FDA clears Stanford Medicine-spawned sepsis test, developed using machine learning, that leverages publicly available medical datasets from around the world.

The BCI is rapidly evolving, but the real challenge has always been the long-term usability of devices implanted in the brain. Because of this, it is exciting to see the early success stories of Neuralink with the three patients who have received chip implants so far. They have all achieved results beyond expectations without any risks, which has made Elon Musk even more confident and ambitious with his implanted chip. He has decided to upgrade the chip to a higher level to support more people with disabilities. At the same time, Musk has shared updates on the condition of the three Neuralink-implanted patients. This year, the number of implant recipients is expected to increase significantly. So, is this a major turning point for people to trust Neuralink? Explore the latest updates now, Welcome to Tesla Car World!
Full NEURALINK Human Trials! Elon Musk Reveals NEW Updates On Three Patient Shocking In 2025! You may not believe it, but from the perspective of many people, Neuralink is one of Elon Musk’s most controversial and ridiculous companies. They argue that Musk should focus on Tesla and SpaceX instead of a less widely accepted field like BCI. Concerns about the dangers of implanting chips in the brain, especially given how new this technology is, remain a hot topic of discussion. Some even fear that brain data could be misused or compromised if Neuralink were hacked. However, despite these concerns, it is undeniable that for the three implanted patients, Neuralink means more than ever. They seem to be living a second life, in fact, Neuralink makes them feel as if they have been reborn.
Full NEURALINK Human Trials! Elon Musk Reveals NEW Updates On Three Patient Shocking In 2025! Imagine losing the ability to move, communicate, or control your own body. Then, one day, something allows you to think and control a computer cursor, communicate with the world through your thoughts, and do things you had once given up hope on. For the three patients who have experienced Neuralink, this is not just an ordinary chip, it is an opportunity, a hope, a real-life miracle.
===
#888999evs #teslacarworld #teslacar #888999 #teslaneuralink #neuralink.
subcribe: https://bit.ly/3i7gILj
Health, vitality and longevity through bioengineering — kevin caldwell — CEO, ossium health.
Kevin Caldwell is CEO, Co-Founder & President of Ossium Health (https://ossiumhealth.com/), a commercial stage bioengineering company that leverages its proprietary organ donor bone marrow banking platform to develop stem cell therapies for patients with life-threatening hematologic conditions, organ transplant rejection, and musculoskeletal defects.
Mr. Caldwell built Ossium from a small startup into the clinical stage bioengineering company it is today, setting the company’s mission to improve human health through bioengineering and designed its platform-based model for cellular therapeutics development. He has led the company’s successful pursuit, negotiation, and execution of more than 50 business relationships, including 5 successful fundraisings and dozens of supply partnerships, clinical partnerships, and commercial contracts with biopharmaceutical companies.
After seven years of strategic engagement and networking, Mr. Caldwell drove the team to successfully secure a transformative federal contract with BARDA (Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority) that validates Ossium’s innovative approach. This milestone represents the culmination of persistent relationship-building, targeted proposals, and unwavering commitment to addressing national biomedical challenges through cutting-edge technology and collaborative partnerships.
Prior to founding Ossium, Mr. Caldwell served as an Engagement Manager at McKinsey’s San Francisco office where he advised clients in the biotechnology and healthcare sectors. His projects ranged from due diligence of acquisition targets in the biotech startup ecosystem to restructuring distressed biopharma companies. Mr. Caldwell led more than 20 engagements with more than a dozen clients, leading teams that advised clients on revenue growth, go to market strategy, and organizational restructuring.
Join us on Patreon! https://www.patreon.com/MichaelLustgartenPhD
Discount Links/Affiliates:
Blood testing (where I get the majority of my labs): https://www.ultalabtests.com/partners/michaellustgarten.
At-Home Metabolomics: https://www.iollo.com?ref=michael-lustgarten.
Use Code: CONQUERAGING At Checkout.
