A few years ago, researchers discovered that abnormalities in microbial communities, or microbiomes, in the intestine appear to contribute to childhood malnutrition. Now comes word that this discovery is being translated into action, with a new study showing that foods formulated to repair the “gut microbiome” may help malnourished kids rebuild their health [1].
In a month-long clinical trial in Bangladesh, 63 children received either regular foods to treat malnutrition or alternative formulations for needed calories and nutrition that also encouraged growth of beneficial microbes in the intestines. The kids who ate the microbiome-friendly diets showed improvements in their microbiome, which helps to extract and metabolize nutrients in our food to help the body grow. They also had significant improvements in key blood proteins associated with bone growth, brain development, immunity, and metabolism; those who ate standard therapeutic food did not experience the same benefit.
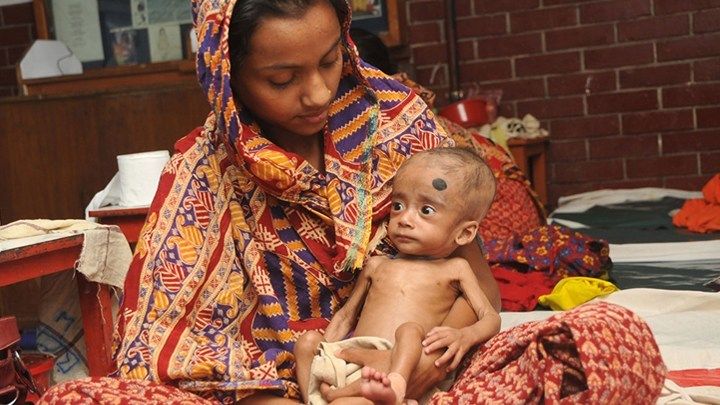
Globally, malnutrition affects an estimated 238 million children under the age 5, stunting their normal growth, compromising their health, and limiting their mental development [2]. Malnutrition can arise not only from a shortage of food but from dietary imbalances that don’t satisfy the body’s need for essential nutrients. Far too often, especially in impoverished areas, the condition can turn extremely severe and deadly. And the long term effects on intellectual development can limit the ability of a country’s citizens to lift themselves out of poverty.