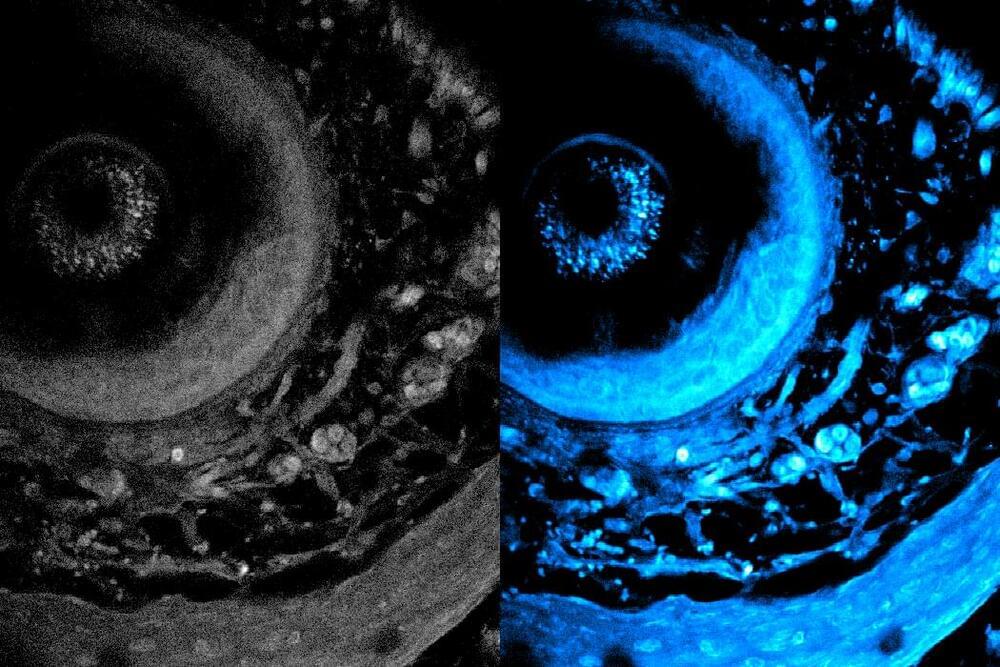
Surprisingly, the organoids were still healthy when they returned from orbit a month later, but the cells had matured faster compared to identical organoids grown on Earth—they were closer to becoming adult neurons and were beginning to show signs of specialization. The results, which could shed light on potential neurological effects of space travel, were published on October 23, 2024, in Stem Cells Translational Medicine.
“The fact that these cells survived in space was a big surprise,” says co-senior author Jeanne Loring, PhD, professor emeritus in the Department of Molecular Medicine and founding director of the Center for Regenerative Medicine at Scripps Research. “This lays the groundwork for future experiments in space, in which we can include other parts of the brain that are affected by neurodegenerative disease.”
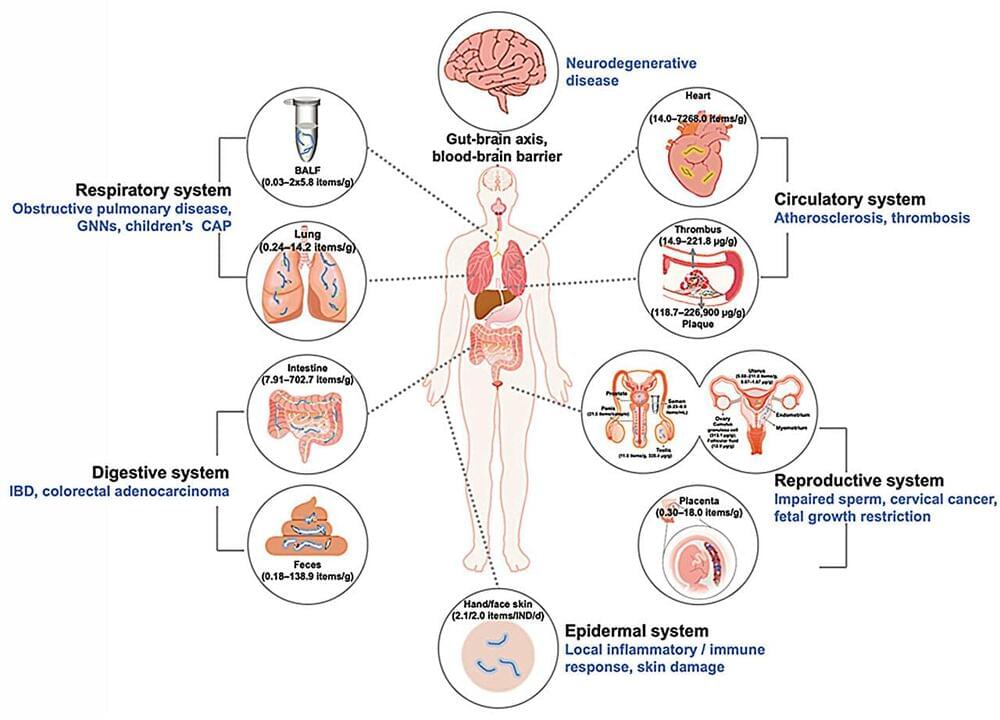
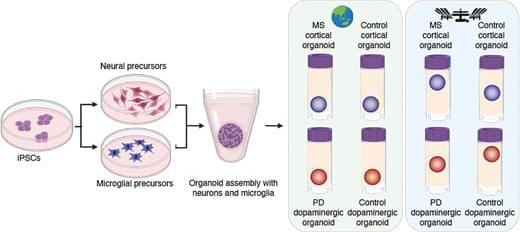
On Earth, the team used stem cells to create organoids consisting of either cortical or dopaminergic neurons, which are the neuronal populations impacted in multiple sclerosis and Parkinson’s disease—diseases that Loring has studied for decades. Some organoids also included microglia, a type of immune cell that is resident within the brain, to examine the impact of microgravity on inflammation.
Abstract. Research conducted on the International Space Station (ISS) in low-Earth orbit (LEO) has shown the effects of microgravity on multiple organs. To investigate the effects of microgravity on the central nervous system, we developed a unique organoid strategy for modeling specific regions of the brain that are affected by neurodegenerative diseases. We generated 3-dimensional human neural organoids from induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) derived from individuals affected by primary progressive multiple sclerosis (PPMS) or Parkinson’s disease (PD) and non-symptomatic controls, by differentiating them toward cortical and dopaminergic fates, respectively, and combined them with isogenic microglia. The organoids were cultured for a month using a novel sealed cryovial culture method on the International Space Station (ISS) and a parallel set that remained on Earth. Live samples were returned to Earth for analysis by RNA expression and histology and were attached to culture dishes to enable neurite outgrowth. Our results show that both cortical and dopaminergic organoids cultured in LEO had lower levels of genes associated with cell proliferation and higher levels of maturation-associated genes, suggesting that the cells matured more quickly in LEO. This study is continuing with several more missions in order to understand the mechanisms underlying accelerated maturation and to investigate other neurological diseases. Our goal is to make use of the opportunity to study neural cells in LEO to better understand and treat neurodegenerative disease on Earth and to help ameliorate potentially adverse neurological effects of space travel.