Clearly Filtered Water Filter: https://get.aspr.app/SHoPY
Epigenetic, Telomere Testing: https://trudiagnostic.com/?irclickid=U-s3Ii2r7xyIU-LSYLyQdQ6…M0&irgwc=1
Use Code: CONQUERAGING
NAD+ Quantification: https://www.jinfiniti.com/intracellular-nad-test/

Chemistry researchers at Case Western Reserve University have identified specific markers that could pave the way for new blood tests to detect diseases.
Almost every disease involves some degree of inflammation, yet standard blood tests cannot precisely identify which organs or tissues are affected.
Now, researchers at Case Western Reserve University have developed an antibody-based method to detect inflammation, which could pave the way for blood tests that identify disease-specific biomarkers. This advancement has potential applications in diagnosing conditions such as heart disease, Alzheimer’s.
Use my code MIC25 for 25% off your first month’s supply of Seed’s DS-01® Daily Synbiotic: https://seed.com/mic.
We need to talk about human brain organoids!
- Links and Sources
Link Page with eBooks and Socials: https://linktr.ee/micthevegan.
Support Me Here: https://www.patreon.com/micthevegan.
Vegan Bootcamp: https://vbcamp.org/Micthevegan.
My New Newsletter Sign-Up:
https://mailchi.mp/2785ad113ff7/micthevegan-emails.
Brain Signature Compared to Human Development:
https://www.cell.com/cell-stem-cell/fulltext/S1934-5909(19)30337-6
Brain Organoids (Can) Remove Animal Testing:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10013781/
Genes Connected to Autism — Mini Brain Research:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-023-06473-y.
Mini Brains and Cancer Treatment:
https://www.cell.com/action/showPdf?pii=S2211-1247%2819%2930242-6
Rett Syndrome Study:
If you think telepathy or mind control is the stuff of science fiction, think again. Advances in artificial intelligence are leading to medical breakthroughs once thought impossible, including devices that can actually read minds and alter our brains.
Can we mobilise society towards a concerted effort against ageing? Dr Aubrey de Grey believes so—with groundbreaking results from studies by the Longevity Escape Velocity (LEV) Foundation on Integrative Rejuvenation, a cutting-edge approach to repairing cellular and molecular damage linked to ageing.
Why does he believe this could be the most promising pathway toward extending healthy human lifespan? Watch on to find out.
Register for upcoming #HealthyLongevity #webinar sessions at https://nus-sg.zoom.us/webinar/regist… The opinions and advice expressed in this webinar are those of the speakers and do not represent the views and opinions of the organizers and National University of Singapore or any of its subsidiaries or affiliates. The information provided in this webinar is for general information purposes only as part of a general discussion on public health. The information is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnoses or treatment; and cannot be relied on in place of consultation with your licensed healthcare provider. All Rights Reserved. All of the proceedings of this webinar, including the presentation of scientific papers, are intended for limited publication only, and all property rights in the material presented, including common-law copyright, are expressly reserved to the speaker or NUS. No statement or presentation made is to be regarded as dedicated to the public domain. Any sound reproduction, transcript or other use of the material presented at this course without the permission of the speaker or NUS is prohibited to the full extent of common-law copyright in such material.
Disclaimer: The opinions and advice expressed in this webinar are those of the speakers and do not represent the views and opinions of the organizers and National University of Singapore or any of its subsidiaries or affiliates. The information provided in this webinar is for general information purposes only as part of a general discussion on public health. The information is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnoses or treatment; and cannot be relied on in place of consultation with your licensed healthcare provider. All Rights Reserved.
All of the proceedings of this webinar, including the presentation of scientific papers, are intended for limited publication only, and all property rights in the material presented, including common-law copyright, are expressly reserved to the speaker or NUS. No statement or presentation made is to be regarded as dedicated to the public domain.
