🧬🔬🍏
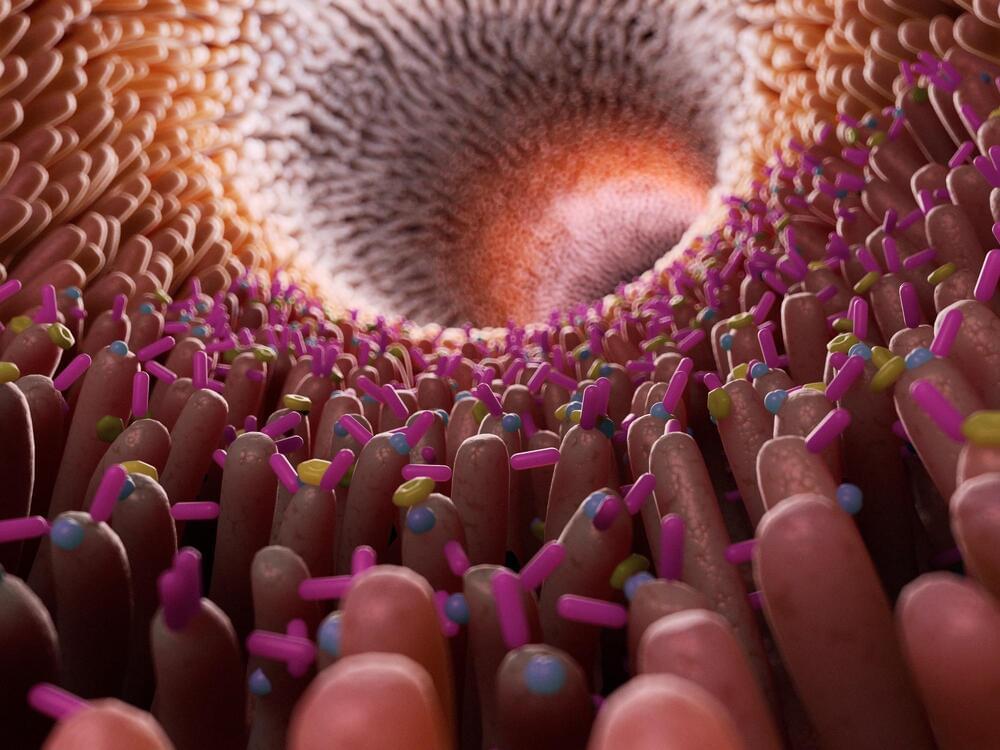
Study explores the differences in gut microbiome composition between prediabetic patients and healthy individuals, revealing significant variations that correlate with altered metabolic functions and potential diabetes progression.
Anyone who needs an unusual mole on their skin checked out may soon get to skip a surgical biopsy, and instead have a virtual biopsy. This tool could be a quick, uninvasive way to identify cancerous cells, as well as reveal any cancerous tissue that might be present and left behind during a surgery. This new tool uses lasers to and generate a three-dimensional reconstruction of cells in a tissue under analysis. Cross-sectional images of that tissue can then be assessed, like slides on a microscope. This work may one day be used not only on skin, but on other parts of the body. The work has been reported in Science Advances.
“We’ve not only created something that can replace the current gold-standard pathology slides for diagnosing many conditions, but we actually improved the resolution of these scans so much that we start to pick up information that would be extremely hard to see otherwise,” said senior study author Adam de la Zerda, PhD, an associate professor of structural biology at Stanford University.

Nanomaterials manufacturing, 3D bioprinting, and astronaut eye health were the main research topics aboard the International Space Station on Friday. The Expedition 71 crew members also continued servicing spacesuits and conducted an emergency drill.
The SpaceX Dragon cargo spacecraft recently delivered to the orbital outpost a biotechnology study to demonstrate the in-space production of nanomaterials that mimic DNA. NASA Flight Engineers Jeanette Epps and Mike Barratt worked on the second portion of that experiment on Thursday mixing then treating the research samples for analysis. Epps began her day mixing solutions in the Life Science Glovebox to create specialized nanomaterials. During the afternoon, Barratt applied sound and light treatments to the samples then stowed them aboard Dragon for analysis back on Earth. Results may lead to advanced therapies for space-caused and Earthbound health conditions.
The duo partnered back together at the end of the day for eye scans using standard medical imaging gear found in an optometrist’s on Earth. Barratt operated the hardware with guidance from doctors on the ground peering into Epp’s eyes and examining her retina and optic nerve for the B Complex eye health investigation.
