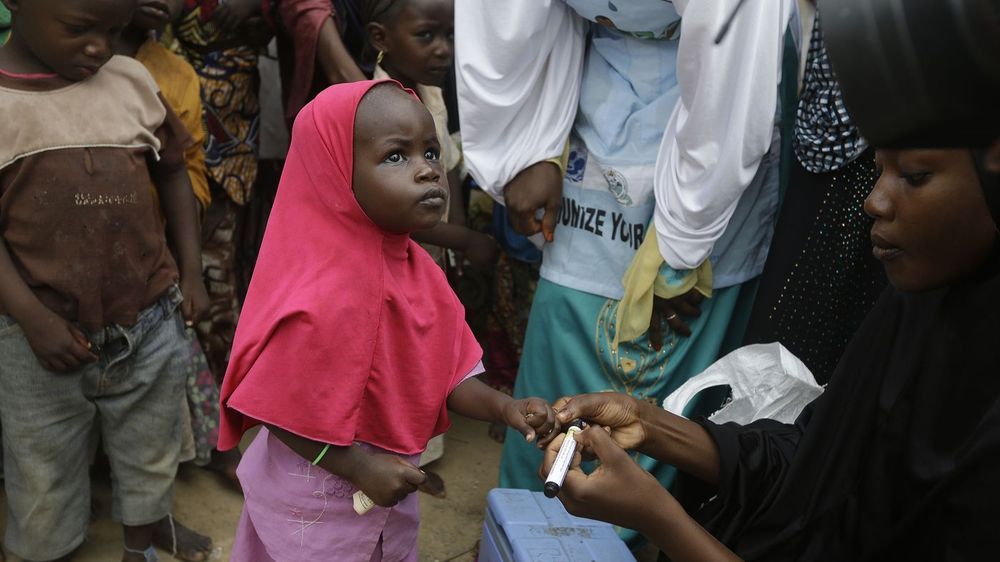
CDC Sends Surge Staffers To Stop Vaccine-Derived Polio Outbreaks In Africa : Goats and Soda Health officials have long known that virus from the oral vaccine can contaminate water supplies; they underestimated how big a problem this would be.


While the transhumanism movement is making progress, it isn’t without its skeptics. Some don’t think it will ever work the way we want it to, because it asks science to turn back a natural process of aging that has an uncountable number of manifestations. Critics of anti-aging research envision any number of dystopian futures, in which we defeat many of the causes of death before very old age, leaving only the most ghastly and intractable — but not directly lethal — maladies.
Lest you think this concept is limited to snake-oil salesmen and science-fiction writers, the idea that aging is not inevitable is now in the mainstream of modern medical research at major institutions around the world. The journal Nature dubbed research from the University of California at Los Angeles a “hint that the body’s ‘biological age’ can be reversed.” According to reporting by Scientific American on research at the Salk Institute for Biological Studies: “Aging Is Reversible — at Least in Human Cells and Live Mice.”

CRISPR, the revolutionary ability to snip out and alter genes with scissor-like precision, has exploded in popularity over the last few years and is generally seen as the standalone wizard of modern gene-editing. However, it’s not a perfect system, sometimes cutting at the wrong place, not working as intended and leaving scientists scratching their heads. Well, now there’s a new, more exacting upgrade to CRISPR called Prime, with the ability to, in theory, snip out more than 90% of all genetic diseases.
Just what is this new method and how does it work? We turned to IEEE fellow, biomedical researcher and dean of graduate education at Tuft University’s school of engineering Karen Panetta for an explanation.
The large-scale study got it right for 83 percent of participants. Would you take the blood test?
This could be happening to me.
