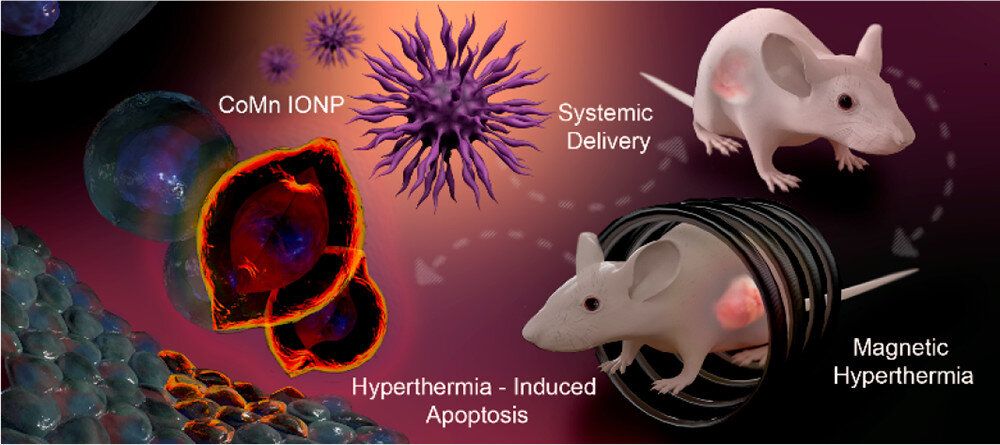
Researchers at Oregon State University have developed an improved technique for using magnetic nanoclusters to kill hard-to-reach tumors.


There are certain enzymes — proteins — plaques that help cause Alzheimer’s, just recently in fact {which I as most could have told them} the gut microbes and mouth microbes are found to assist in Dementia and Alzheimers. But I and Hippocrates as others have been declaring that fact for quite some time… Respect AEWR wherein the amazing gathered data of mankind has yielded the many causes and a cure for aging…
For decades, research into Alzheimer’s has made slow progress, but now a mother and daughter team think they have finally found a solution – a vaccine that could inoculate potential sufferers.
In one of the biggest breakthroughs in recent history, scientists have created a synthetic genome that can self-replicate. So what does this mean? Are we about to become gray goo?
Led by Craig Venter of the J. Craig Venter Institute (JCVI), the team of scientists combined two existing techniques to transplant synthetic DNA into a bacteria. First they chemically synthesized a bacterial genome, then they used well-known nuclear transfer techniques (used in IVF) to transplant the genome into a bacteria. And apparently the bacteria replicated itself, too, thus creating a second generation of the synthetic DNA. The process is being hailed as revolutionary.
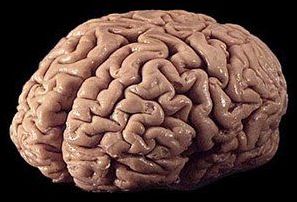
Sydney — Post-mortem examinations have found a degenerative brain disease linked to repeated blows to the head in two elite Australian rugby league players, the first cases found in the sport, researchers said on Thursday.
The researchers said the players both had chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE), which has been widely diagnosed among former US National Football League (NFL) players but is little studied elsewhere.
The Sydney-based study said the condition, once known as ‘punch drunk syndrome’ occurred when repeated brain trauma led to a long-term decline in cognitive function.


Nano Lett. 2017 Sep 13;17:5836–5842. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.7b03081. Epub 2017 Aug 14.
Syringe-injectable mesh electronics represent a new paradigm for brain science and neural prosthetics by virtue of the stable seamless integration of the electronics with neural tissues, a consequence of the macroporous mesh electronics structure with all size features similar to or less than individual neurons and tissue-like flexibility. These same properties, however, make input/output (I/O) connection to measurement electronics challenging, and work to-date has required methods that could be difficult to implement by the life sciences community. Here we present a new syringe-injectable mesh electronics design with plug-and-play I/O interfacing that is rapid, scalable, and user-friendly to nonexperts. The basic design tapers the ultraflexible mesh electronics to a narrow stem that routes all of the device/electrode interconnects to I/O pads that are inserted into a standard zero insertion force (ZIF) connector.
