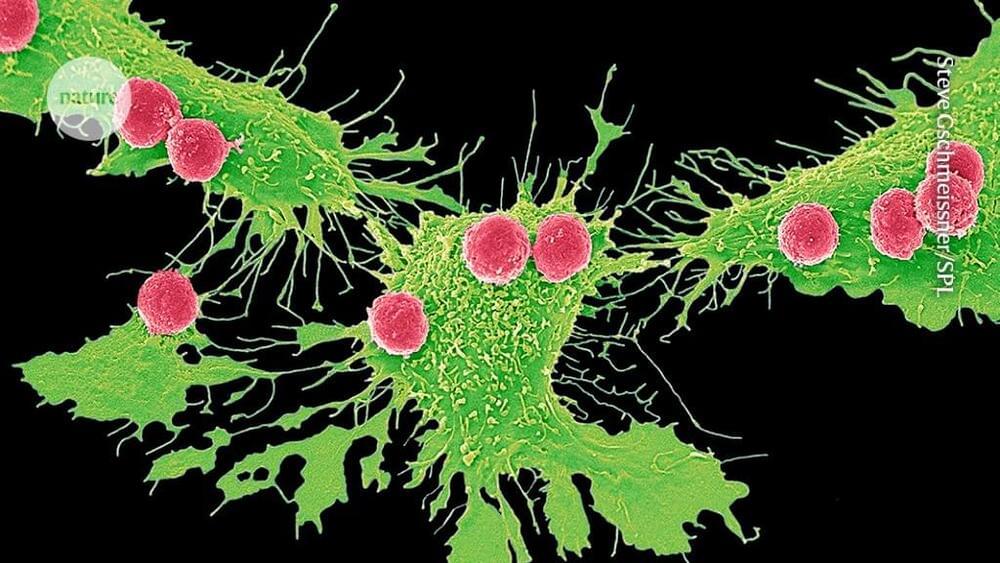
Review synthesizes research on NK cells’ role in cancer immunity and their potential in therapeutics through bioengineering, immune checkpoint inhibitors, and cell engagers, highlighting ongoing preclinical and clinical trials.
In 1940, 12 years after Alexander Fleming discovered penicillin, microbiologists made a concerning discovery: a strain of the bacteria Escherichia coli had developed resistance to the new, life-saving drug. Antibiotic resistance of disease-causing bacteria is now a global problem, with bacteria continually evolving mechanisms that prevent such drugs from killing the organisms or inhibiting their growth. Now Vanderlei Bagnato of the University of São Paulo and his colleagues have developed a light-based approach that could help reduce this trend in a Staphylococcus bacterium that can cause skin infections and pneumonia [1]. The researchers presented their technique at the recent SPIE Photonics West 2024 conference in San Francisco.
If the current trend continues, epidemiologists predict that the number of people infected by antibiotic-resistant bacteria will reach 225 million worldwide by 2030. By 2050 these bacteria will cause 10 million deaths annually. Studies show that infections acquired in hospital are increasingly prone to this problem. “People are dying every day in [intensive care wards] from resistant bacteria. If someone acquires pneumonia, and antibiotics don’t work, they’re in trouble,” Bagnato says.
One route to tackling antibiotic resistance is to develop new drugs, which is a costly process. Another route—and one that is becoming increasingly popular—is to inhibit antibiotic-eluding mechanisms that a bacterium develops as it evolves. This inhibition can be achieved using light, a process those in the field call photodynamics, and the route Bagnato and his colleagues have taken. “We’re using photodynamics to reverse resistance so that antibiotics can act again,” he says.
