Las células cancerígenas habían formado en el pulmón del paciente un minisistema digestivo con estómago, duodeno e intestino.


Announces the publication of a new open-access quarterly report: AI for Drug Discovery, Biomarker Development and Advanced R&D Landscape Overview 2019/Q1. Except for providing the analysis of 350 investors, 50 corporations and 150 companies operating in the field, the main events that took place in the industry from January to March 2019 are covered. The report also features the list of 30 leading R&D centers that provide important researches in the segment.
Link to the Report: https://www.ai-pharma.dka.global/quarter-1-2019
#AI #artificialintelligence #drugdiscovery
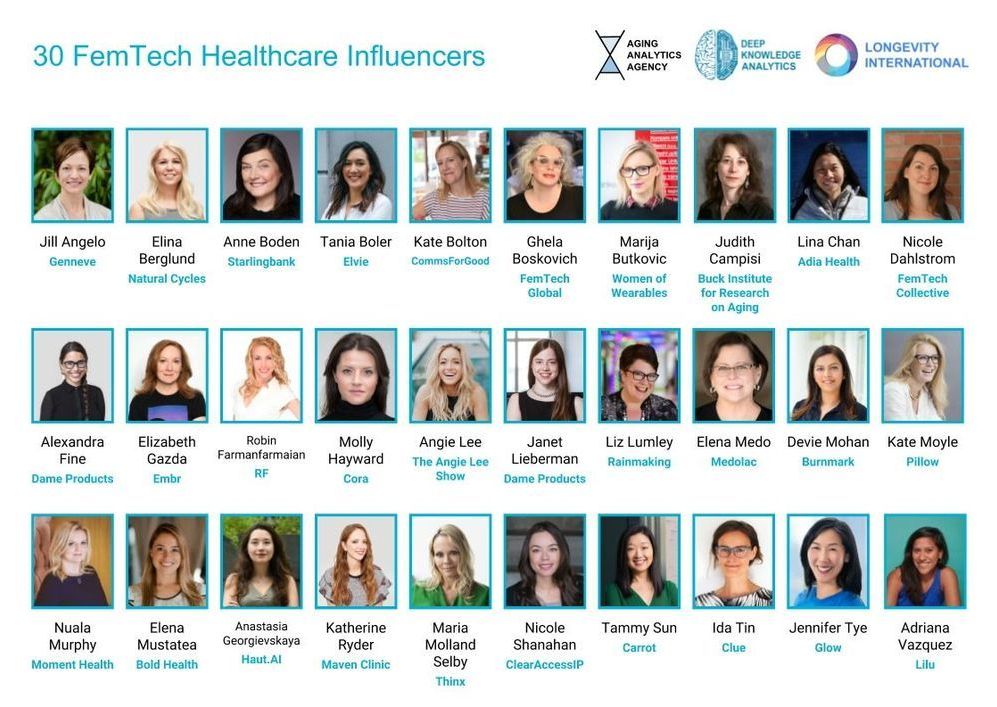
Presents its list of the top 30 FemTech Influencers, whose efforts in the FemTech Healthcare, FemTech Preventive Medicine and FemTech Longevity sectors have helped to grow the industry to its current state of maturity.
Jill Angelo genneve Elina Berglund Natural Cycles Starling Bank Tania Boler Elvie Ghela Boskovich Judith Campisi Adia Femtech Collective Dame Products EMBR Robin Starbuck Farmanfarmaian Cora Lifestyle Angie Lee Janet Lieberman Nuala Murphy Moment.Health Elena Mustatea Bold Health Anastasia Georgievskaya Haut.AI Maven Clinic THINX Nicole Shanahan Clearaccessip, Inc. Tammy Sun Ida Tin
Link to the Report: https://www.aginganalytics.com/femtech-healthcare-q1-2019
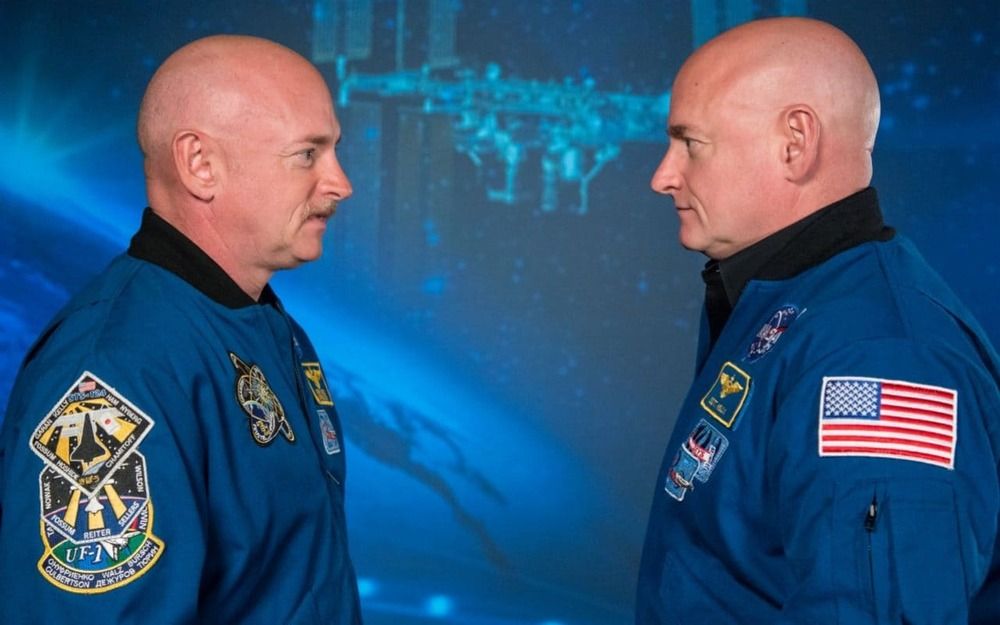

