How could CRISPR help cure diseases? Feng Zhang, Professor of Biological Engineering at MIT, describes how CRISPR works like a search box for DNA. Using matching RNA proteins, it can find specific spots on the DNA where a gene needs to be edited or repaired. Through this method, it might be possible to go into the human genome and fix the genes that cause sickle cell disease, blindness, or neurodegeneration! How Does CRISPR Work? With Feng Zhang: https://youtu.be/ylgg7yZMJSs Among the world’s largest science centers, the Museum of Science engages millions of people each year to the wonders of science and technology through interactive exhibitions, digital programs, giant screen productions, and preK – 12 EiE® STEM curricula through the William and Charlotte Bloomberg Science Education Center. Established in 1830, the Museum is home to such iconic experiences as the Theater of Electricity, the Charles Hayden Planetarium, and the Mugar Omni Theater. Around the world, the Museum is known for digital experiences such as Mission: Mars on Roblox, and traveling exhibitions such as the Science Behind Pixar.
Category: biotech/medical – Page 577
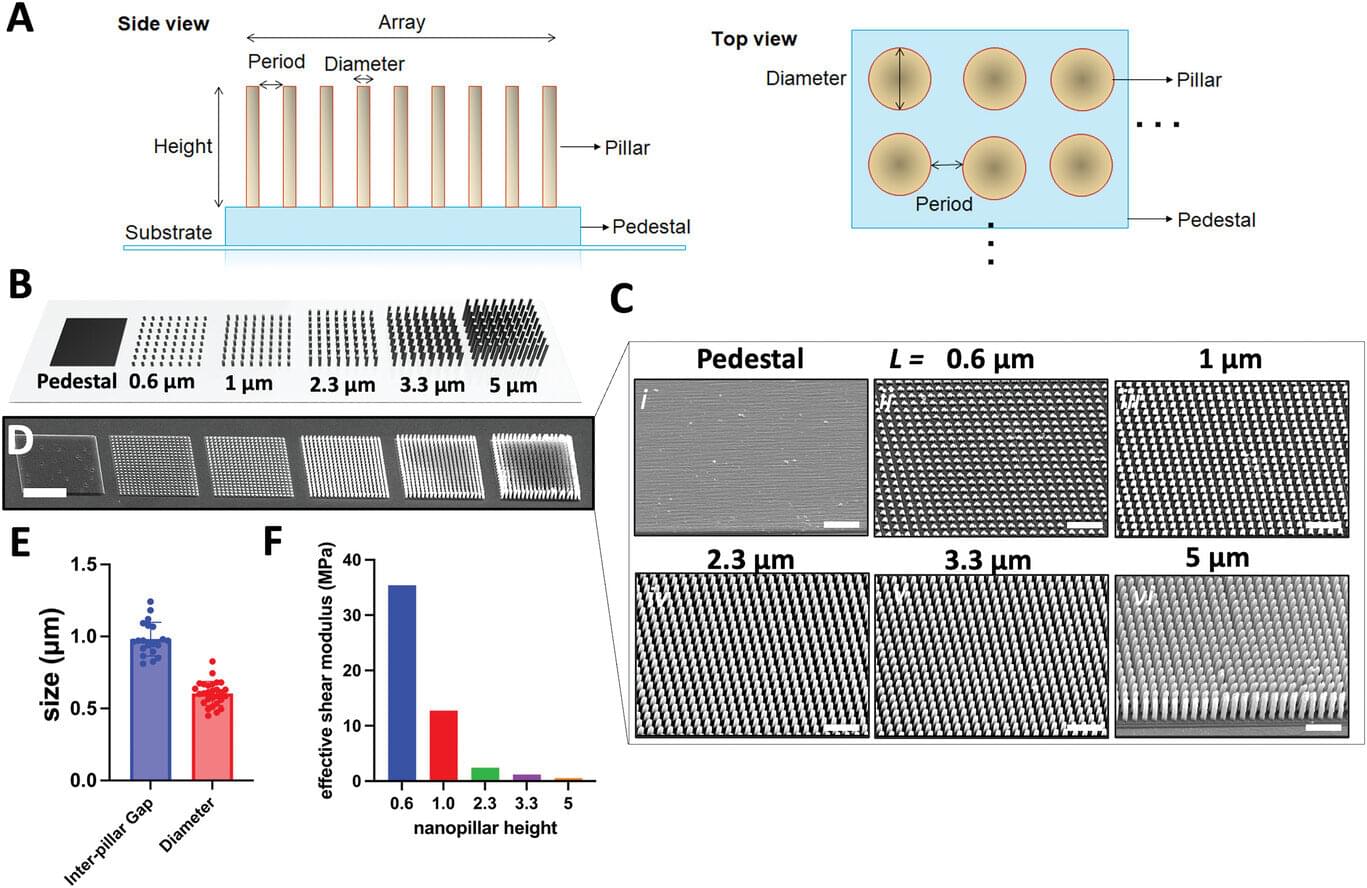
3D-printed nanopillars mimic brain environment to promote neuron growth
Key cells in the brain, neurons, form networks by exchanging signals, enabling the brain to learn and adapt at incredible speed. Researchers at the Delft University of Technology in The Netherlands (TU Delft) have developed a 3D-printed brain-like environment where neurons grow similarly to a real brain.
