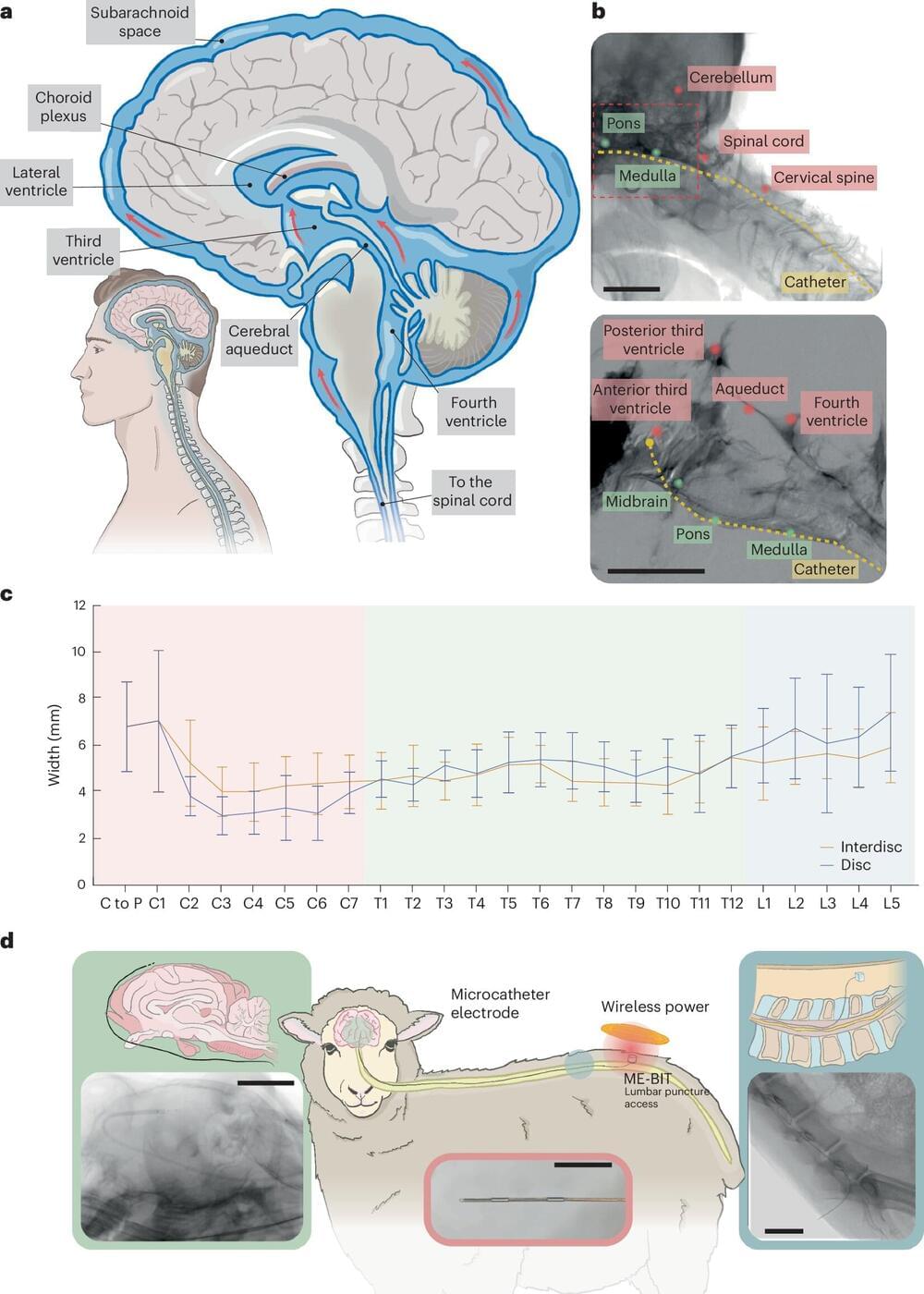
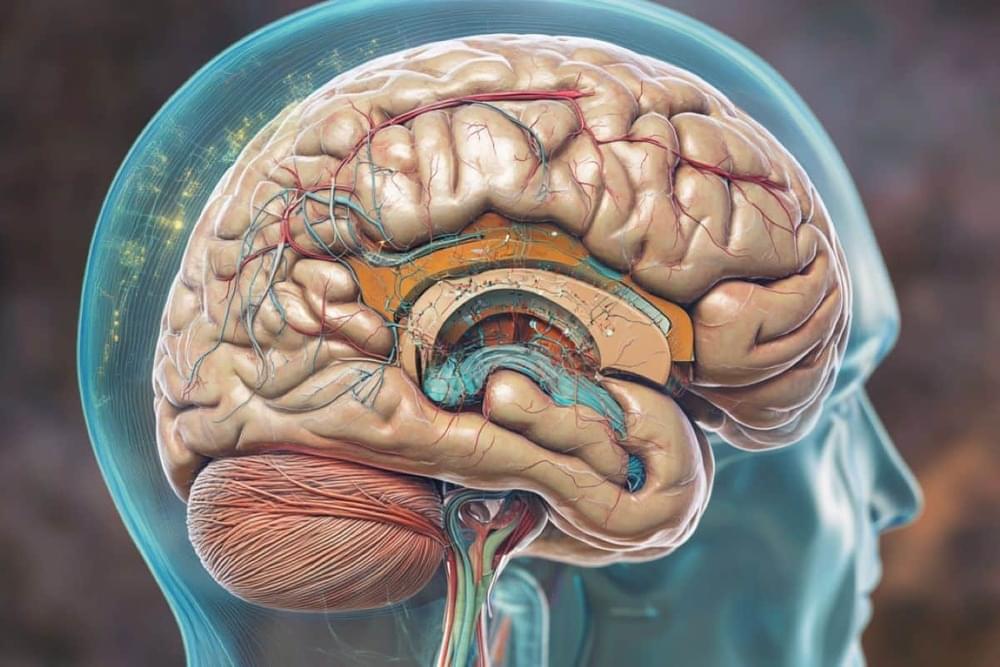
A team of researchers led by Rice University’s Jacob Robinson and the University of Texas Medical Branch’s Peter Kan has developed a technique for diagnosing, managing and treating neurological disorders with minimal surgical risks. The team’s findings were published in Nature Biomedical Engineering.
While traditional approaches for interfacing with the nervous system often require creating a hole in the skull to interface with the brain, the researchers have developed an innovative method known as endocisternal interfaces (ECI), allowing for electrical recording and stimulation of neural structures, including the brain and spinal cord, through cerebral spinal fluid (CSF).
“Using ECI, we can access multiple brain and spinal cord structures simultaneously without ever opening up the skull, reducing the risk of complications associated with traditional surgical techniques,” said Robinson, professor of electrical and computer engineering and bioengineering.