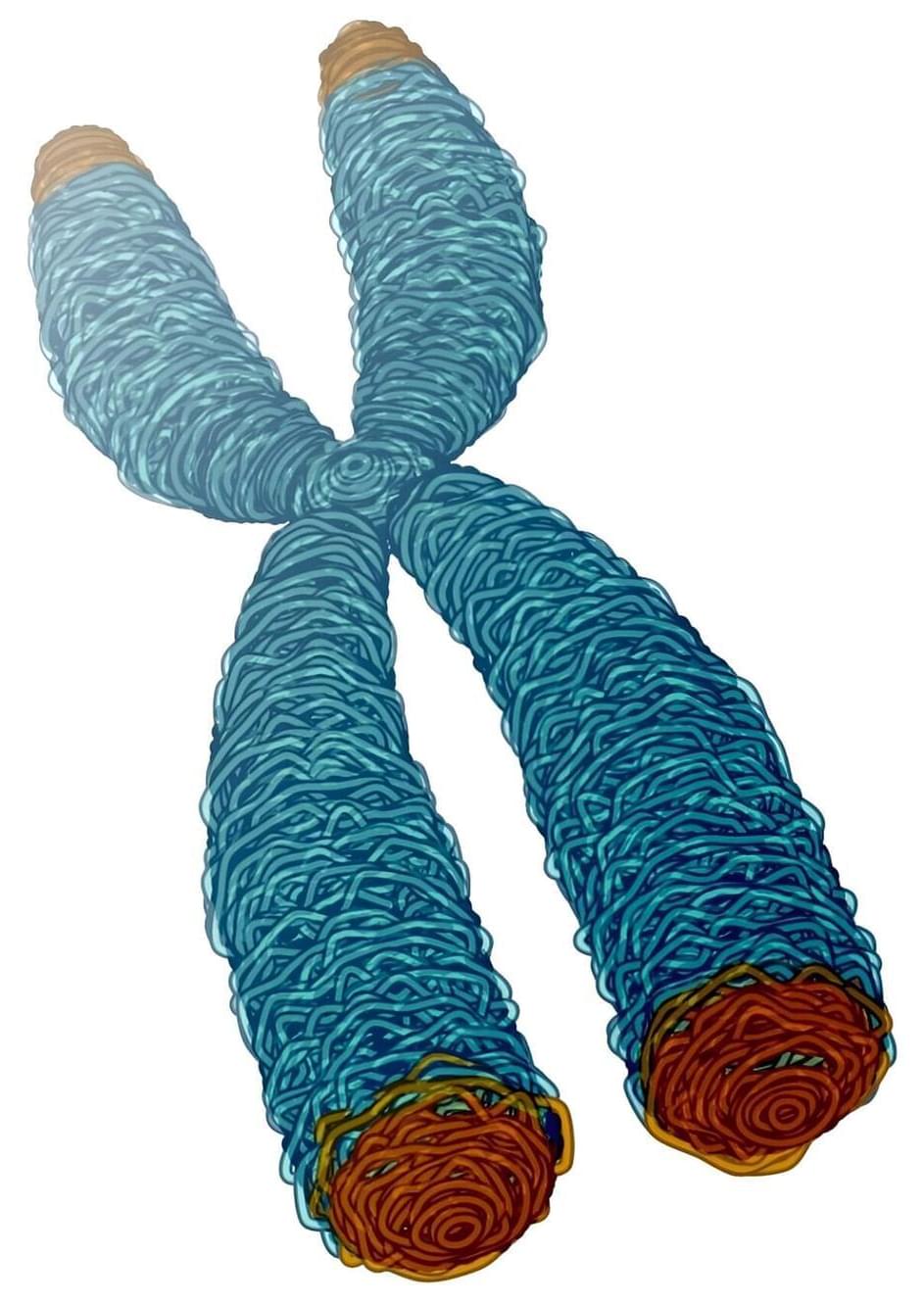
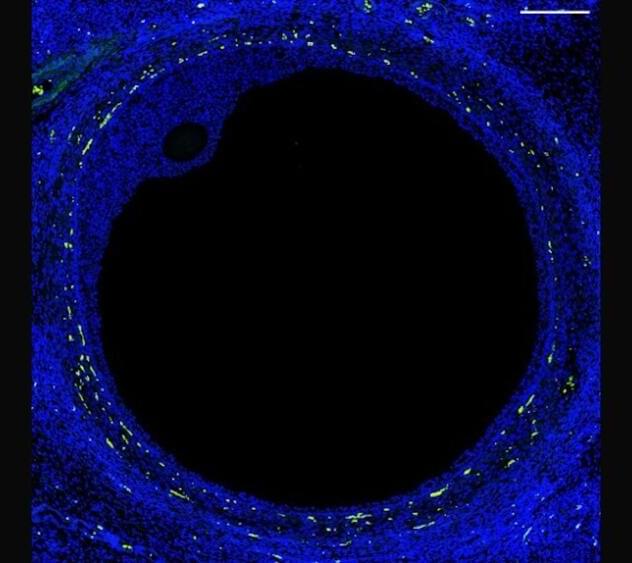
We depend on our cells being able to divide and multiply, whether it’s to replace sunburnt skin or replenish our blood supply and recover from injury. Chromosomes, which carry all of our genetic instructions, must be copied in a complete way during cell division. Telomeres, which cap the ends of chromosomes, play a critical role in this cell-renewal process—with a direct bearing on health and disease.

