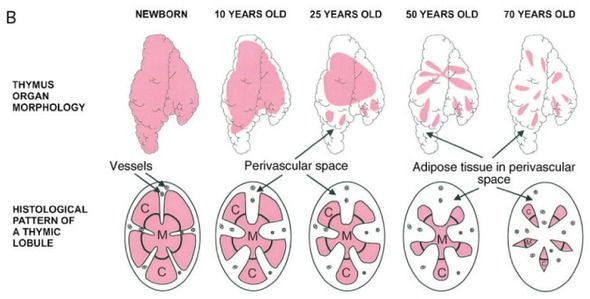
Researchers have designed a machine learning algorithm that predicts the outcome of chemical reactions with much higher accuracy than trained chemists and suggests ways to make complex molecules, removing a significant hurdle in drug discovery.
University of Cambridge researchers have shown that an algorithm can predict the outcomes of complex chemical reactions with over 90% accuracy, outperforming trained chemists. The algorithm also shows chemists how to make target compounds, providing the chemical “map” to the desired destination. The results are reported in two studies in the journals ACS Central Science and Chemical Communications.
A central challenge in drug discovery and materials science is finding ways to make complicated organic molecules by chemically joining together simpler building blocks. The problem is that those building blocks often react in unexpected ways.