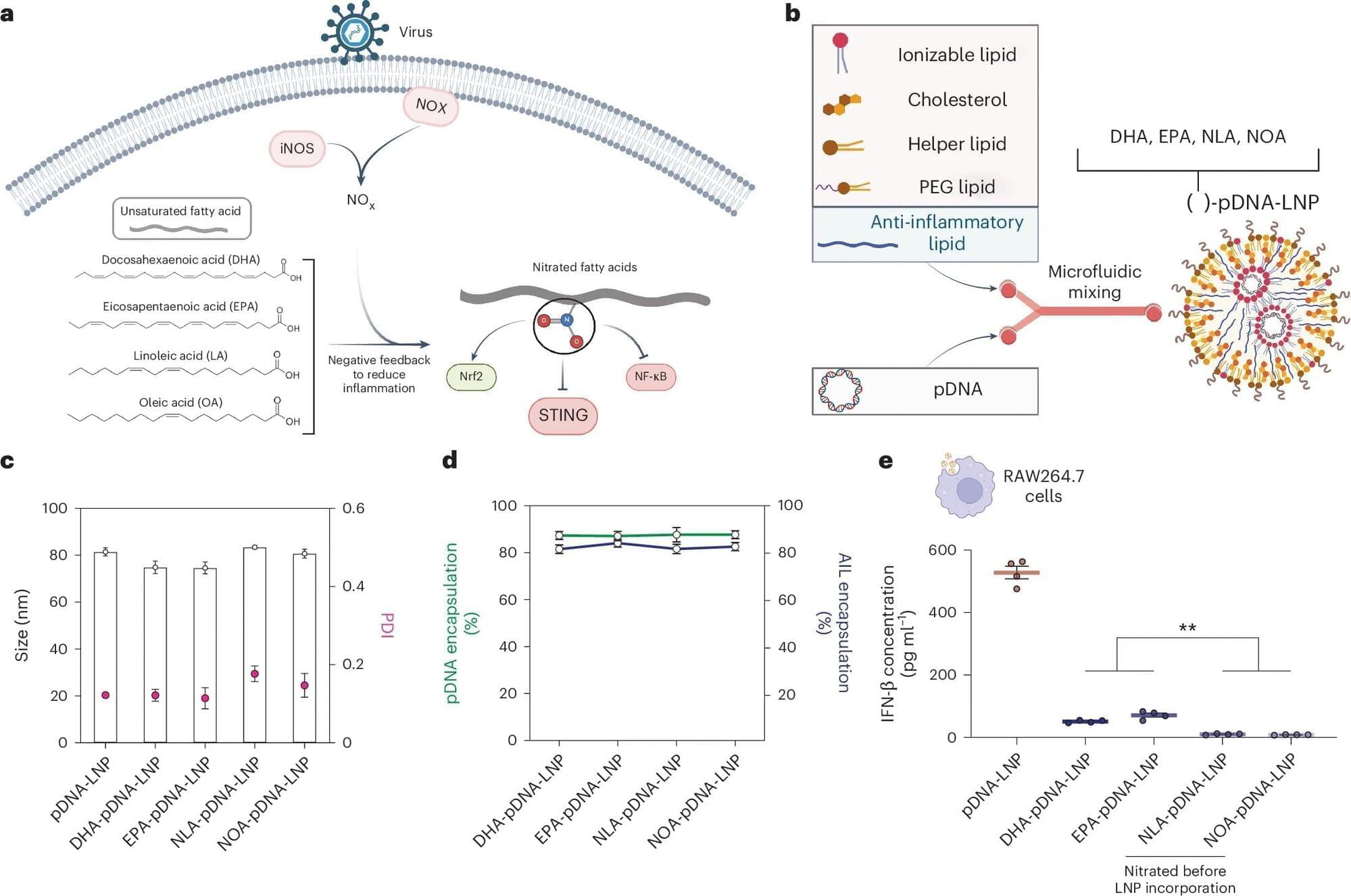
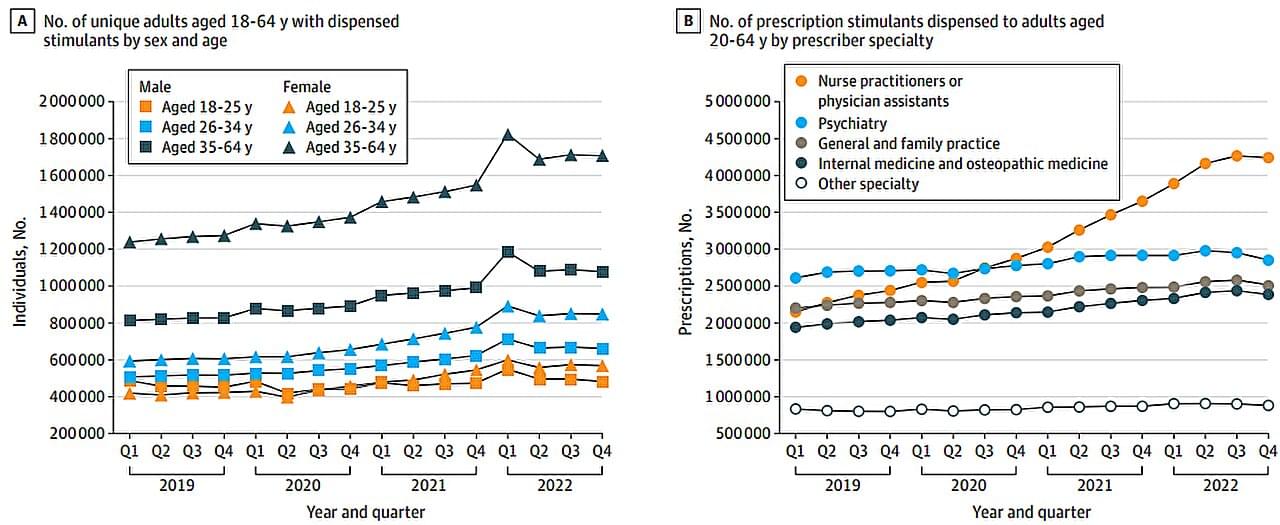
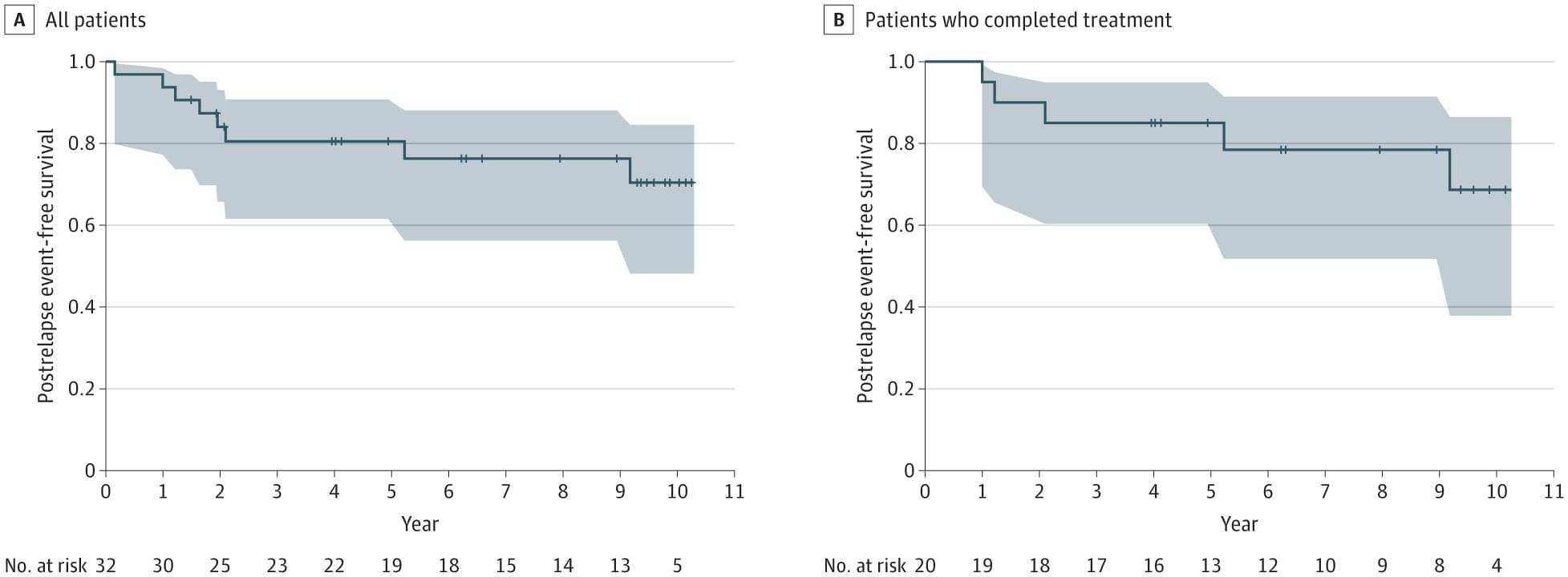
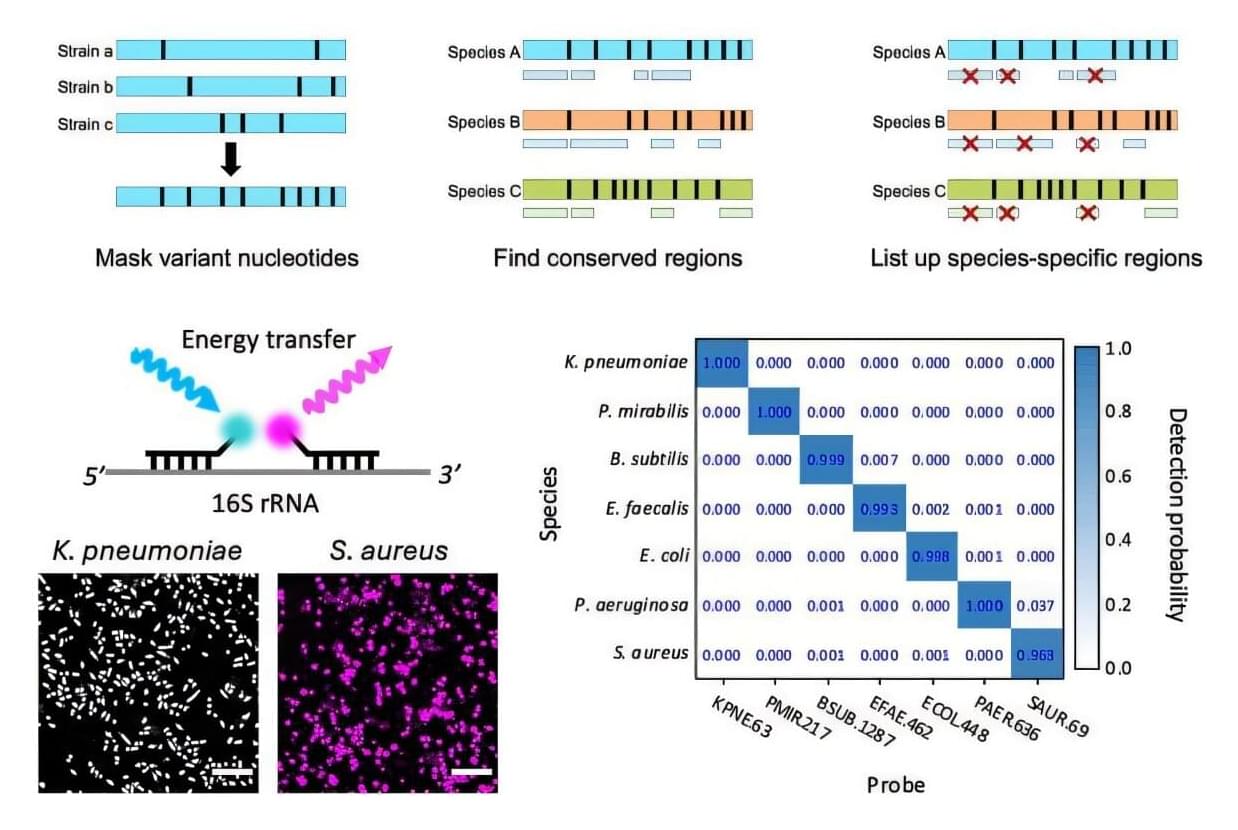
A breakthrough in safely delivering therapeutic DNA to cells could transform treatment for millions suffering from common chronic diseases like heart disease, diabetes, and cancer.
A new process that transports DNA into cells using tiny fat-based carriers called lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) developed by researchers at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania improved the process of turning on the DNA’s instructions in mice to make proteins inside cells, which is crucial in fighting disease. Signs also point to an improvement in reducing treatment risks, such as immune reactions, as compared to older DNA transfer techniques.
The team’s findings were recently published in Nature Biotechnology.