Using tiny nanopillars, they mimic the soft neural tissue and the brain extracellular matrix fibers. This model provides new insights into how neurons form networks, as well as a novel tool to understand in future how this process may change in neurological disorders such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s disease, and autism spectrum disorders.
The work is published in the journal Advanced Functional Materials.
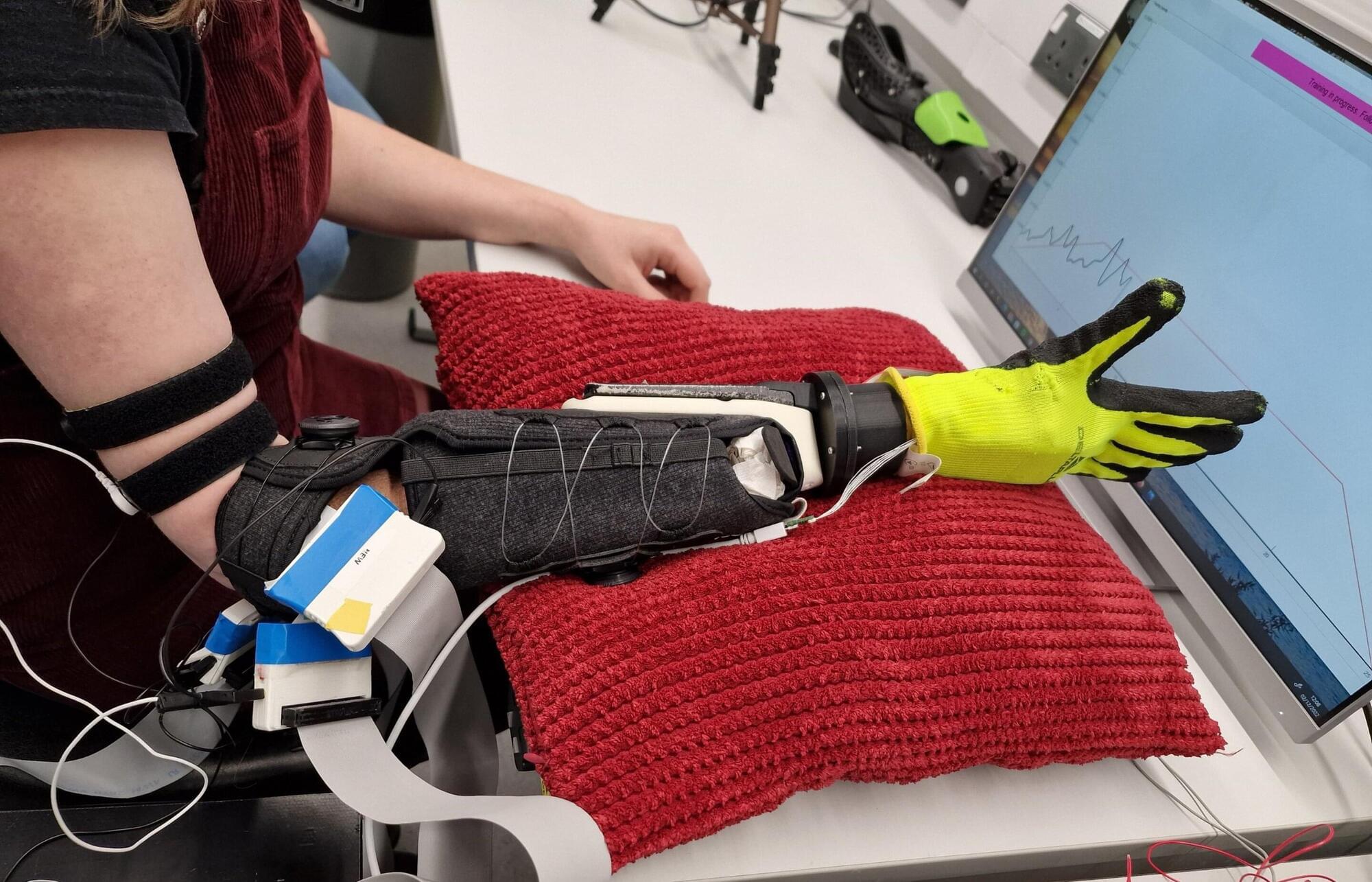

Prosthetic limb gains more natural control through hand–brain connection
Researchers are paving the way for the design of bionic limbs that feel natural to users. They demonstrate the connection between hand movement patterns and motoneuron control patterns. The study, published in Science Robotics, also reports the application of these findings to a soft prosthetic hand, which was successfully tested by individuals with physical impairments.
