During 2014’s Ebola outbreak, there were no treatments on hand to fight the virus. Now, researchers have found a human protein that could change that.


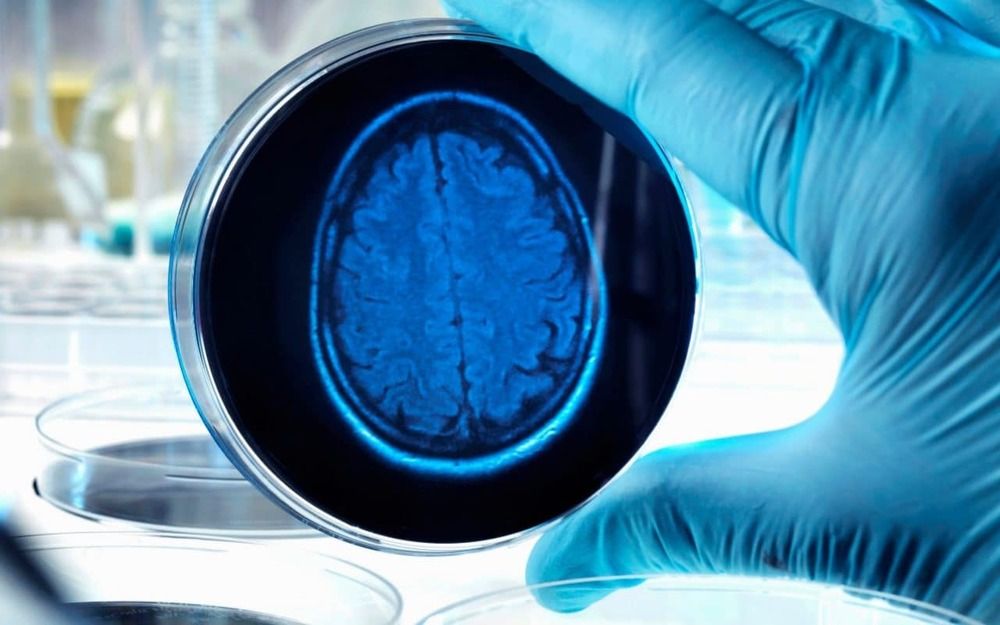
An injection capable of halting the progress of Alzheimer’s could be available to patients within a decade, Britain’s leading dementia organisation predicts.
The Alzheimer’s Society says a series of recent breakthroughs in treatments that disrupt harmful genes has brought scientists to a “tipping point” in their fight against the disease.
For decades, researchers have sought without success a treatment for Alzheimer’s based on targeting damaging proteins that build up in the brain.
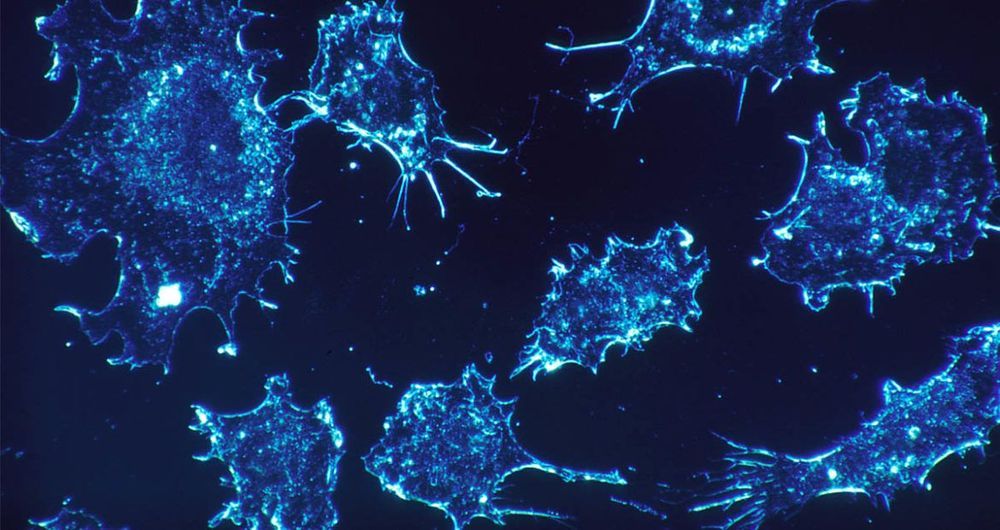
A quick and easy test devised by scientists from the University of Queensland could transform cancer diagnosis as we know it.
