The ability to analyze gene expression at the single-cell level—known as single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq)—has transformed life sciences, driving discoveries across immunology, oncology, and developmental biology. Over 40,000 studies have leveraged this technique to map the complex diversity of cells within tissues and organisms.
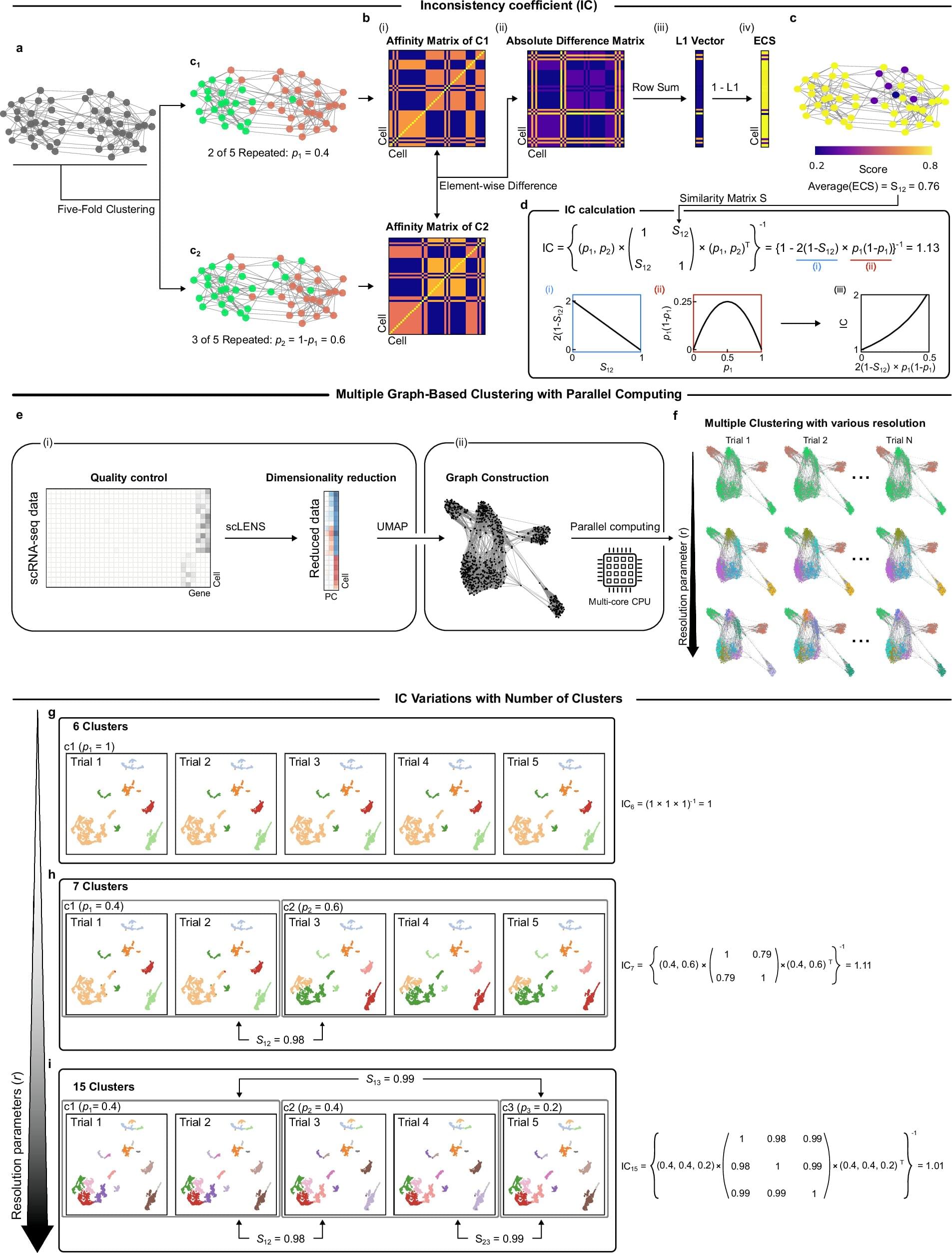
Yet beneath this explosive growth lies a persistent problem: clustering instability. When researchers attempt to group cells by expression patterns to identify cell types or disease states, they often face inconsistent results—even when analyzing the same dataset repeatedly.
Inaccurate clustering can lead to misclassifying normal cells as cancerous or missing rare but critical cell types—jeopardizing interpretation and therapeutic decisions. This “reliability crisis” forces scientists to rerun analyses or rely on computationally expensive pipelines to extract trustworthy insights.