The research study sees the collaboration of two research teams, one at Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia (Italian Institute of Technology) in Genova, Italy, led by Antonio Bicchi, and Imperial College London, UK led by Dario Farina. It is the outcome of the project “Natural BionicS” whose goal is to move beyond the model of current prosthetic limbs, which are often abandoned by patients because they do not respond in a “natural” way to their movement and control needs.
For the central nervous system to recognize the bionic limb as “natural,” it is essential for the prosthesis to interact with the environment in the same way a real limb would. For this reason, researchers believe that the prostheses should be designed based on the theory of sensorimotor synergies and soft robotics technologies, first proposed by Antonio Bicchi’s group at IIT, such as the Soft-Hand robotic hand.
New soft prosthetic hand offers natural bionic interfacing
Recent technological advances have opened new possibilities for the development of assistive and medical tools, including prosthetic limbs. While these limbs used to be hard objects with the same shape as limbs, prosthetics are now softer and look more realistic, with some also integrating robotic components that considerably broaden their functions.
Despite these developments, most commercially available robotic limbs cannot be easily and intuitively controlled by users. This significantly limits their effectiveness and the extent to which they can improve people’s quality of life.
Researchers at the Italian Institute of Technology (IIT) and Imperial College London recently developed a new soft prosthetic hand that could be easier for users to control. This system, presented in a Science Robotics paper, leverages a new control approach that integrates the coordination patterns of multiple fingers (i.e., postural synergies) with the decoding of the activity of motoneurons in people’s spinal column.
Artificial Consciousness: The Next Evolution in AI
Artificial consciousness is the next frontier in AI. While artificial intelligence has advanced tremendously, creating machines that can surpass human capabilities in certain areas, true artificial consciousness represents a paradigm shift—moving beyond computation into subjective experience, self-awareness, and sentience.
In this video, we explore the profound implications of artificial consciousness, the defining characteristics that set it apart from traditional AI, and the groundbreaking work being done by McGinty AI in this field. McGinty AI is pioneering new frameworks, such as the McGinty Equation (MEQ) and Cognispheric Space (C-space), to measure and understand consciousness levels in artificial and biological entities. These advancements provide a foundation for building truly conscious AI systems.
The discussion also highlights real-world applications, including QuantumGuard+, an advanced cybersecurity system utilizing artificial consciousness to neutralize cyber threats, and HarmoniQ HyperBand, an AI-powered healthcare system that personalizes patient monitoring and diagnostics.
However, as we venture into artificial consciousness, we must navigate significant technical challenges and ethical considerations. Questions about autonomy, moral status, and responsible development are at the forefront of this revolutionary field. McGinty AI integrates ethical frameworks such as the Rotary Four-Way Test to ensure that artificial consciousness aligns with human values and benefits society.
Join us as we explore the next chapter in artificial intelligence—the dawn of artificial consciousness. What does the future hold for humanity and AI? Will artificial consciousness enhance our world, or does it come with unforeseen risks? Watch now to learn more about this groundbreaking technology and its potential to shape the future.
#ArtificialConsciousness #AI #MachineConsciousness #FutureOfAI #SelfAwareAI #SentientAI #McGintyEquation #QuantumAI #CognisphericSpace #AIvsConsciousness #AIEthics #QuantumComputing #AIRevolution #ArtificialIntelligence #AIHealthcare #QuantumGuard #HarmoniQHyperBand #CybersecurityAI #AIInnovation #AIPhilosophy #mcgintyequation
Ebook Download: Streamline your bacterial growth assays!