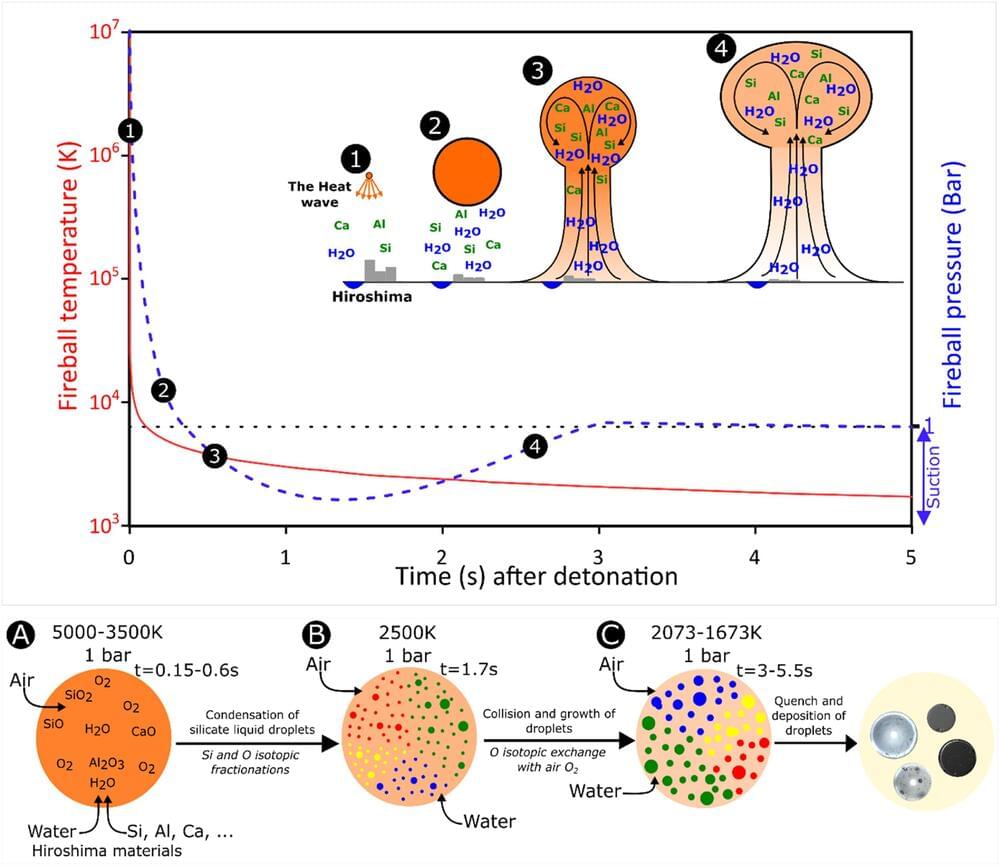
The atomic bombing of Hiroshima, Japan, by the United States in August 1945 was not only devastating at the time, resulting in the deaths of hundreds of thousands of people, but it has had long-standing impacts to the present day, particularly the elevated incidence of cancer from radiation.
Continued research of Hiroshima Bay has uncovered a new kind of debris from the fallout, known as Hiroshima glasses. These formed from vaporized materials of the bomb and the surrounding landscape and infrastructure being targeted.
New research published in Earth and Planetary Science Letters has analyzed the chemical and isotopic compositions of these glasses to ascertain their formation process during the nuclear event.
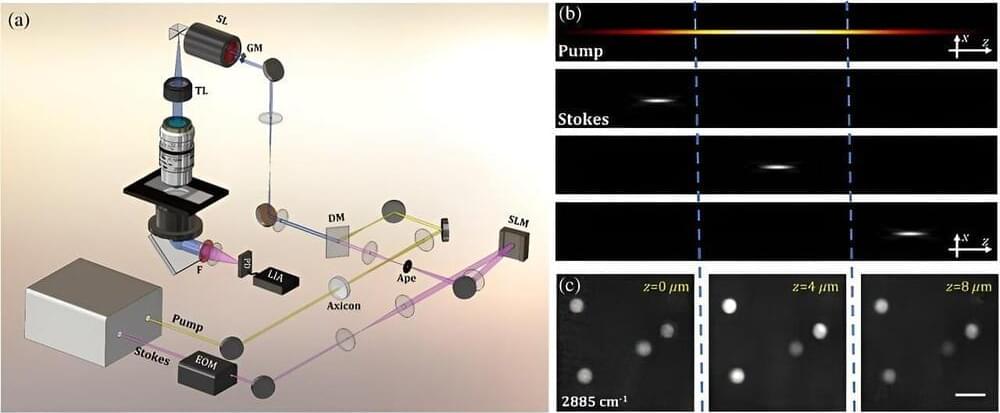
Understanding complex biological and biomedical systems is greatly aided by 3D imaging, which provides much more detailed information than traditional two-dimensional methods. However, live cell and tissue imaging remain challenging due to factors like limited imaging speed and significant scattering in turbid environments.
In this context, multimodal microscopy techniques are notable. Specifically, nonlinear techniques like CRS (coherent Raman scattering) use optical vibrational spectroscopy, providing precise chemical imaging in tissues and cells in a label-free way.
Furthermore, stimulated Raman scattering (SRS) microscopy, a CRS method, can accurately capture images of biomolecules due to the linear relationship between stimulated Raman intensity and the concentration of target molecules. It does so with high sensitivity and without interference from unwanted nonresonant backgrounds.

Researchers from the University of Illinois Chicago and Harvard University have created an antibiotic that may provide medicine a new tool to combat bacteria resistant to drugs and the illnesses they trigger.
The antibiotic, cresomycin, described in Science, effectively suppresses pathogenic bacteria that have become resistant to many commonly prescribed antimicrobial drugs.
The promising novel antibiotic is the latest finding for a longtime research partnership between the group of Yury Polikanov, associate professor of biological sciences at UIC, and colleagues at Harvard. The UIC scientists provide critical insights into cellular mechanisms and structure that help the researchers at Harvard design and synthesize new drugs.
