AI joins the fight against Leukemia.
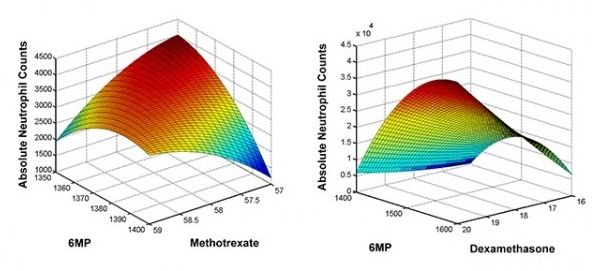


More proof that Precision Medicine can predict and solve complex health issues.
Brain scans could help predict response to psychotherapy for anxiety and depression.
Nov. 10, 2016 – Brain imaging scans may one day provide useful information on the response to psychotherapy in patients with depression or anxiety, according to a review of current research in the November/December issue of the Harvard Review of Psychiatry, published by Wolters Kluwer.


This is a BIG DEAL in QC, and Russian Scientists solved it.
Abstract: Scientists from the Institute of Physics and Technology of the Russian Academy of Sciences and MIPT have let two electrons loose in a system of quantum dots to create a quantum computer memory cell of a higher dimension than a qubit (a quantum bit). In their study published in Scientific Reports, the researchers demonstrate for the first time how quantum walks of several electrons can help to implement quantum computation.
“By studying the system with two electrons, we solved the problems faced in the general case of two identical interacting particles. This paves the way toward compact high-level quantum structures,” comments Leonid Fedichkin, Expert at the Russian Academy of Sciences, Vice-Director for Science at NIX (a Russian computer company), and Associate Professor at MIPT’s Department of Theoretical Physics.
In a matter of hours, a quantum computer would be able to hack through the most popular cryptosystem used even in your web browser. As far as more benevolent applications are concerned, a quantum computer would be capable of molecular modeling that takes into account all interactions between the particles involved. This in turn would enable the development of highly efficient solar cells and new drugs. To have practical applications, a quantum computer needs to incorporate hundreds or even thousands of qubits. And that is where it gets tricky.
Progress with Alzheimers and this time approaching it from the direction of Tau as a target rather than Beta Amyloid. This therapy has been tested in people and whilst it is only the first step hopefully this will lead to an effective treatment for this horrific diseases and and end to the suffering it brings.
Progress towards immunotherapies that can clear tau for Alzheimers here. Most therapies are focused on misfolded amyloid-β proteins but this particular approach targets Tau and the first in human test has proceeded!
“The authors of the study have developed a vaccine that stimulates the production of an antibody that specifically targets pathological tau, discovering its “Achilles’ heel”. It is able to do this because healthy tau undergoes a series of changes to its structure forming a new region that the antibody attacks. This new region (the “Achilles’ heel”), while not present in healthy tau, is present in diseased tau early on. Therefore, the antibody tackles all the different varieties of pathological tau. In addition to this important specificity, the antibody is coupled to a carrier molecule that generates a considerable immune response with the added benefit that it is not present in humans, thus avoiding the development of an immune reaction towards the body itself.”
#aging #crowdfundthecure
Tiny machines like nanorockets are ideal candidates for drug delivery in the human body. Chemists at Radboud University now demonstrate the first complete movement regulation of a nanorocket, by providing temperature responsive brakes. An interesting feature for practical applications, since temperature sensitivity enables the rocket to stop in diseased tissues where temperatures are higher. Nature Chemistry publishes their results on December 12.
The soft nanosystems that the bio-organic chemists at Radboud University work with self assemble, which means that they spontaneously form functional units. This allows the nanorockets to change shape, making them ideal candidates for containing cargo like medicine. ‘Our biggest challenge is to provide our nanorockets with various functionalities’, says Daniela Wilson, head of Radboud University’s Bio-organic chemistry department and Nanomedicine theme leader ‘We now demonstrate the first molecularly built brake system, enabling the rockets to start and stop at desired locations.’
After getting off its $100 million-plus IPO in the summer, gene editing biotech Intellia Therapeutics is getting ready for human tests of its preclinical CRISPR tech with new digs designed to help bolster its research capabilities.
The biotech, which has the backing and partnerships of the likes of Atlas, Novartis and Regeneron, is on the move as it heads over to its new lab facilities at 40 Erie Street, in Cambridge, MA.
“The field of genome editing is rapidly evolving and our work to develop therapies for patients requires that we have the infrastructure necessary for R&D growth and prepare for preclinical studies and clinical trials,” said Dr. Nessan Bermingham, CEO and founder of Intellia Therapeutics.

Removing Glucosepane crosslinks from tissue is one of the most important things groups like SENS Research Foundation are doing and their progress relies on our support.
In this interesting open access paper, the authors propose that too little attention has been given to immune cell behavior in tissues rather than in blood, and that means that researchers have overlooked the possibility that age-related changes in the extracellular matrix structures that support tissues might be a significant cause of the growing immune dysfunction that takes place in later life. One of the more important of these changes in the extracellular matrix is the growing presence of cross-links, persistent sugary compounds produced as a byproduct of normal metabolic operations that chain together the large molecules of the extracellular matrix. In doing so these cross-links change the chemical and structural properties of the matrix and the tissue as a whole, producing results such as loss of elasticity in skin and blood vessels, which in turn contribute to a variety of age-related diseases. If cross-linking does indeed contribute to immunosenescence, the decline of the immune system with age, then that only increases the importance of ongoing research funded by the SENS Research Foundation aimed at safely breaking down this unwanted form of metabolic waste. In humans near all persistent cross-links appear to involve a single class of compound, glucosepane. So in theory there is only a single target here, needing just one drug development program to make a large difference to long-term health and longevity.

This is one of the Nextbigfuture article series reviewing developments in 2016 and looking ahead to developments over the next few years. Here we look at 2016 in space. Later articles will look at medicine, life extension, energy and other areas. Previously we reviewed computers and artificial intelligence
The biggest developments in space in 2016.
SpaceX had several successful launches and landed several rocket stages but had an accident which has grounded SpaceX. They hope to launching again in January 2017.