Any sound reproduction, transcript or other use of the material presented at this course without the permission of the speaker or NUS is prohibited to the full extent of common-law copyright in such material.
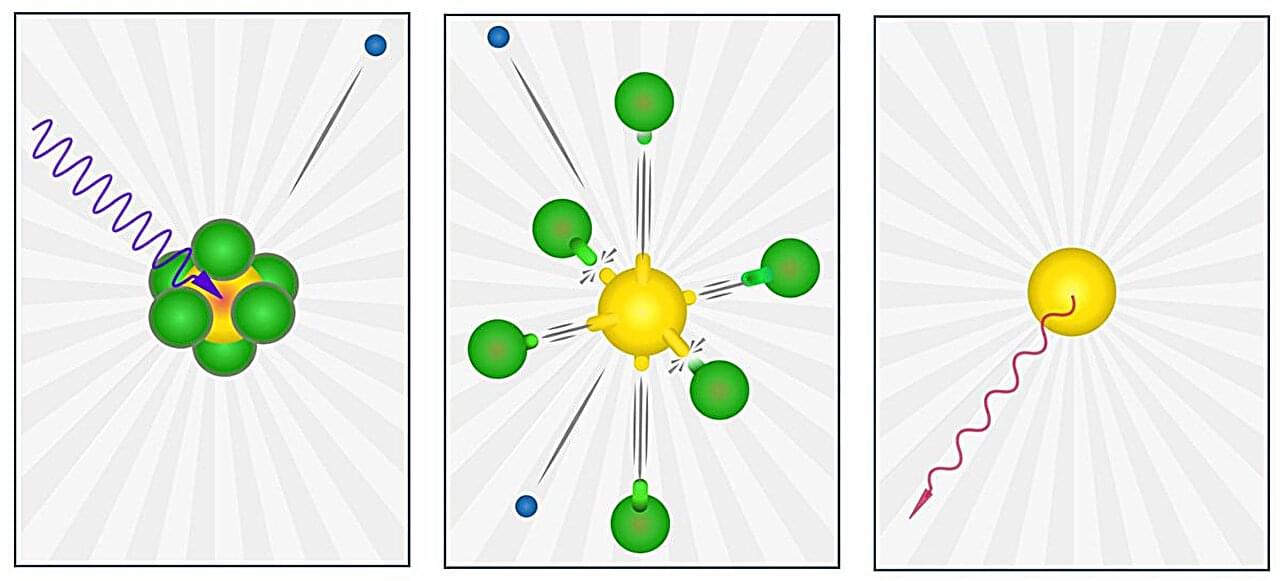
An international team of scientists has unveiled new insights into the dissociation dynamics of sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) under high-energy X-ray excitation. The study, conducted using advanced synchrotron radiation techniques, sheds light on the formation of neutral sulfur atoms during the decay of deep core holes in SF6. The work is published in Physical Review Letters.
Understanding the interaction of X-rays with matter is fundamental to both scientific research and practical applications, including medical and technological advancements. These interactions involve complex processes including absorption, ionization, scattering, and the decay of excited states, which emit electrons or photons.
In 1978, young scientists named Joseph Nordgren and Hans Ågren discovered an unusual spectral feature in sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) that defied explanation at the time. Their discovery was made at the Siegbahn Laboratory of Uppsala University, founded by the late Nobel Prize laureate Kai Siegbahn. Despite further investigations, the nature of this spectral anomaly remained unclear.

“ tabindex=”0” acid reflux at a significantly faster rate than those without. This highlights the urgent need for a healthcare system that treats both mental and physical health together, rather than in isolation.
Depression’s Lasting Impact on Physical Health
Adults with a history of depression develop chronic physical conditions about 30% faster than those without, according to a study published on February 13 in PLOS Medicine. Researchers, led by Kelly Fleetwood from the University of Edinburgh, suggest that depression should be recognized as a “whole-body” condition, emphasizing the need for integrated care that addresses both mental and physical health.