Patients with oligometastatic pancreatic cancer showed better progression-free survival after receiving metastasis-directed therapy with chemotherapy. Adding metastasis-directed therapy to chemotherapy showed some benefit in patients with…

Wear your support for the show with a Closer To Truth hoodie, T-shirt, or tank: https://bit.ly/3P2ogje.
What is it about human brains that enable both the regulation of bodily activities and the generation of mental thoughts? What are the mechanisms of human brain function? How do they integrate to give the sense of mental unity? What happens when something in the brain goes wrong—abnormalities, injury, disease? What is the future of brain science?
Dr. Kelsey Martin is Dean of the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA as well as a professor of biological chemistry, psychiatry and biobehavioral sciences. Her research focuses on the cell biology of transcription-dependent forms of synaptic plasticity, particularly those underlying learning and memory.
Donate to Closer To Truth and help us keep our content free and without paywalls: https://shorturl.at/OnyRq.
Closer To Truth, hosted by Robert Lawrence Kuhn and directed by Peter Getzels, presents the world’s greatest thinkers exploring humanity’s deepest questions. Discover fundamental issues of existence. Engage new and diverse ways of thinking. Appreciate intense debates. Share your own opinions. Seek your own answers.
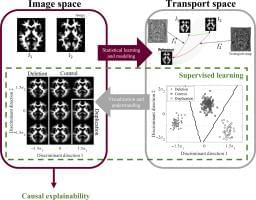
Their…
A multi-university research team co-led by University of Virginia engineering professor Gustavo K. Rohde has developed a system that can spot genetic markers of autism in brain images with 89 to 95% accuracy.
Their findings suggest doctors may one day see, classify and treat autism and related neurological conditions with this method, without having to rely on, or wait for, behavioral cues. And that means this truly personalized medicine could result in earlier interventions.
“Autism is traditionally diagnosed behaviorally but has a strong genetic basis. A genetics-first approach could transform understanding and treatment of autism,” the researchers wrote in a paper published June 12 in the journal Science Advances.
About the Episode
What if it were possible to generate tissues and cells that replicate the functions of human organs, and then use them to study and treat human conditions?
It’s an area of research Dr. Thomas Hartung has been extensively involved with for decades. As the former head of the European Commission Center, he was in tune with all the ways researchers tried to study diseases through alternative methods. He strongly believes organoids have the intelligence necessary to accelerate research and therapeutic development without the need for animal models.

Cellular senescence is a diverse phenotype characterised by permanent cell cycle arrest and an associated secretory phenotype (SASP) which includes inflammatory cytokines. Typically, senescent cells are removed by the immune system, but this process becomes dysregulated with age causing senescent cells to accumulate and induce chronic inflammatory signalling. Identifying senescent cells is challenging due to senescence phenotype heterogeneity, and senotherapy often requires a combinatorial approach. Here we systematically collected 119 transcriptomic datasets related to human fibroblasts, forming an online database describing the relevant variables for each study allowing users to filter for variables and genes of interest. Our own analysis of the database identified 28 genes significantly up-or downregulated across four senescence types (DNA damage induced senescence (DDIS), oncogene induced senescence (OIS), replicative senescence, and bystander induced senescence) compared to proliferating controls. We also found gene expression patterns of conventional senescence markers were highly specific and reliable for different senescence inducers, cell lines, and timepoints. Our comprehensive data supported several observations made in existing studies using single datasets, including stronger p53 signalling in DDIS compared to OIS. However, contrary to some early observations, both p16 and p21 mRNA levels rise quickly, depending on senescence type, and persist for at least 8–11 days. Additionally, little evidence was found to support an initial TGFβ-centric SASP. To support our transcriptomic analysis, we computationally modelled temporal protein changes of select core senescence proteins during DDIS and OIS, as well as perform knockdown interventions. We conclude that while universal biomarkers of senescence are difficult to identify, conventional senescence markers follow predictable profiles and construction of a framework for studying senescence could lead to more reproducible data and understanding of senescence heterogeneity.
Multiple studies now suggest that the accumulation of senescent cells is causal in ageing (Childs et al., 2015; Mylonas and O’Loghlen, 2022; van Deursen, 2014; Wlaschek et al., 2021), and their ablation extends healthspan and mean lifespan in rodents (Baker et al., 2016; Baker et al., 2011). Novel senolytic and senostatic drugs are in development (Kim and Kim, 2019; Niedernhofer and Robbins, 2018) with some drugs in clinical trials (Hickson et al., 2019; Justice et al., 2019) which might shortly lead to treatments capable of improving healthspan and extending lifespan in humans. However, the exact nature of senescent cells is often difficult to define, with multiple studies indicating that the most common biomarkers of senescence show different profiles across cell lines, types of senescence inducer, and the timepoint after the initial stimulus (Avelar et al., 2020; Basisty et al., 2020; Casella et al., 2019; Hernandez-Segura et al., 2017; Neri et al., 2021).
Organoid Intelligence is the fusion of stem cell-derived mini-organs and AI. It promises more human-like AI but also ethical questions.
Gain a deep understanding of the intricate interconnections within technological, economic, societal, biomedical, and environmental systems by earning a Master of Science degree in Complex Systems Science. https://asuonline.asu.edu/online-degr…
Hey remember that time you waved at a stranger who was actually waving at someone behind you? The universe can, at least in its own way. If you thought gravitational waves were wild, just wait until you hear about this thing called gravitational memory.
Hosted by: Niba @NotesbyNiba (she/her)
———
Support us for $8/month on Patreon and keep SciShow going!
/ scishow.
Or support us directly: https://complexly.com/support.
Join our SciShow email list to get the latest news and highlights:
https://mailchi.mp/scishow/email.
———
Huge thanks go to the following Patreon supporters for helping us keep SciShow free for everyone forever: Odditeas, Garrett Galloway, DrakoEsper, Kenny Wilson, J. Copen, Friso, Lyndsay Brown, Jeremy Mattern, Jaap Westera, Rizwan Kassim, Harrison Mills, Christoph Schwanke, Jeffrey Mckishen, Eric Jensen, Chris Mackey, Adam Brainard, Ash, You too can be a nice person, Piya Shedden, charles george, Alex Hackman, Kevin Knupp, Chris Peters, Kevin Bealer, Jason A Saslow.
———
Looking for SciShow elsewhere on the internet?
SciShow Tangents Podcast: https://scishow-tangents.simplecast.com/
TikTok: / scishow.
Twitter: / scishow.
Instagram: / thescishow.
Facebook: / scishow.