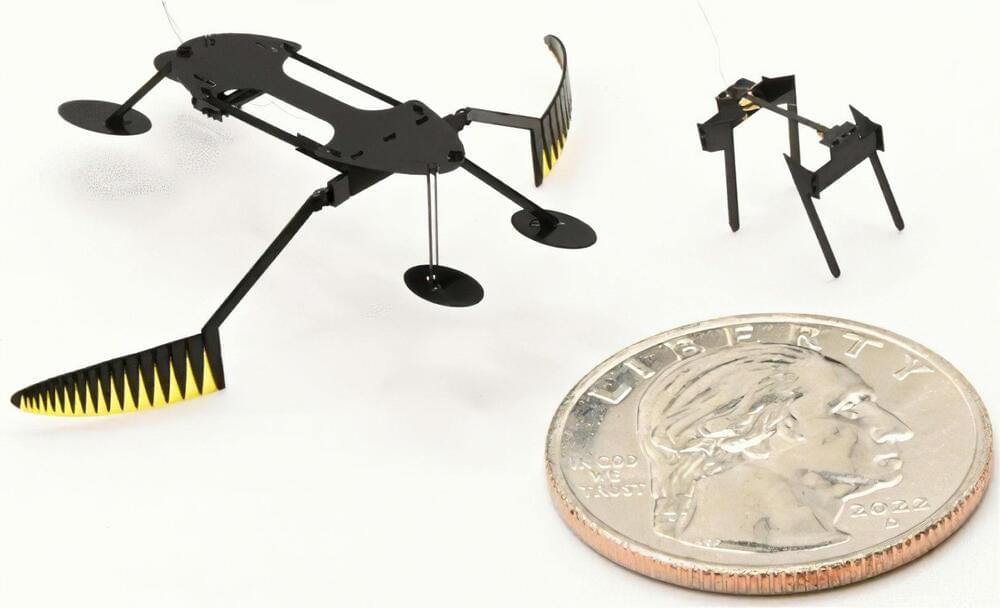

Two insect-like robots, a mini-bug and a water strider, developed at Washington State University, are the smallest, lightest and fastest fully functional micro-robots ever known to be created.
Such miniature robots could someday be used for work in areas such as artificial pollination, search and rescue, environmental monitoring, micro-fabrication, or robotic-assisted surgery. Reporting on their work in the proceedings of the IEEE Robotics and Automation Society’s International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, the mini-bug weighs in at eight milligrams while the water strider weighs 55 milligrams. Both can move at about six millimeters a second.
A new tool has been developed to detect skin cancer; it utilizes a biosensor that can identify small changes in the characteristics of cells. | Clinical And Molecular Dx.

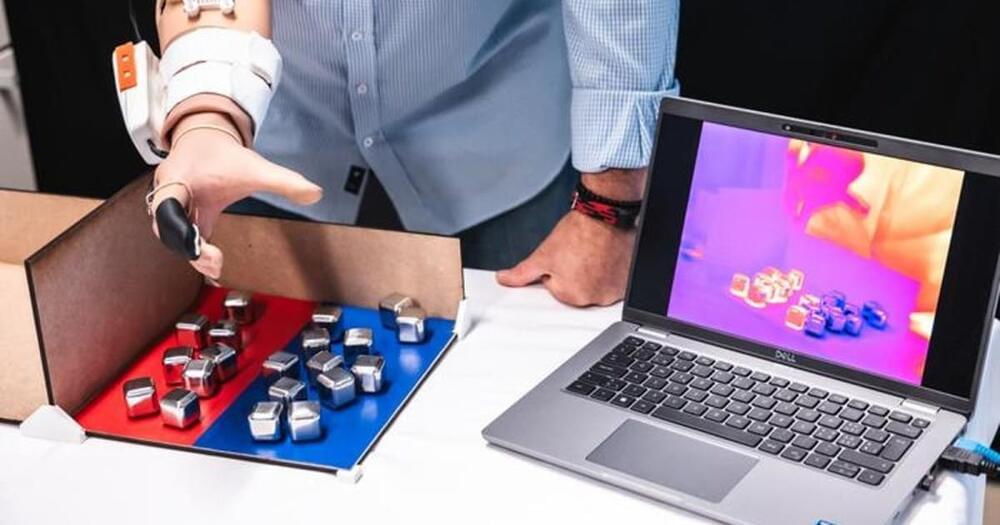
Envision a game-changing technology that grants the power of expression to those facing speech challenges.
An innovative solution has emerged thanks to an incredible collaboration between NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory and Eyegaze Inc.
They have created Eyegaze Edge, an eye-driven communication device.