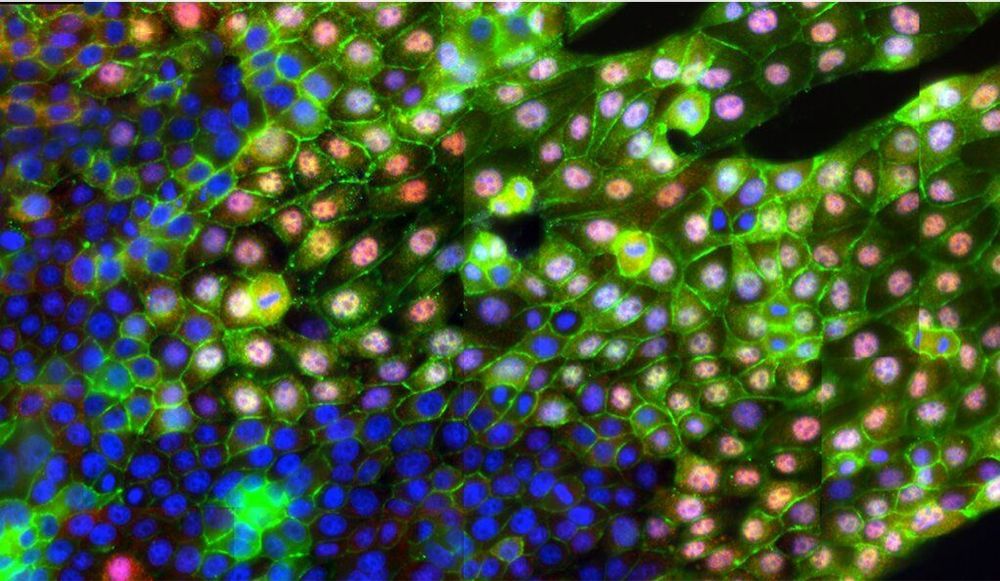
Yale researchers have discovered how metastasis, the spread of cancer cells throughout the body, is triggered on the molecular level, and have developed a tool with the potential to detect those triggers in patients with certain cancers. The discovery could lead to new ways for treating cancer.
The study was led by Andre Levchenko, the John C. Malone Professor of Biomedical Engineering and director of the Yale Systems Biology Institute at Yale’s West Campus. It was published June 26 in the journal Nature Communications. Levchenko is a member of the Yale Cancer Center.
One way metastasis occurs is through epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), a process that breaks neighboring cells apart from each other and sets them in motion. It’s been long assumed that chemical signals or genetic changes in the cells trigger EMT. But Levchenko’s research team found that it could be caused by a simple change in the texture of the extracellular matrix (ECM), which acts as a scaffold for cells. They discovered that an alignment of the matrix’s fibers (a common biological occurrence) can trigger the EMT process without or other stimuli.
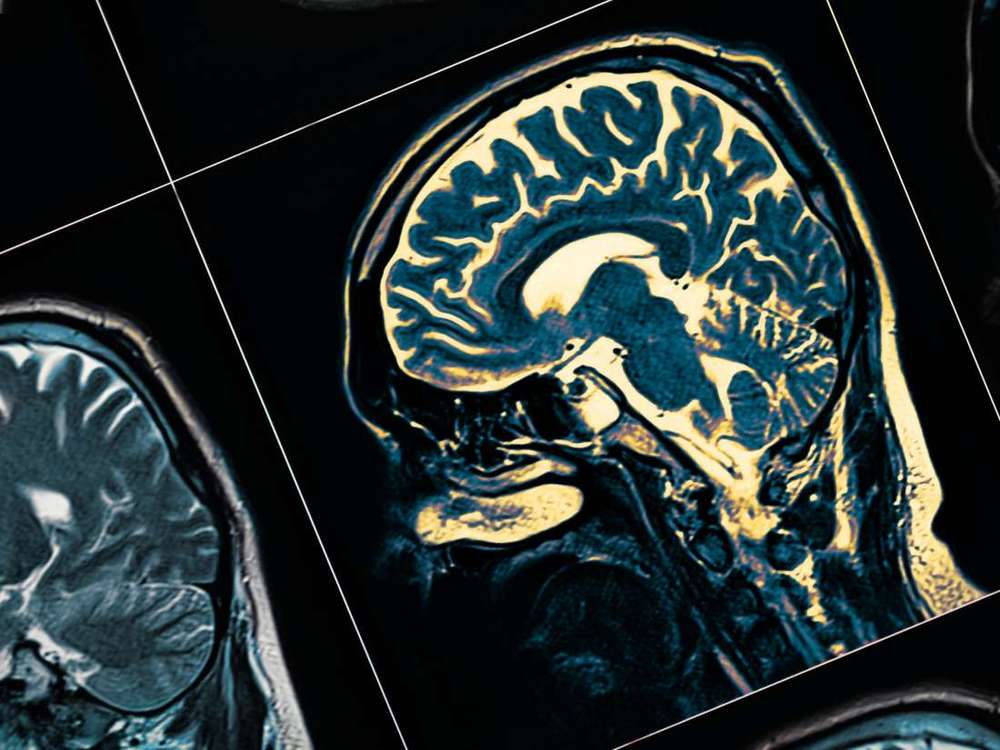
Researchers at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, in Baltimore, MD, conducted their investigation in a new mouse model of Parkinson’s disease.
The new model replicates a number of early and late signs and symptoms of Parkinson’s disease, including some that are not movement-related.