IT is the backbone of modern healthcare, from patient records and medication management to diagnostic equipment, networking and communication systems. These healthcare IT professionals play a pivotal role in ensuring the accuracy, security, reliability and accessibility of health data. Hospital IT professionals also ensure that the technological backbones of these hospital systems operate correctly.
They ensure that doctors have real-time access to patient information, nurses can track medication schedules accurately and communication between departments is fluid and efficient. Without this critical support, the efficiency and safety of patient care is severely compromised. Simply put, the work of hospital IT teams is vital to the smooth operation of hospitals.
It is fair and appropriate to say that hospital IT teams are unsung heroes. The nature of working in IT is to keep everything running smoothly at all times. These dedicated, talented and hardworking IT experts are often ignored unless the infrastructure is not working or has failed. Nobody notices when hospital IT systems are operating properly; the IT teams only get noticed when things go wrong, and typically receive negative attention.
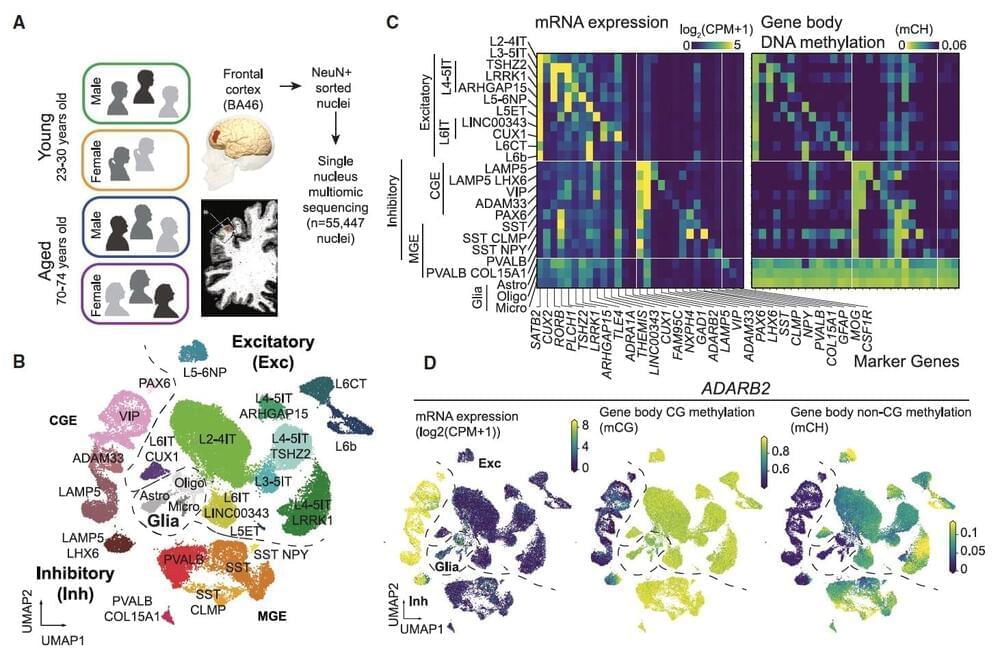
Aging is known to have profound effects on the human brain, prompting changes in the composition of cells and the expression of genes, while also altering aspects of the interaction between genes and environmental factors. While past neuroscience studies have pinpointed many of the molecular changes associated with aging, the age-related genetic factors influencing specific neuron populations remains poorly understood.
Recent studies on flies, mice, primates and human brain tissue utilizing single-cell or single-nucleus RNA-sequencing and genetic experimental techniques shed new light on these cell-type-specific changes. For instance, they unveiled the effects of aging on glial cells in the mouse and human brain, associations between cell-specific changes and modified chromatin proteins, and the influence of DNA methylation in the aging of various tissues.
Researchers at University of California (UC) San Diego and Salk Institute recently carried out a study aimed at better understanding how both age and sex impact human cortical neurons at a single-cell level. Their findings, published in Neuron, offer new insights into how aging affects cell composition, gene expression and DNA methylation across human brain cell types, while also uncovering differences between gene expression and DNA methylation in females and males.
MIT’s soft drone flies and grasps, swiftly picking up a bottle in a demo video:
Interestingly, the drone’s new capabilities allow it to catch objects that are moving at speeds of up to 0.3 meters per second.
Researchers have been developing drones that can perch on surfaces and perform tasks such as inspecting structures and collecting DNA samples from trees. Surprisingly, this drone can do this in the near future. The video shows the drone hovering over a table, reaching out with its gripper, and successfully gripping a bottle.
This technology has several possible uses, ranging from simple activities like parcel delivery to more difficult missions in dangerous settings.