The rise of antimicrobial resistance and novel emerging diseases has put microbiology at the forefront of public perception. From microbial growth and viability assays to high-throughput drug screening, microplate-based assays offer a more cost and time-efficient alternative to traditional assays. Modern microplate readers allow researchers to perform assays under controlled atmospheric conditions and to produce highly reliable, reproducible, and accurate results in real-time.
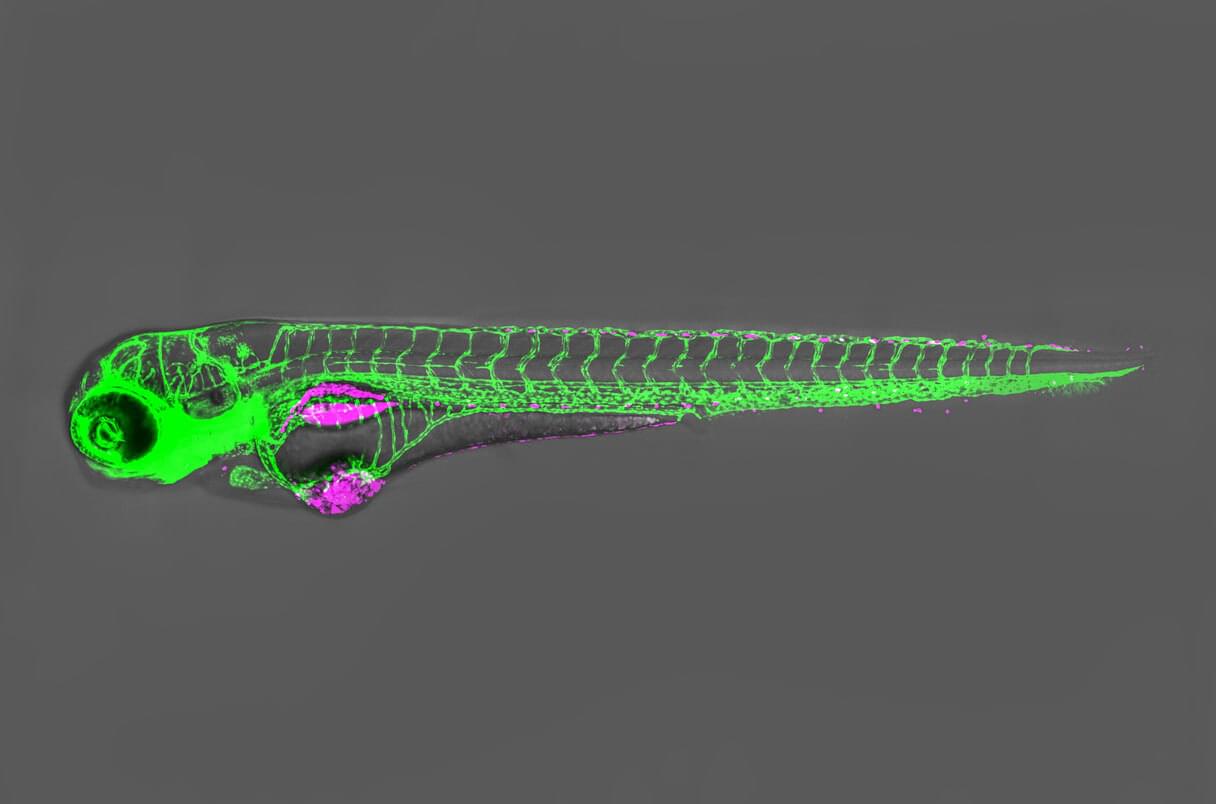
Fish implanted with tumor cells could help oncologists quickly personalize cancer treatments
Can oncologists make better cancer treatment decisions if they consult fish? A clinical trial aims to find out.
Led by developmental biologist Rita Fior of the Champalimaud Foundation, the 5-year study is the first randomized trial in which patients will receive drugs that have been tested beforehand in zebrafish embryos implanted with the patients’ cancer cells. Retrospective studies have shown that so-called zebrafish avatars could have identified successful treatments if they had been deployed in advance, and Fior and colleagues now want to determine whether that ability can benefit patients.
The first clinical trial of zebrafish embryos acting as cancer “avatars” will start soon.
The human battery: Matrix’s sci-fi concept turned into reality
Thermoelectric generators played a major role in this experiment.