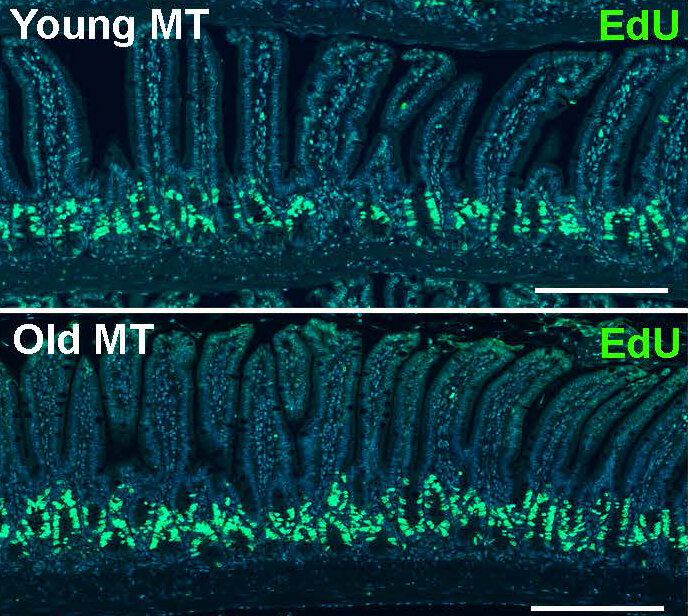
An international research team led by Nanyang Technological University, Singapore (NTU Singapore) has found that microorganisms living in the gut may alter the aging process, which could lead to the development of food-based treatment to slow it down.
All living organisms, including human beings, coexist with a myriad of microbial species living in and on them, and research conducted over the last 20 years has established their important role in nutrition, physiology, metabolism and behavior.
Using mice, the team led by Professor Sven Pettersson from the NTU Lee Kong Chian School of Medicine, transplanted gut microbes from old mice (24 months old) into young, germ-free mice (six weeks old). After eight weeks, the young mice had increased intestinal growth and production of neurons in the brain, known as neurogenesis.
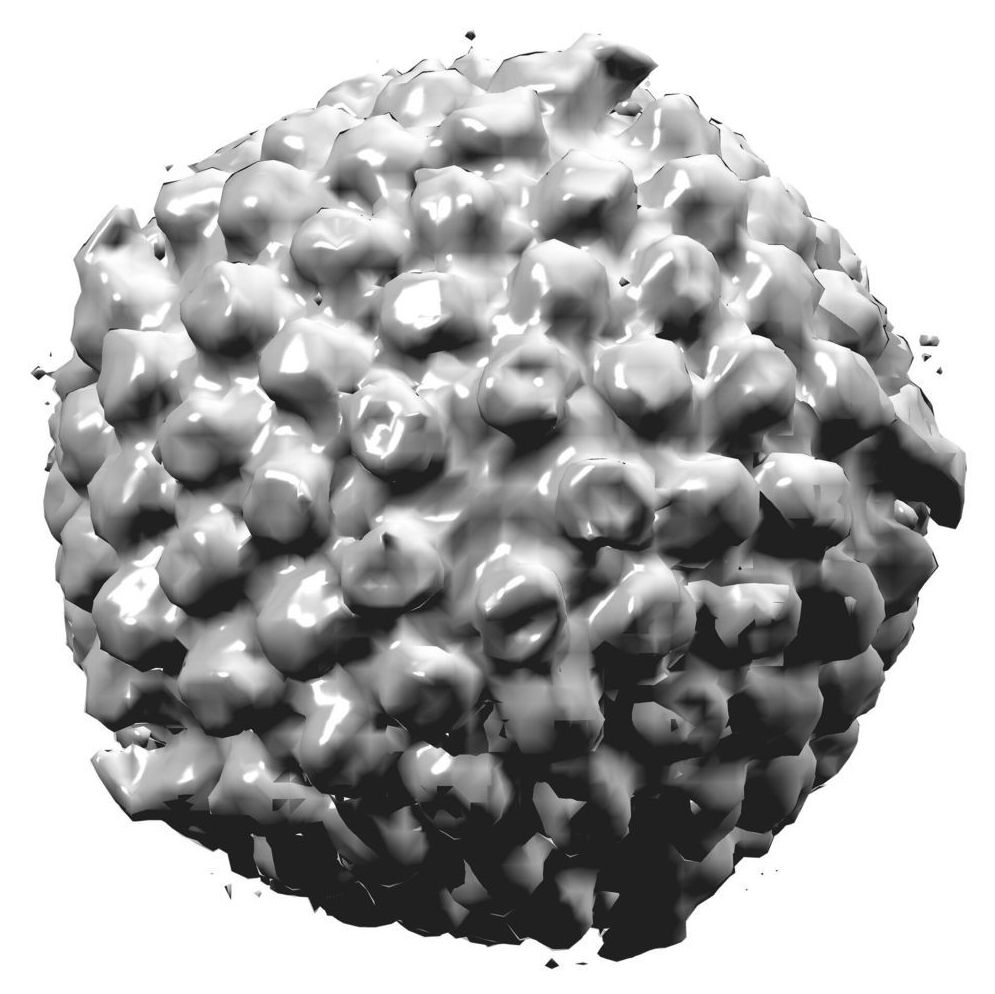
New research from Dr. Luis M. Schang and his group at the Baker Institute for Animal Health has identified a new mechanism that plays a role in controlling how the herpes virus alternates between dormant and active stages of infection.
The herpes virus causes cold sores and genital sores, as well as life-threatening infections in newborns, encephalitis and corneal blindness.
Treatment of the virus is difficult, because it hides out in nerve cells and emerges months or years later to reactivate the infection.
I HAVE not heard of or seen this Debate-video??? I thought poor Doctor Aubrey de Grey had shot with “escape velocity” let us say past debates about the probability-guarantee of ending aging. Vadim has his beliefs and yet his beliefs are wrong. {As I have stated and have posted memes for many years that state “WHO IN SCIENCE IS CORRECT??? THE SCIENTISTS WHO ARE WRONG OR THE SCIENTISTS WHO ARE RIGHT??? De Grey is correct as am I. I am a mere data researcher solutions analyst {Yet very dedicated.} So with my dedication I have taken the data of Mankind and found all causes of aging and I have found a cure sitting in data.}.