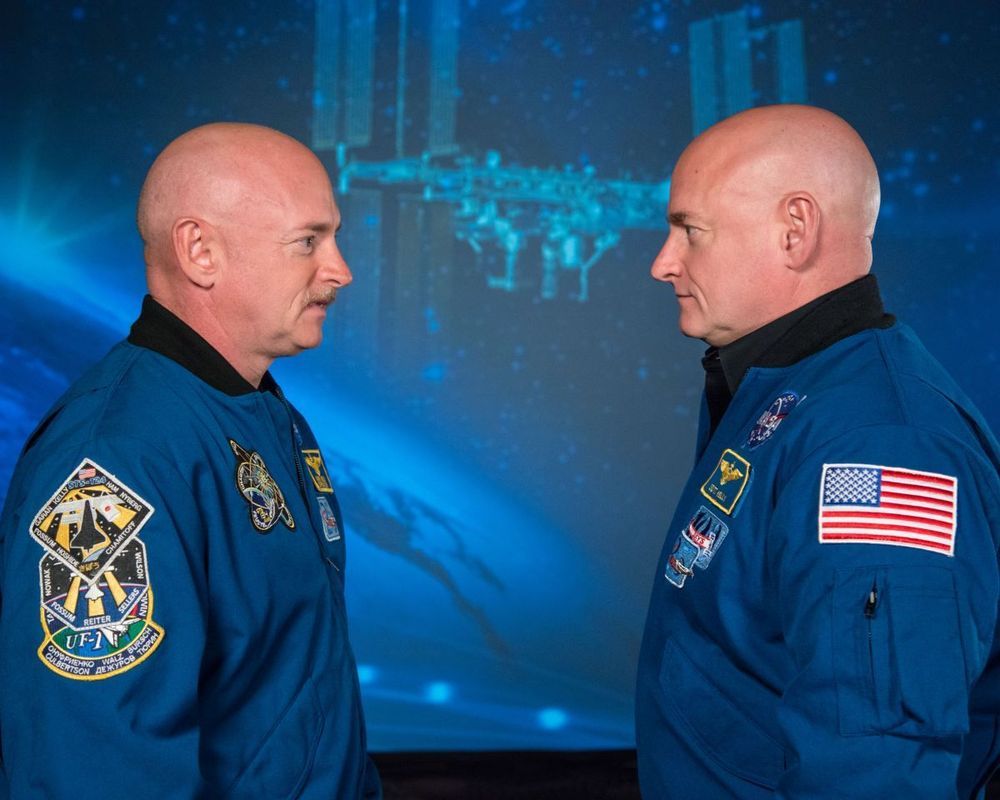
When NASA set out to study identical twin astronauts, leaving one on Earth and sending the other to the International Space Station (ISS) for a year, they expected that the rigours of microgravity would have largely negative impacts.
But on board the ISS, Scott Kelly, 51, underwent a very strange transformation which has left scientists scratching their heads.
The telomeres in his white blood cells got longer. Telomeres are the protective caps which sit at the end of chromosomes, protecting the DNA inside, like the plastic aglets on the end of shoelaces.

As a genetic material, DNA is responsible for all known life. But DNA is also a polymer. Tapping into the unique nature of the molecule, Cornell engineers have created simple machines constructed of biomaterials with properties of living things.
Using what they call DASH (DNA-based Assembly and Synthesis of Hierarchical) materials, Cornell engineers constructed a DNA material with capabilities of metabolism, in addition to self-assembly and organization – three key traits of life.
“We are introducing a brand-new, lifelike material concept powered by its very own artificial metabolism. We are not making something that’s alive, but we are creating materials that are much more lifelike than have ever been seen before,” said Dan Luo, professor of biological and environmental engineering in the College of Agriculture and Life Sciences.

If you happen to be thirsty in the woods, there are a lot of things you can stick in your canteen to help clean up your drinking water. There are chlorine pills and filters (not crystals — never crystals). And now scientists have identified a certain kind of moss that could do it, too.
The moss is called Warnstorfia fluitans. It grows in Swedish wetlands contaminated with the toxic arsenic from nearby mining operations. Researchers found that the moss brought the arsenic levels of water down to drinkable levels surprisingly quickly, according to research published in the journal Environmental Pollution.
In northern Sweden, iron mines have contaminated much of the water with arsenic, a metal that is also toxic to humans. That harmful combination works its way into agricultural products like rice, traveling throughout the food web.

At Undoing Aging 2019, we interviewed some of the best researchers who are involved in discovering therapies for the root causes of aging. Their research aims to ameliorate the damages of aging and may one day lead to a future without the diseases of aging.
We were glad to have the opportunity to conduct a joint interview with Dr. Kelsey Moody and Dr. Huda Suliman. They offered several keen insights on the future of Ichor Therapeutics and the nature of the rejuvenation biotechnology industry.
K: I’m Dr. Kelsey Moody. I’m the Chief Executive Officer of Ichor Therapeutics and its portfolio of companies. Ichor itself is a biopharmaceutical company that does drug discovery in the aging space, and we have a variety of portfolio companies, each of which is designed to target a different type of age-associated damage. Through these companies, we’re developing classes of different drugs to move into the clinic for conventional therapeutic applications as well as, hopefully, more anti-aging targeted therapies as well.