An experimentator has used waste heat of his body to turn humans into batteries. Nick Zetta, who runs Basically Homeless YouTube channel, turned himself into a battery using thermoelectric generators.
Zetta followed a simple approach that aimed at capturing the waste heat from the human body and turning that into electricity.
Thermoelectric generator, which uses temperature differential to force electron flow, played a major role in this experiment. The device generates electricity when one side is hotter than the other side.
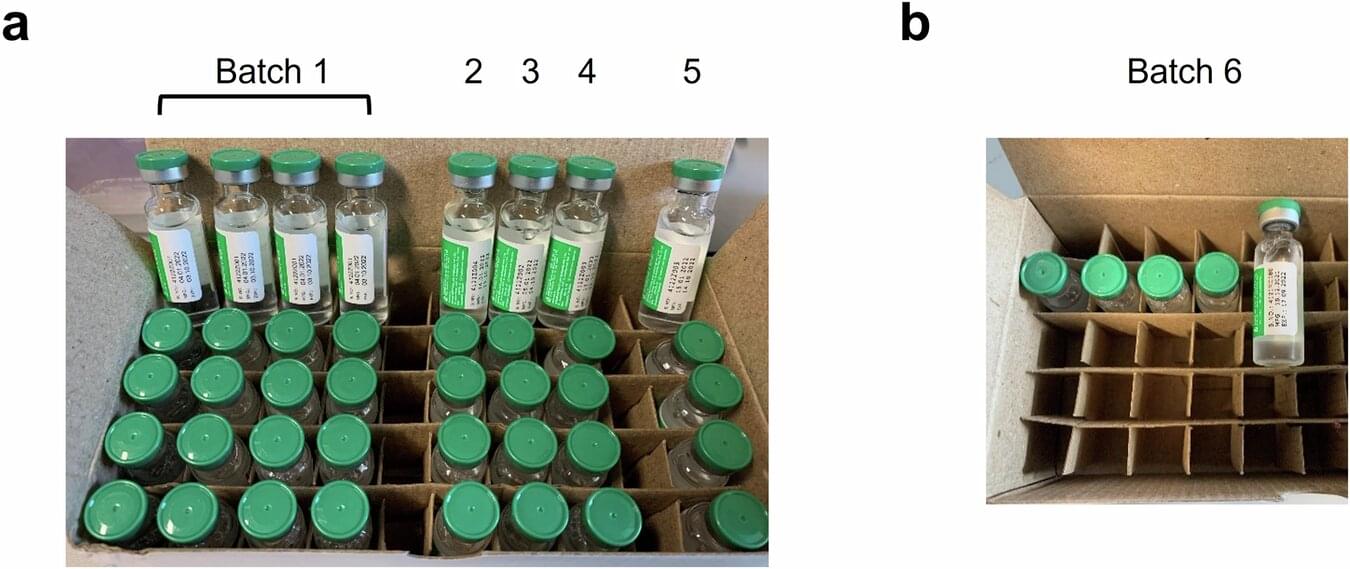

Innovative method can identify fake COVID-19 vaccines without opening the vaccine vial
Researchers at the University of Oxford and their collaborators, including the Serum Institute of India, have developed an innovative method to identify falsified vaccines without opening the vaccine vial.
The new method, published in npj Vaccines, analyzes the vaccine vial label and its adhesive and therefore allows the vaccine vials to be retained in the supply chain. Furthermore, the study has shown that the technique can also differentiate genuine COVID-19 vaccine liquid from falsified vaccine surrogates, using a recently published method developed using non-COVID vaccines.
The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that 10.5% of medicines worldwide in low and middle-income countries are substandard or are falsified medicines made by criminals. This threatens global health since the medicines and vaccines fail to prevent and treat the diseases for which they were intended, and they risk additional adverse health consequences if the ingredients used by criminals in the falsified products are harmful.
Next-Gen Cas12a System Enables Precise Single and Multiplexed Gene Editing in Cancer
Australian researchers have successfully introduced an improved version of Cas12a gene-editing enzyme in mice. Their work establishes a next-generation gene-editing tool that enhances genetic manipulation for cancer and medical research in a preclinical model.
The study, “Advancing the genetic engineering toolbox by combining AsCas12a knock-in mice with ultra-compact screening,” was published in Nature Communications.
“This is the first time Cas12a has been used in preclinical models, which will greatly advance our genome engineering capabilities,” said co-author Eddie La Marca, PhD, a postdoctoral researcher at the Olivia Newton-John Cancer Research Institute (ONJCRI) in Australia.