“This study is a first step in uncovering how we can mitigate risks of THC when used in medicine, and also is targeted at making cannabis safer for the general, non-therapeutic consumer,” said Dr. Tory Spindle.
Can cannabis be modified to decrease certain side effects, specifically anxiety, that is caused by tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)? This is what a recent study published in Drug and Alcohol Dependence hopes to address as a team of researchers led by the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine investigated whether adding d-limonene, which is a known cannabis oil, to THC could help alleviate common feelings of anxiety or paranoia that cannabis users traditionally experience. This study holds the potential to help improve medicinal cannabis while decreasing risks to users of recreational cannabis, as well.
For the study, the researchers enlisted 20 healthy adult participants with an average age of 26 years old who completed 10 six-hour sessions involving them using vaporized THC alone (15 mg or 30 mg), vaporized d-limonene alone (1 mg or 5 mg), both together, and finally a placebo. The sessions were double-blinded, meaning both the researchers and participants were unaware who was vaporizing which sample.
While all 20 participated in nine sessions, 12 participants conducted the tenth session comprised of the higher dose of THC and an even higher dose of d-limonene at 15 mg. The goal of the sessions was to ascertain the overall drug effects, specifically vital signs, mood, and cognitive functions, along with blood and urine samples during and after each session to measure THC and d-limonene levels.

“People don’t believe there’s wildlife here, but we’re really very, very rich in wildlife because we’re on the Atlantic Flyway and we have so many places for the birds to stop over during migration,” McMahon said.
Researchers and local students spent nearly two years collecting samples from a wide range of birds, including ones we see often like ducks and geese, to raptors.
Their findings were published earlier this month.
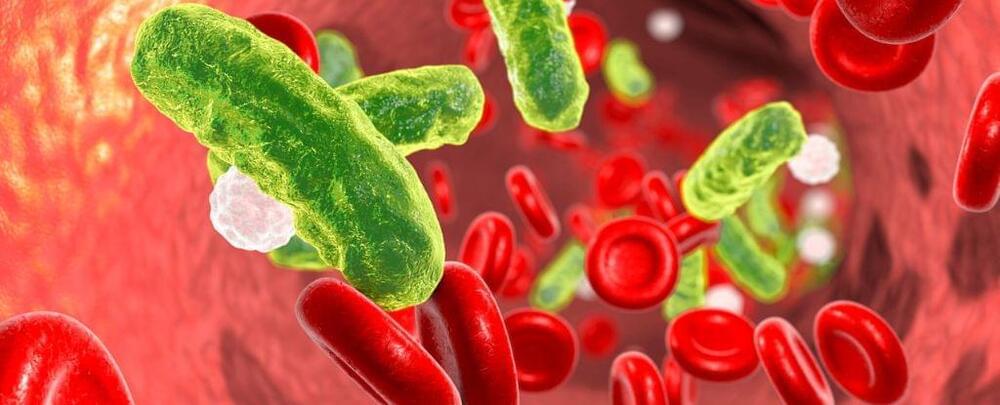
Scientists have figured out a whole new way to cut the legs out from underneath drug-resistant bacterial infections.
The new class of antibiotic was identified by researchers at Uppsala University in Sweden, and while it has only been tested on mice, the team hopes that further development of the drug can “make an important contribution to the ongoing struggle against antibiotic resistance.”
The unique medicine, like many other antibiotics currently in development, targets the double membrane that surrounds gram-negative bacteria, like Escherichia coli, which can cause bowel and blood infections, and Klebsiella pneumoniae, which can cause lung, bladder, and blood infections.
Aging is a life process where the body slowly breaks down and becomes more vulnerable to external stimuli. For example, bones in older individuals become frail and muscle deteriorates. Additionally, older individuals are more susceptible to disease with a compromised immune system. In many cases there are protocols and guidelines in place to protect those with high susceptibility to disease. During the COVID-19 pandemic older patients had to be extremely careful to avoid contracting COVID-19.
Unfortunately, aging is a natural part of life. However, scientists are working to make the process of aging a little easier. Due to the increased average lifespan, aging has been a progressively growing field. Physicians and scientists are working to understand how we age and if there are secrets to be uncovered that would help avoid, prevent, or cure age-related diseases, such as cancer.
Stem cells are self-renewing cells in the body with the ability to differentiate into any cell type. The outcome to which final cell type it turns into is dependent on what the body needs. Regarding the immune system, the body generates more myeloid immune cells. Aging of the immune system is best characterized by an imbalance of these immune cells. Other immune cells including lymphoid cells related to adaptive immunity are reduced in number while myeloid cells and inflammatory pathologies are increased. Many believe that stem cells may be the cause of this imbalance.