David Sinclair. Of note in this lecture:
Category: biotech/medical – Page 3,089
AgeMeter: Physiological Biomarkers to Determine Functional Age
Today Lifespan.io / Life Extension Advocacy Foundation has launched the fifth research project since we began 1.5 years ago. We are working with the Centers for Age Control Inc who plan to develop a multiple aging biomarker system to aid clinical research, healthcare providers and enthusiasts.
For more details check out the press release here: http://www.leafscience.org/introducing-agemeter/
Developing a diagnostic system to measure human functional age in comparison to chronological age, and assist in the assessment of anti-aging therapeutics.

Altering Microglia Types to Combat Degenerative Eye Diseases
Tweaking the types of microglia to favour a healing type over an inflammatory type has been the focus of a number of recent studies. This time the tremedous regenerative ability of zebrafish is the focus of research.
The evidence that the immune system, and in particular the various types of tissue resident macrophages play an important role in the regeneration of tissue continues to mount up.
The difference in the behaviour of these macrophages varies between species and may significantly contribute to the differences in regenerative capacity observed between slow regenerative species like mice and humans and species capable of robust rejuvenation such as salamanders and zebrafish. The latter two species being able to regenerate lost limbs and organs and the former two being far more limited.
There has been considerable interest recently in adjusting macrophage populations and types in order to encourage healing which we have talked about in articles here, here and here. Today we are going to have a look at some related research again dealing with altering types of tissue resident macrophages.
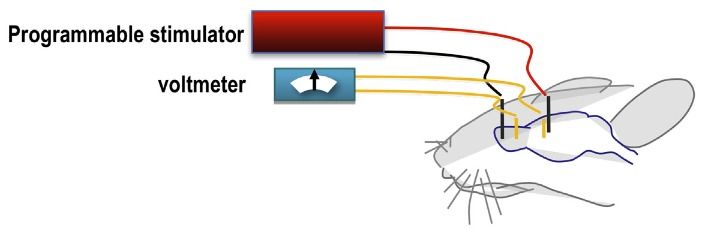
Neural stem cells steered by electric fields can repair brain damage
Electric fields can be used to guide transplanted human neural stem cells — cells that can develop into various brain tissues — to repair brain damage in specific areas of the brain, scientists at the University of California, Davis have discovered.
It’s well known that electric fields can locally guide wound healing. Damaged tissues generate weak electric fields, and research by UC Davis Professor Min Zhao at the School of Medicine’s Institute for Regenerative Cures has previously shown how these electric fields can attract cells into wounds to heal them.
A New Technique Transforms Human Skin Into Brain Cells
“Microglia play an important role in Alzheimer’s and other diseases of the central nervous system. Recent research has revealed that newly discovered Alzheimer’s-risk genes influence microglia behavior,” Jones said in an interview for a UCI press release. “Using these cells, we can understand the biology of these genes and test potential new therapies.”
A Renewable Method
The skin cells had been donated by patients from UCI’s Alzheimer’s Disease Research Center. These were first subjected to a genetic process to convert them into induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells — adult cells modified to behave as an embryonic stem cell, allowing them to become other kinds of cells. These iPS cells were then exposed to differentiation factors designed to imitate the environment of developing microglia, which transformed them into the brain cells.
How Scientists Are Bringing People Back From The Dead
One afternoon in February 2011, Kelly Dwyer strapped on a pair of snowshoes and set out to hike a beaver pond trail near her home in Hooksett, New Hampshire. When the sun dropped below the horizon hours later, the 46-year-old environmental educator still hadn’t returned home. Her husband, David, was worried. Grabbing his cellphone and a flashlight, he told their two daughters he was going to look for Mom. As he made his way toward the pond, sweeping his flashlight beam across the darkening winter landscape, he called out for Kelly. That’s when he heard the moans.
Running toward them, David phoned their daughter Laura, 14, and told her to call 911. His flashlight beam soon settled on Kelly, submerged up to her neck in a hole of dark water in the ice. As David clutched her from behind to keep her head above water, Kelly slumped into unconsciousness. By the time rescue crews arrived, her body temperature was in the 60s and her pulse was almost too faint to register. Before she could reach the ambulance, Kelly’s heart stopped. The EMTs attempted CPR—a process doctors continued for three hours at a hospital in nearby Manchester. They warmed her frigid body. Nothing. Even defibrillation wouldn’t restart her heart. Kelly’s core temperature hovered in the 70s. David assumed he’d lost her for good.
Lab-grown capillaries are here, 3D-printed organs are just around the corner
Scientists have demonstrated a method for growing capillaries, the tiny vessels responsible for transporting blood around the body.
Epigenetics between the generations: Researchers prove that we inherit more than just genes
We are more than the sum of our genes. Epigenetic mechanisms modulated by environmental cues such as diet, disease or lifestyle take a major role in regulating the DNA by switching genes on and off. It has been long debated if epigenetic modifications accumulated throughout the entire life can cross the border of generations and be inherited to children or even grand children. Now researchers from the Max Planck Institute of Immunobiology and Epigenetics in Freiburg show robust evidence that not only the inherited DNA itself but also the inherited epigenetic instructions contribute in regulating gene expression in the offspring. Moreover, the new insights by the Lab of Nicola Iovino describe for the first time biological consequences of this inherited information. The study proves that mother’s epigenetic memory is essential for the development and survival of the new generation.
Humans have than 250 different cell types. They all contain the exact same DNA bases in exactly the same order; however, liver or nerve cells look very different and have different skills. What makes the difference is a process called epigenetics. Epigenetic modifications label specific regions of the DNA to attract or keep away proteins that activate genes. Thus, these modifications create, step by step, the typical patterns of active and inactive DNA sequences for each cell type. Moreover, contrary to the fixed sequence of ‘letters’ in DNA, epigenetic marks can also change throughout life and in responses to environment or lifestyle. For example, smoking changes the epigenetic makeup of lung cells, eventually leading to cancer. Other influences of external stimuli like stress, disease or diet are also supposed to be stored in the epigenetic memory of cells.
It has long been thought that these epigenetic modifications never cross the border of generations. Scientists assumed that epigenetic memory accumulated throughout life is entirely cleared during the development of sperms and egg cells. Just recently a handful of studies stirred the scientific community by showing that epigenetic marks indeed can be transmitted over generations, but exactly how, and what effects these genetic modifications have in the offspring is not yet understood. “We saw indications of intergenerational inheritance of epigenetic information since the rise of the epigenetics in the early nineties. For instance, epidemiological studies revealed a striking correlation between the food supply of grandfathers and an increased risk of diabetes and cardiovascular disease in their grandchildren.
How to hack your gut to ward off Parkinson’s and obesity
The wonder of your gut: Experts explain why a healthy digestive system can trigger weight loss, fight depression, and ward off Parkinson’s.
- Jasenka Zubcevic works in Physiological Sciences, and Christopher Martynuik in Toxicology at the University of Florida
- They have been investigating how gut bacteria affect all other body parts
- Here they explain everything we know thus far about the gut
By Jasenka Zubcevic and Christopher Martynuik For The Conversation