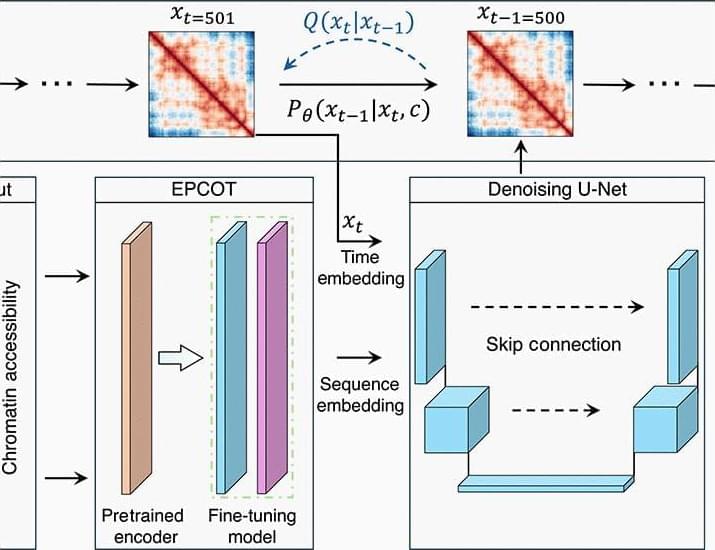
An interesting paper where Schuette et al. develop a generative diffusion-based AI model for predicting the 3D structure of chromatin. Their model takes chromatin accessibility sequence data as input and outputs a statistical distribution of predicted 3D chromatin structures. Remarkably, their model generalizes across cell types, making it broadly useful! #computationalbiology #ai #generativeai
Computational approaches for predicting chromatin conformations de novo using only sequencing data remain scarce. Compared to existing polymer simulation–based prediction approaches, ChromoGen maintains unique advantages. The generative nature of ChromoGen enables efficient production of statistically independent samples, thus avoiding the inefficient navigation of state space that polymer simulations require to produce a diverse set of conformations. Moreover, ChromoGen’s transformer-based front end provides additional advantages, extracting features from sequencing data and placing the information in low-dimensional embeddings that the diffusion model handles efficiently. This powerful design markedly reduces the computational cost of each diffusion step, providing a practical means to achieve cell type–specific de novo predictions with the full benefit of DNA sequence and chromatin accessibility data. In contrast, incorporating DNA sequence information into polymer models has long been a challenging task that is often indirectly addressed by incorporating various histone marks.
In its current form, ChromoGen can be immediately applied to any cell type with available DNAse-seq data, enabling a vast number of studies into the heterogeneity of genome organization both within and between cell types to proceed. However, several improvements could enhance its utility. Notably, the current model exclusively predicts chromatin conformations in 1.28-Mb regions at 20-kb resolution, the latter restriction primarily stemming from our decision to maximize resolution within the constraints imposed by the available Dip-C data. However, higher-resolution single-cell datasets are becoming available, such as those at 5-kb resolution (50), and we anticipate that ChromoGen will require no modifications to perform well after training on these improved datasets. Similarly, we anticipate that ChromoGen can be directly applied to longer genomic regions if using a lower resolution, e.g.