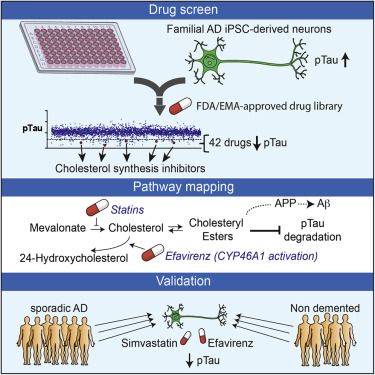
Genetic, epidemiologic, and biochemical evidence suggests that predisposition to Alzheimer’s disease (AD) may arise from altered cholesterol metabolism, although the molecular pathways that may link cholesterol to AD phenotypes are only partially understood. Here, we perform a phenotypic screen for pTau accumulation in AD-patient iPSC-derived neurons and identify cholesteryl esters (CE), the storage product of excess cholesterol, as upstream regulators of Tau early during AD development. Using isogenic induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) lines carrying mutations in the cholesterol-binding domain of APP or APP null alleles, we found that while CE also regulate Aβ secretion, the effects of CE on Tau and Aβ are mediated independent pathways. Efficacy and toxicity screening in iPSC- derived astrocytes and neurons showed that allosteric activation of CYP46A1 lowers CE specifically in neurons and is well tolerated by astrocytes. These data reveal that CE independently regulate Tau and Aβ and identify a druggable CYP46A1-CE-Tau axis in AD.
Van der Kant et al. performed a repurposing drug screen in iPSC-derived AD neurons and identified compounds that reduce aberrant accumulation of phosphorylated Tau (pTau). Reduction of cholesteryl ester levels or allosteric activation of CYP46A1 by lead compounds enhanced pTau degradation independently of APP and Aβ.