Is comprehensive damage repair feasible? A debate at Undoing Aging 2019 between Vadim Gladyshev, Harvard Medical School and Aubrey de Grey, SENS Research Foundation.
Connect with Undoing Aging:
Videos: https://www.undoing-aging.org/videos
News: https://www.undoing-aging.org/news
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/showcase/12631536/admin/

MOUNTAIN VIEW, Calif., Nov. 14, 2019 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) — Underdog Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (Underdog), and SENS Research Foundation (SRF) today announced the launch of Underdog and the completion of its seed round, providing $3.95 million to promote Underdog’s development of disease-modifying treatments for atherosclerosis and other age-related diseases. SRF also announced two senior appointments.
The Underdog round is led by Michael Greve’s Kizoo Technology Capital, part of the Forever Healthy Group and one of the premier organizations focusing on accelerating rejuvenation biotechnologies. It also includes Oculus co-founder Michael Antonov through Tubus, LLC, and financier Harald McPike through Chambray Worldwide, Ltd.
Underdog was built from an SRF flagship program that has driven two years of applied development designed to explore and repair the underlying causes of cardiovascular disease. Its co-founders are Matthew O’Connor, Ph.D. and Michael Kope, formerly the V.P. of Research and the founding CEO, respectively, of SRF.
When an undiagnosed rare genetic disease caused his young son’s kidneys to fail, Professor Chris Toumazou vowed to find a way of uncovering hidden health risks.
The professor of biomedical engineering realised that, although his son’s condition could not have been prevented, the family could have managed his lifestyle very differently had they known about his condition.
So, he embarked on a mission to help people change their lifestyles and avoid getting sick.