This incredible 3D printer can create living human tissue.
Category: biotech/medical – Page 2,947

The Fourth Industrial Revolution is Here!
So much talk about AI and robots taking our jobs. Well, guess what, it’s already happening and the rate of change will only increase. I estimate that about 5% of jobs have been automated — both blue collar manufacturing jobs, as well as, this time, low-level white collar jobs — think back office, paralegals, etc. There’s a thing called RPA, or Robot Process Automation, which is hollowing out back office jobs at an alarming rate, using rules based algorithms and expert systems. This will rapidly change with the introduction of deep learning algorithms into these “robot automation” systems, making them intelligent, capable of making intuitive decisions and therefore replacing more highly skilled and creative jobs. So if we’re on an exponential curve, and we’ve managed to automate around 5% of jobs in the past six years, say, and the doubling is every two years, that means by 2030, almost all jobs will be automated. Remember, the exponential math means 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 100%, with the doubling every two years.
We are definitely going to need a basic income to prevent people (doctors, lawyers, drivers, teachers, scientists, manufacturers, craftsmen) from going homeless once their jobs are automated away. This will need to be worked out at the government level — the sooner the better, because exponentials have a habit of creeping up on people and then surprising society with the intensity and rapidity of the disruptive change they bring. I’m confident that humanity can and will rise to the challenges ahead, and it is well to remember that economics is driven by technology, not the other way around. Education, as usual, is definitely the key to meeting these challenges head on and in a fully informed way. My only concern is when governments will actually start taking this situation seriously enough to start taking bold action. There certainly is no time like the present.
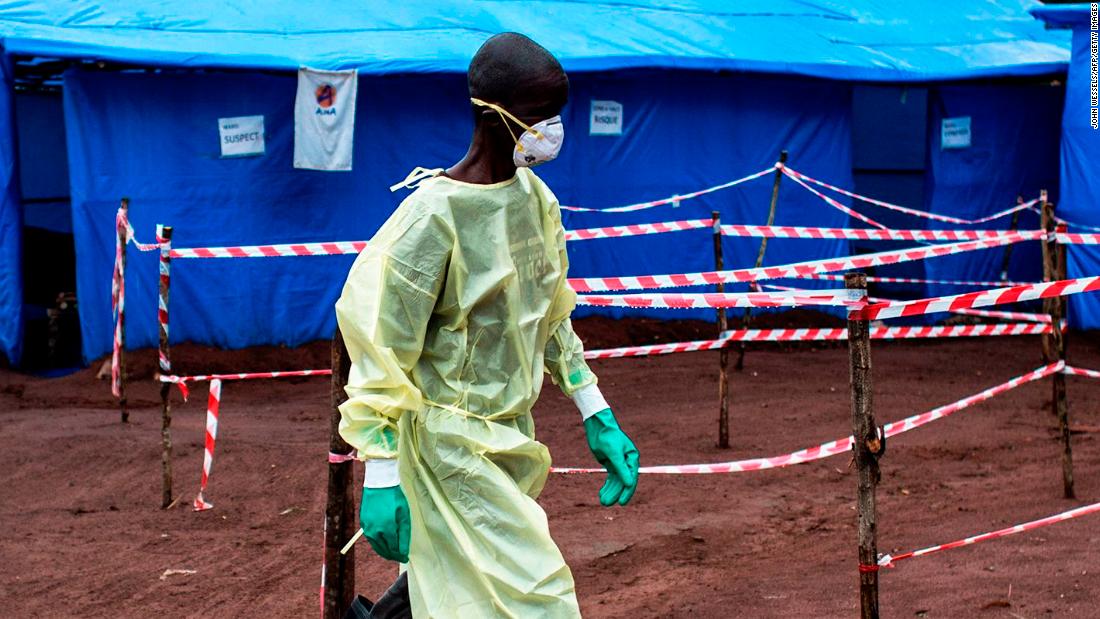
Ebola outbreak declared in Democratic Republic of Congo
The government of the Democratic Republic of Congo declared an outbreak of Ebola hemorrhagic fever, a rare and deadly disease, on Tuesday, the World Health Organization reported. The declaration came after laboratory results confirmed two cases of the disease in the province of Bikoro in the northwestern part of the country.
Ebola virus disease, which most commonly affects people and nonhuman primates (monkeys, gorillas and chimpanzees), is caused by one of five Ebola viruses. The virus is transmitted to people from wild animals and spreads in the human population through human-to-human transmission. The average case fatality rate is around 50%.
A government statement released Tuesday states that the Ministry of Health has “taken all necessary measures to respond promptly and effectively to this new epidemic of Ebola in the DRC’s national territory”.


UCSD Scientists Using Genome Editing Technology to Cure Genetic Diseases
Crispr could eliminate Genetic disease.
It’s so small it can’t be seen with the naked eye, but research is showing that CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats) is bringing sight to the blind.
UC San Diego researchers are using CRISPR, a technology that allows scientists to edit genomes, to cure disease.
For the last two years, Ophthalmologist Dr. Kang Zhang and UC San Diego researchers have been working with CRISPR, injecting CRISPR into the eyes of mice to cure retinitis pigmentosa – a genetic form of blindness. “What we’ve seen in mice is that we can bring back actually 30 percent of vision sometimes even 50 percent of vision,” Dr. Zhang told NBC 7.

Recoding Human Cells to Make them Virus Proof
On May 1, around 200 scientists from the Genome Project-write (GP-write) met in Boston and announced the first target of their project: the creation of cells that cannot be infected by viruses.
What is the Genome Project-write?
GP-write includes sub-projects like the Human Genome Project-write (HGP-write), which was formally announced on June 2, 2016, and is an extension of the Genome Projects, which were launched in 1984. These projects were created to develop ways to read DNA in microbes, plants and multiple animal species, including humans.
DARPA Wants to Jolt the Nervous System with Electricity, Lasers, Sound Waves, and Magnets
Viewing the body as a chemical system and treating maladies with pharmaceuticals is so 20th century. In 21st century medicine, doctors may consider the body as an electrical system instead, and prescribe therapies that alter the electrical pulses that run through the nerves.
The defense agency announces funding for 7 projects under its new ElectRx program.

How cholesterol in the brain may accelerate the onset of Alzheimer’s disease
A landmark study has revealed that cholesterol in the brain may play a fundamental role in catalyzing the formation of amyloid beta clusters, thought to be a central mechanism leading to the devastating degenerative symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease.
An international team of researchers, led by the University of Cambridge, set out to uncover what causes amyloid beta proteins to cluster into the plaques that slowly accumulate and cause the primary degenerative symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease.
“The levels of amyloid-beta normally found in the brain are about a thousand times lower than we require to observe it aggregating in the laboratory – so what happens in the brain to make it aggregate?” asks Michele Vendruscolo, lead on the new research.