Cancer is a difficult disease to diagnose because different types are characterised by different signatures. Until now, scientists have been unable to find a unique signature common to all forms of cancer that would set it apart from healthy cells.
That’s what University of Queensland researchers Dr Laura Carrascosa, Dr Abu Sina and Professor Matt Trau have addressed. They have discovered a unique DNA nanostructure that seems to be common to all types of cancer and is visible when cancer cells are placed in water.


In 1961, Nancy Grace Roman was already the first Chief of Astronomy in NASA’s Office of Space Science. She developed that program in a time before the second wave of the Women’s Movement in the United States began, when banks often refused women credit in their own names and there was still an active medical debate about whether women could ever physically endure spaceflight someday. But Roman opened the skies to humanity in new ways without ever leaving the ground.
She earned her Ph.D. in astronomy at the University of Chicago in 1949 and worked at the Yerkes Observatory there for six years afterward. She joined the radio astronomy group at the Naval Research Laboratory, becoming the head of the microwave spectroscopy section. As she recalled in 1980 in an oral history interview with National Air and Space Museum curator David DeVorkin, when she heard that NASA might set up a space astronomy program, she wanted to lead it: “The idea of coming in with an absolutely clean slate to set up a program that I thought was likely to influence astronomy for 50 years was just a challenge that I couldn’t turn down. That’s all there is to it.” She joined NASA in 1959, just after the agency’s founding.
Roman opened the skies to humanity in new ways without ever leaving the ground.
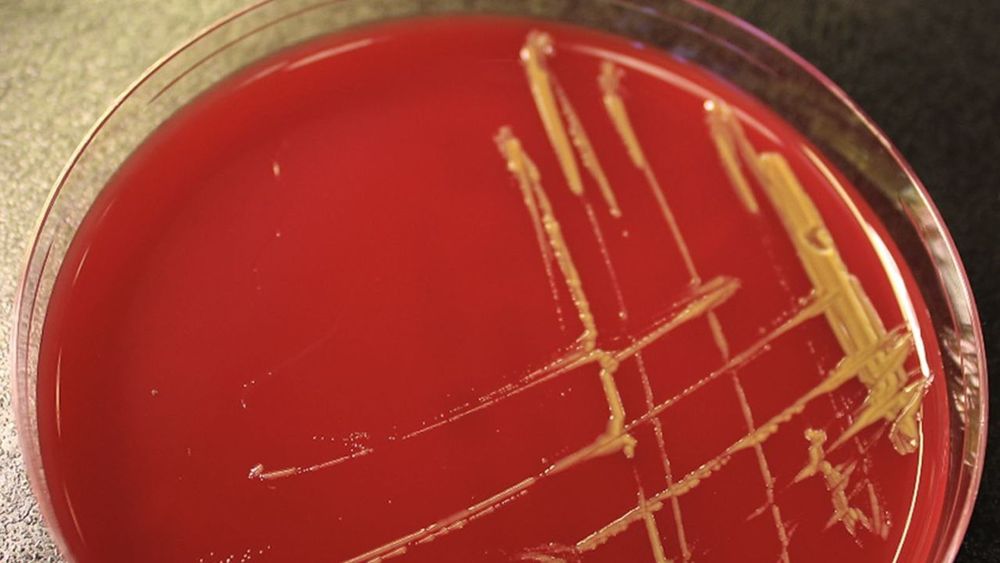
In 2016, a mysterious illness spread inside the National Institutes of Health’s Clinical Center, the U.S. government’s most prominent research hospital, in Bethesda, Maryland. Patients were somehow being sickened by an antibiotic-resistant strain of bacteria that practically never causes disease in humans. Two years later, a new study seems to finally have confirmed where this bug likely came from: the hospital’s own plumbing.
During a six-month period in 2016, six patients came down with infections caused by Sphingomonas bacteria. Four of the patients had an antibiotic-resistant strain of a particular species, Sphingomonas koreensis, which was first discovered in some of Korea’s natural mineral water spots in the early 2000s.


WASHINGTON (AP) — Most Americans say it would be OK to use gene-editing technology to create babies protected against a variety of diseases — but a new poll shows they’d draw the line at changing DNA so children are born smarter, faster or taller.
A month after startling claims of the births of the world’s first gene-edited babies in China, the poll by The Associated Press-NORC Center for Public Affairs Research finds people are torn between the medical promise of a technology powerful enough to alter human heredity and concerns over whether it will be used ethically.
Jaron Keener, a 31-year-old exhibit designer at Pittsburgh’s Carnegie Museum of Natural History, said he’s opposed to “rich people being able to create designer babies.”
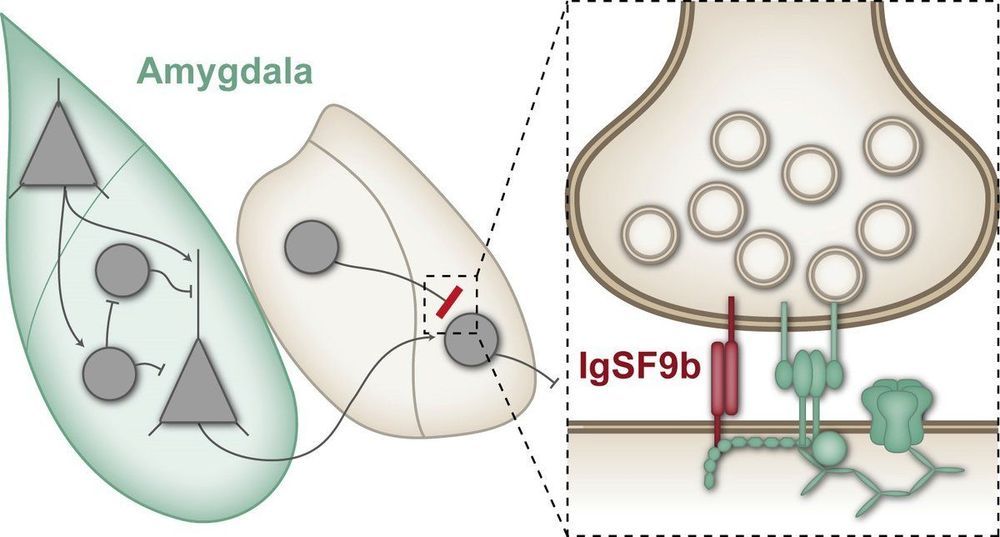
Anxiety disorders are severe mental disorders in which patients suffer from intense fears and anxiety or from sudden, inexplicable panic attacks. In extreme cases, the affected individuals barely leave their homes, which can have serious consequences for their relationships with family and friends as well as for their professional lives. Scientists at the Max Planck Institute for Experimental Medicine in Göttingen have now identified a synaptic protein which, when inactivated, has an anxiolytic effect in mice.
Around 10 percent of the population suffer from anxiety disorders, and current treatment options only offer effective help for a proportion of those affected. One of the changes observed in the brains of patients with anxiety disorders is an increased neuronal activity in the amygdala, a brain region that plays a key role in processing emotions such as anxiety or fear. An overactivation of the amygdala is thought to be involved in causing exaggerated anxiety. Many anxiolytic medications such as benzodiazepines presumably normalize this overactivation by strengthening the function of inhibitory synapses.
Synapses are connections between nerve cells in the brain, at which information is transmitted from one nerve cell to another. At inhibitory synapses, this transmission results in a reduction in the activity of the neighbouring nerve cells. In the amygdala, for instance, this inhibits the transmission of stimuli that trigger fear and anxiety. Benzodiazepines strengthen this inhibitory effect—but unfortunately they affect not only those inhibitory synapses that transmit anxiogenic stimuli but also many other inhibitory synapses in the brain. This can lead to significant side effects such as pronounced sedation and impaired concentration. Accordingly, scientists are searching for new, more specific targets for anxiolytic medications.

The next step for our Forever Healthy Berlin meetup…
We are a community collaborating on how to implement our early stage rejuvenation treatments.
The world has started the transition from an era where we were utterly helpless about our aging process to one where aging is under full medical control, and age-related diseases are a thing of the dark past.
We are not there yet, but the theoretical groundwork has been laid out, and scientists have successfully started working on the fundamentals. The first human rejuvenation therapies are under development and with Senolytics, NAD+ Restoration, Lipid Replacement, Decalcification, mTOR Modulation, Geroprotectors, and others some of those therapies are already available to the early adopters today.